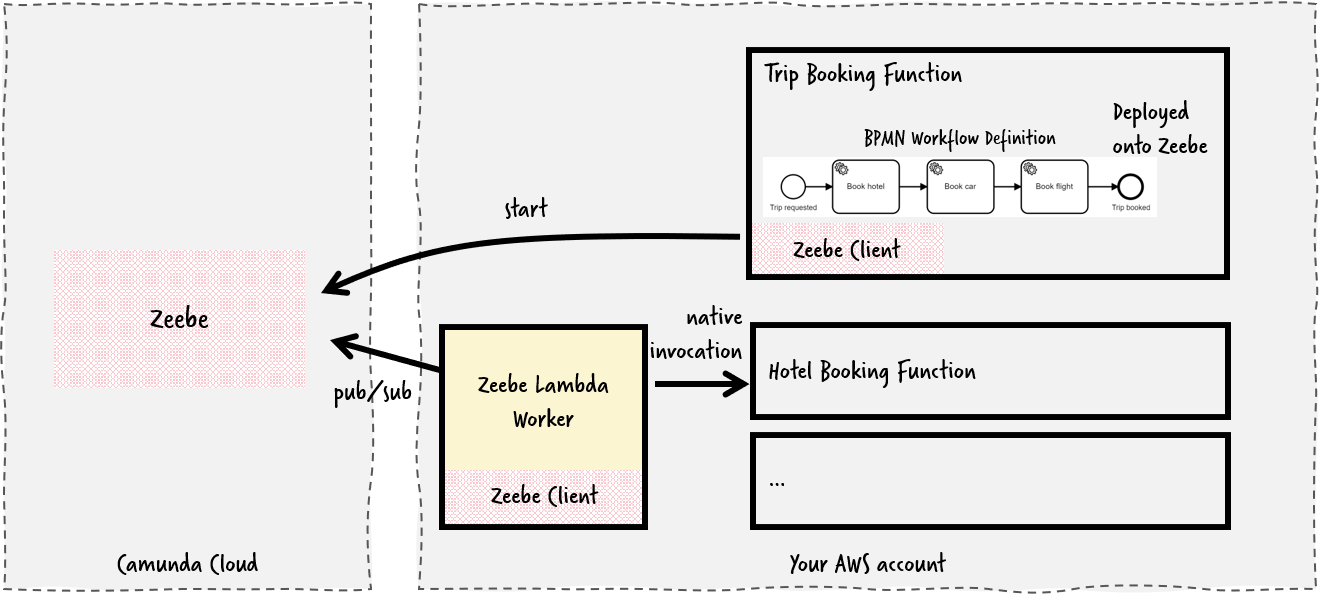
A Zeebe connector to invoke AWS Lambdas (Serverless functions), allowing to orchestrate functions. It uses the AWS SDK to connect to Lambda.
Requirements: Java 11
Important Note: This is a community extension and does not give you any guarantees. In fact, it was developed as part of a POC and might not be ready for production usage yet.
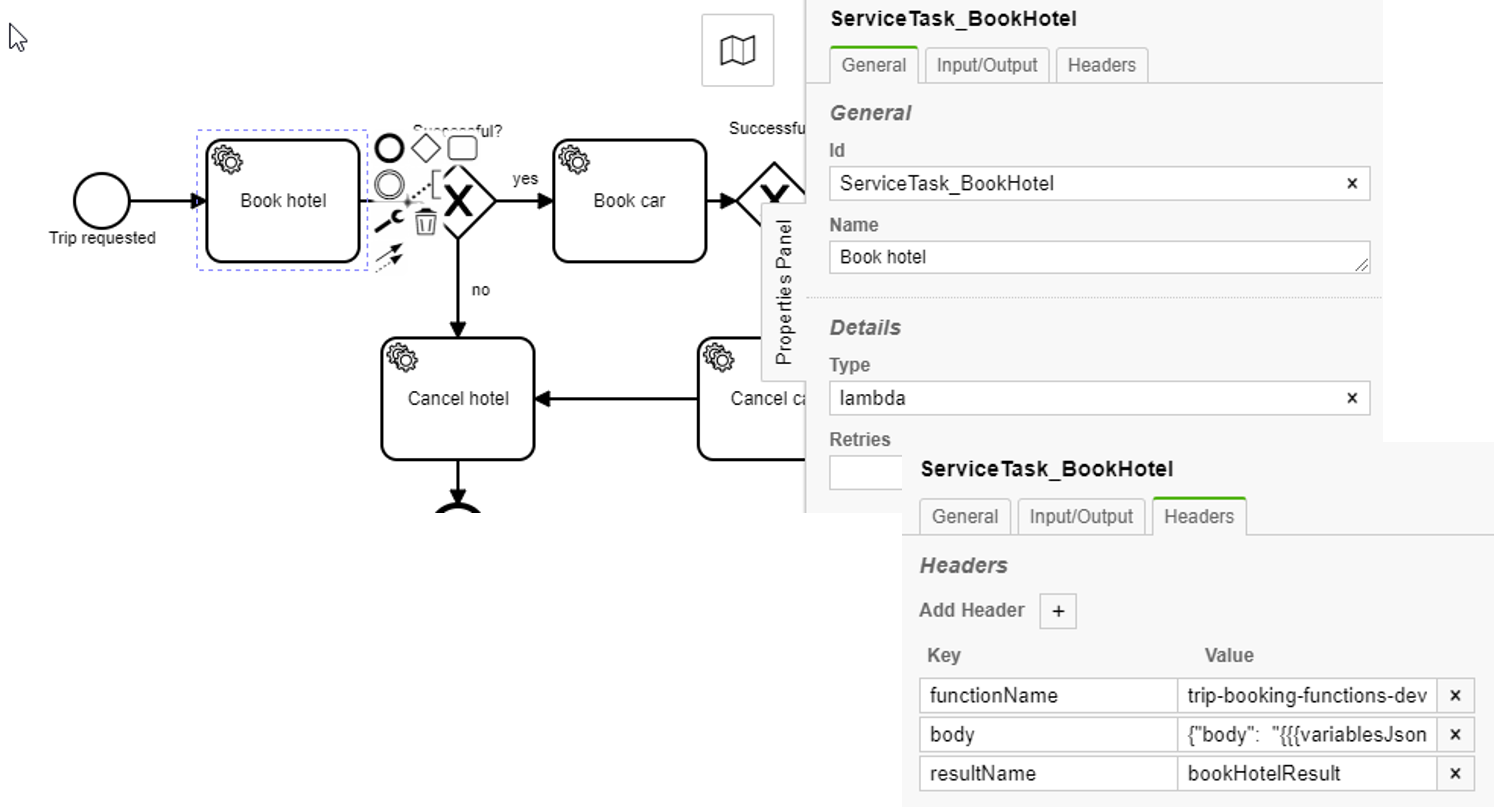
Example service task in BPMN:
Or in the BPMN XML:
<bpmn:serviceTask id="BookHotel" name="Book Hotel">
<bpmn:extensionElements>
<zeebe:taskDefinition type="lambda" />
<zeebe:taskHeaders>
<zeebe:header key="functionName" value="trip-booking-functions-dev-book-hotel" />
<zeebe:header key="body" value="{"body": "{{{variablesJsonEscaped}}}" }" />
<zeebe:header key="resultName" value="bookHotelResult" />
</zeebe:taskHeaders>
</bpmn:extensionElements>
</bpmn:serviceTask>
-
the worker is registered for the type
lambda -
required headers:
functionName- the function name of the Lambda to invoke
-
Optional Headers
body- the payload to send over to the function, can be constructed using placeholders (as explained below)resultName- the variable the result shall be written to (another variableresultNameStatusCodeandresultNameJsonStringis written additionally, see example below)functionErrorCode- If the function results in an error (status code != 200), you can define a BPMN Error that is raised in this case, which allows to react to failures in your BPMN model (TODO: Think about if the statusCode itself should end up in the BPMN error code, then you could react differently to different errors)
Please note that the current way of handling placeholders is subject to change in the future, especially with camunda/camunda#3417 and the new FEEL expressions.
You can use placeholders in the form of {{PLACEHOLDER}} at all places, they will be replaced by
- custom headers from the BPMN model
- Workflow variables
- Configuration Variables from URL (see below)
workflowInstanceKeyorjobKey
Mustache is used for replacing the placeholders, refer to their docs to check possibilities.
If you want to avoid that the resulting string gets quoted, you have to use triple quotes: {{{PLACEHOLDER}}}. This is handy to e.g. pass all variables into the request in the body attribute (which can be the case if your functions are also called via API Gateway):
{"body": "{{{variablesJsonEscaped}}}" }
Example:
<bpmn:serviceTask id="http-get" name="stargazers check">
<bpmn:extensionElements>
<zeebe:taskDefinition type="lambda" />
<zeebe:taskHeaders>
<zeebe:header key="functionName" value="{{FUNCTION_BASE}}-book-hotel" />
</zeebe:taskHeaders>
</bpmn:extensionElements>
</bpmn:serviceTask>FUNCTION_BASE could be configured by the configuration variables from the URL or environment properties.
You can use
- Single Variables by name
variablesJsonuses all variable as Json objectvariablesJsonEscapedincludes all variables as Json String, escaped, to be used as String attribute, e.g. used to call a function that is also called via API Gateway) - use {{{ to prevent the templating to add quotes:
{"body": "{{{variablesJsonEscaped}}}" }
-
Build the JAR file
mvn clean build -
Execute the JAR via
java -jar target/zeebe-lambda-worker-{VERSION}.jar
docker run camunda/zeebe-lambda-worker:SNAPSHOT
Set environment variables as described below to configure the worker. So for example to connect to Camunda Cloud and AWS it could look like this:
docker run -e ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLUSTERID=x -e ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTID=y -e ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTSECRET=z -e AWS_ACCESSKEY=a -e AWS_SECRET=b -e AWS_REGION=c -p 8080:8080 camunda/zeebe-lambda-worker:SNAPSHOT
Or even easier using environment files:
docker run --env-file camunda.env --env-file aws.env -p 8080:8080 camunda/zeebe-lambda-worker:SNAPSHOT
with camunda.env:
ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLUSTERID=x
ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTID=y
ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTSECRET=z
and aws.env:
AWS_REGION=eu-central-1
AWS_ACCESSKEY=x
AWS_SECRET=y
Of course you can also services like AWS Fargate to run this container.
You can check health of the worker:
http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
This uses the Spring Actuator, so other metrics are available as well
The connection to the broker Zeebe can be changed by setting the environment variables
ZEEBE_CLIENT_BROKER_CONTACTPOINT(default:127.0.0.1:26500).ZEEBE_CLIENT_SECURITY_PLAINTEXT(default: true).
or if you want to connect to Camunda Cloud:
ZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLUSTERIDZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTIDZEEBE_CLIENT_CLOUD_CLIENTSECRET
You also need to specify the AWS credentials to talk to your Lambda:
AWS_ACCESSKEYAWS_SECRETAWS_REGION
You could adjust the topic or worker name itself (if you know what you are doing - leave untouched otherwise)
ZEEBE_CLIENT_WORKER_DEFAULTNAME(defaultlambda-worker)ZEEBE_CLIENT_WORKER_DEFAULTTYPE(defaultlambda)
This worker uses Spring Zeebe underneath, so all configuration options available there are also available here.
You can load additional configuration values used to substitute placeholders. Therefor the worker will query an HTTP endpoint and expects a JSON back:
[
{
"key": "someValue",
"value": 42
},
{
"key": "anotherValue",
"value": 42
}
]
To load additional config variables from an URL set these environment variables:
ENV_VARS_URL(e.g.http://someUrl/config, default: null)ENV_VARS_RELOAD_RATE(default15000)ENV_VARS_M2M_BASE_URLENV_VARS_M2M_CLIENT_IDENV_VARS_M2M_CLIENT_SECRETENV_VARS_M2M_AUDIENCE
This project adheres to the Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct. By participating, you are expected to uphold this code. Please report unacceptable behavior to code-of-conduct@zeebe.io.