Official site: http://rpcx.site
you can use other programming languages besides Go to access rpcx services.
- rpcx-gateway: You can write clients in any programming languages to call rpcx services via rpcx-gateway
- http invoke: you can use the same http requests to access rpcx gateway
- Java Services/Clients: You can use rpcx-java to implement/access rpcx servies via raw protocol.
If you can write Go methods, you can also write rpc services. It is so easy to write rpc applications with rpcx.
install the basic features:
go get -u -v github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...
If you want to use reuseport、quic、kcp, zookeeper, etcd, consul registry, use those tags to go get 、 go build or go run. For example, if you want to use all features, you can:
go get -u -v -tags "reuseport quic kcp zookeeper etcd consul ping rudp utp" github.com/smallnest/rpcx/...tags:
- quic: support quic transport
- kcp: support kcp transport
- zookeeper: support zookeeper register
- etcd: support etcd register
- consul: support consul register
- ping: support network quality load balancing
- reuseport: support reuseport
rpcx is a RPC framework like Alibaba Dubbo and Weibo Motan.
rpcx 3.0 has been refactored for targets:
- Simple: easy to learn, easy to develop, easy to intergate and easy to deploy
- Performance: high perforamnce (>= grpc-go)
- Cross-platform: support raw slice of bytes, JSON, Protobuf and MessagePack. Theoretically it can be used with java, php, python, c/c++, node.js, c# and other platforms
- Service discovery and service governance: support zookeeper, etcd and consul.
It contains below features
- Support raw Go functions. There's no need to define proto files.
- Pluggable. Features can be extended such as service discovery, tracing.
- Support TCP, HTTP, QUIC and KCP
- Support multiple codecs such as JSON, Protobuf, MessagePack and raw bytes.
- Service discovery. Support peer2peer, configured peers, zookeeper, etcd, consul and mDNS.
- Fault tolerance:Failover, Failfast, Failtry.
- Load banlancing:support Random, RoundRobin, Consistent hashing, Weighted, network quality and Geography.
- Support Compression.
- Support passing metadata.
- Support Authorization.
- Support heartbeat and one-way request.
- Other features: metrics, log, timeout, alias, circuit breaker.
- Support bidirectional communication.
- Support access via HTTP so you can write clients in any programming languages.
- Support API gateway.
- Support backup request, forking and broadcast.
rpcx uses a binary protocol and platform-independent, which means you can develop services in other languages such as Java, python, nodejs, and you can use other prorgramming languages to invoke services developed in Go.
There is a UI manager: rpcx-ui.
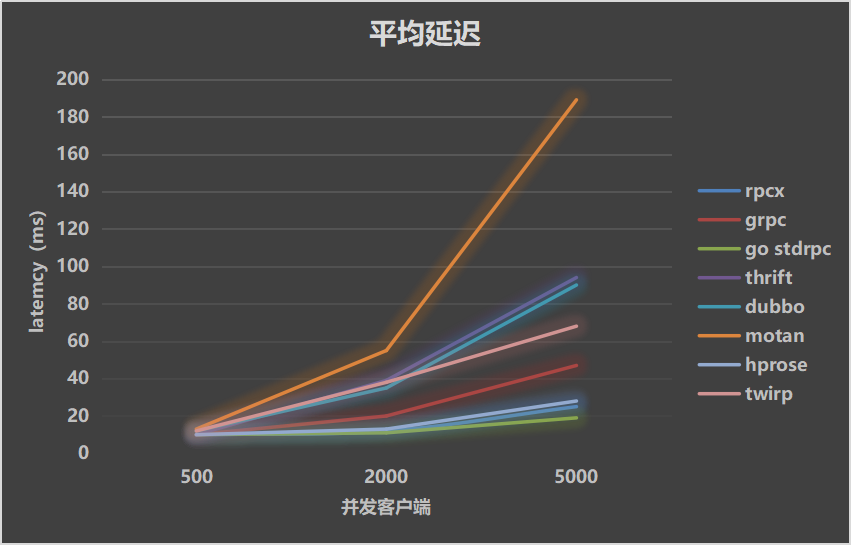
Test results show rpcx has better performance than other rpc framework except standard rpc lib.
Test Environment
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2630 v3 @ 2.40GHz, 32 cores
- Memory: 32G
- Go: 1.9.0
- OS: CentOS 7 / 3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
Use
- protobuf
- the client and the server on the same server
- 581 bytes payload
- 500/2000/5000 concurrent clients
- mock processing time: 0ms, 10ms and 30ms
Test Result
| Throughputs | Mean Latency | P99 Latency |
|---|---|---|
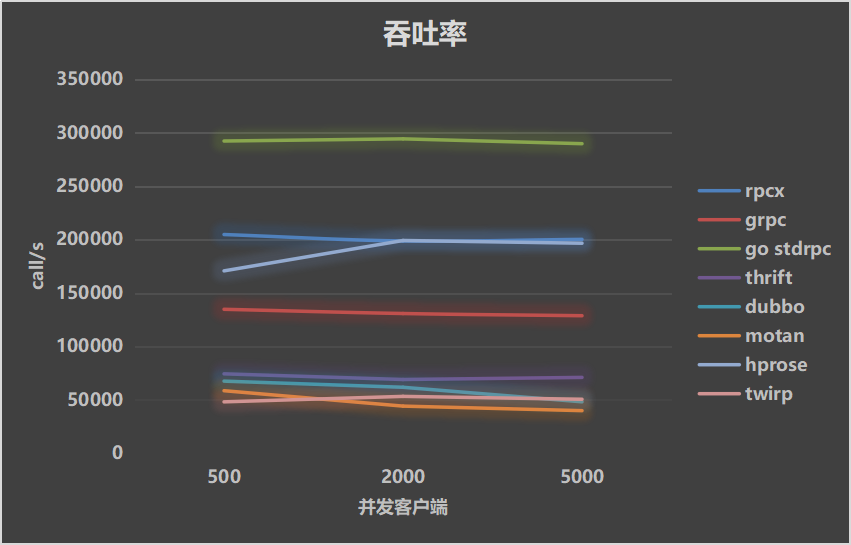 | 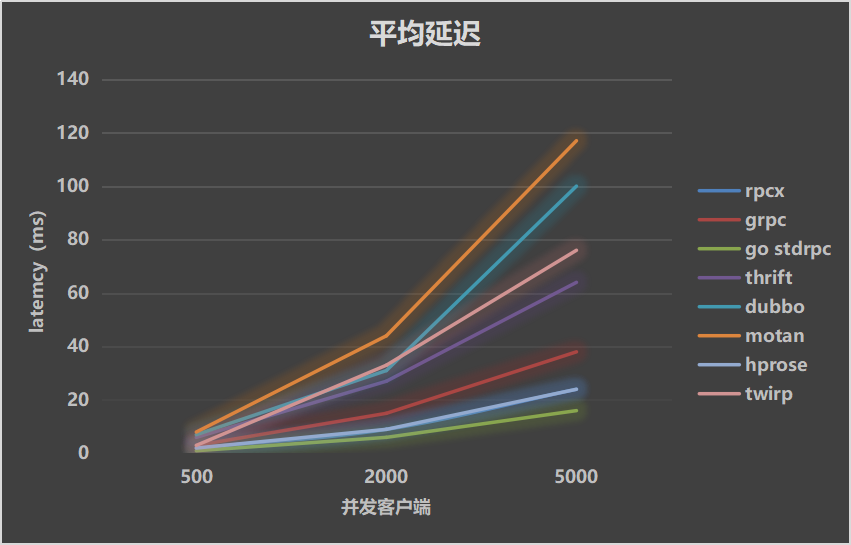 | 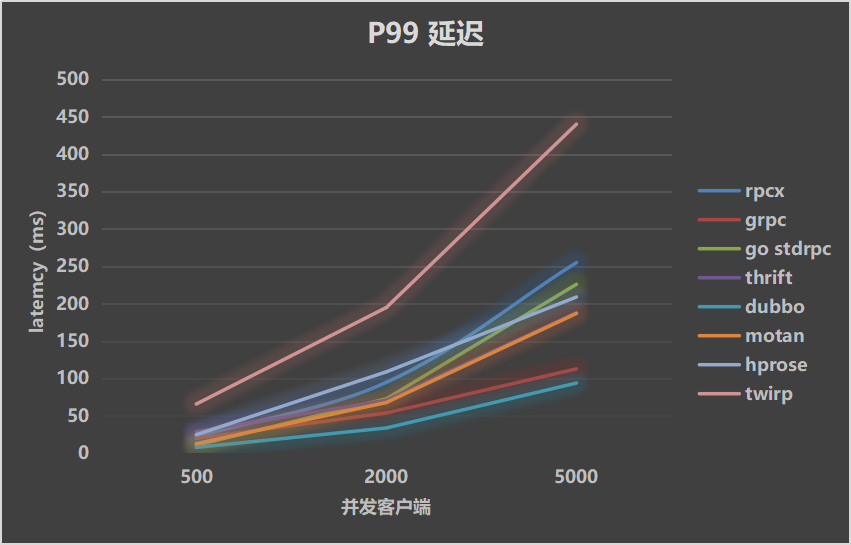 |
| Throughputs | Mean Latency | P99 Latency |
|---|---|---|
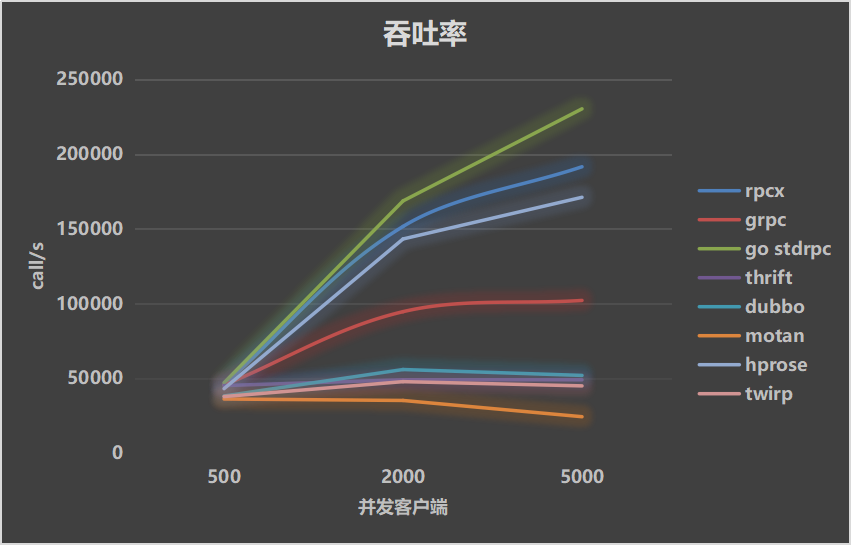 |  | 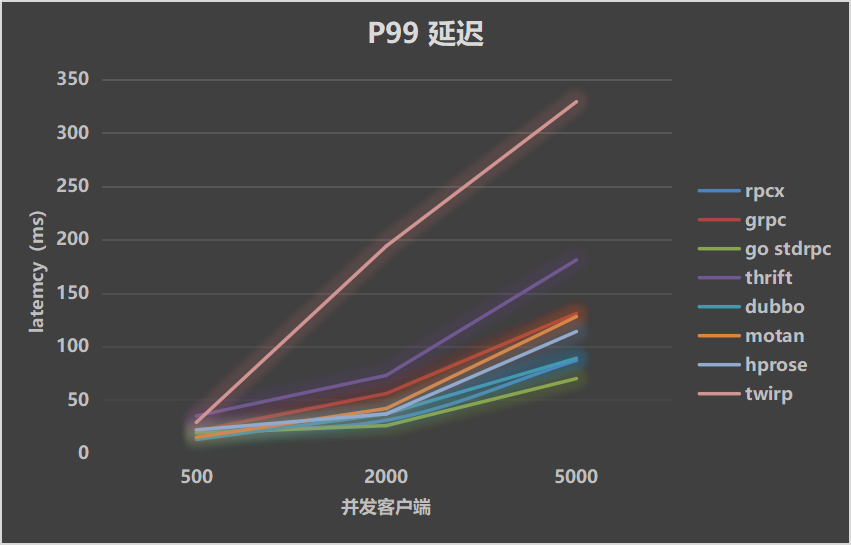 |
| Throughputs | Mean Latency | P99 Latency |
|---|---|---|
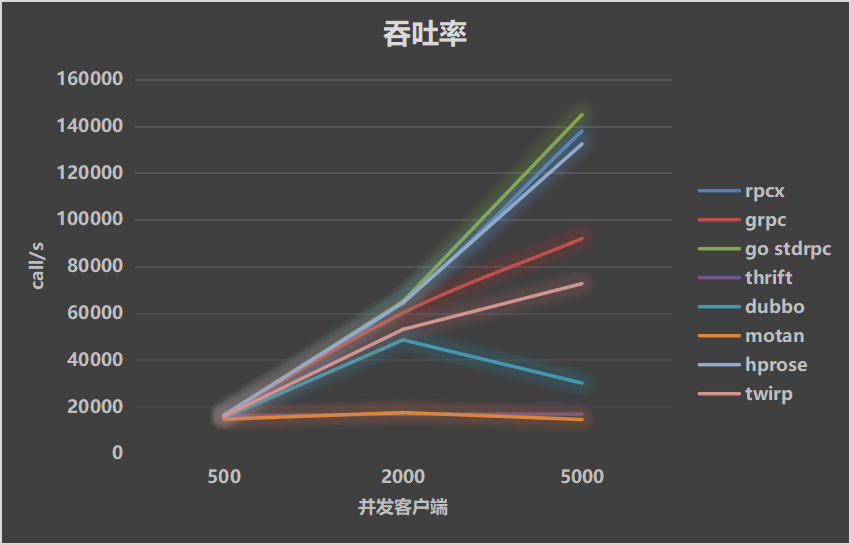 | 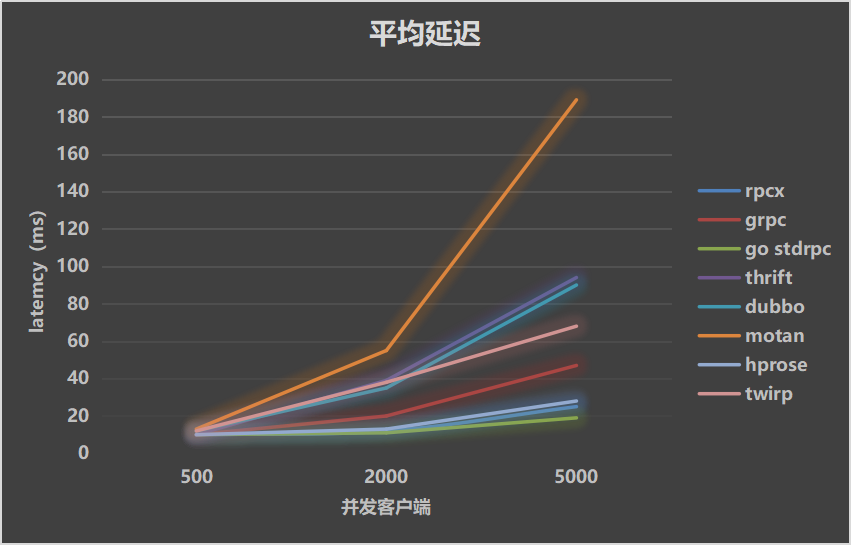 | 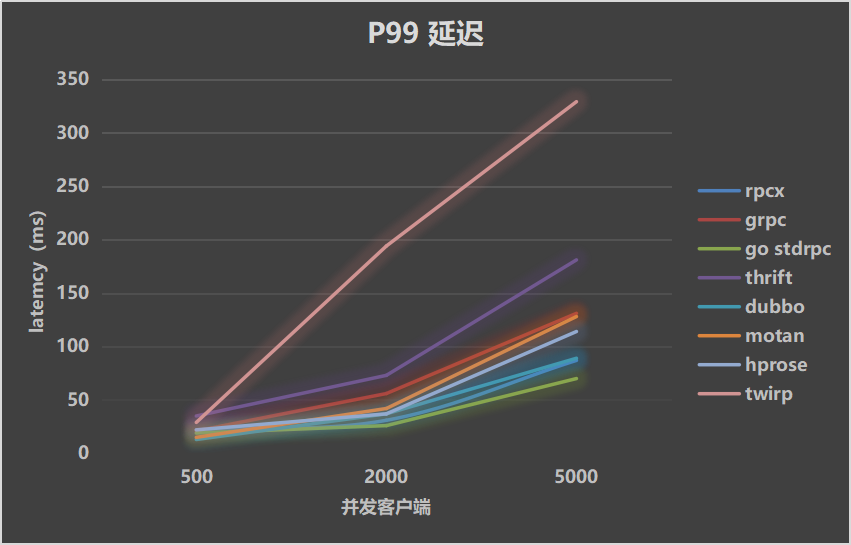 |
You can find all examples at rpcx-ecosystem/rpcx-examples3.
The below is a simple example.
Server
// define example.Arith
……
s := server.NewServer()
s.RegisterName("Arith", new(example.Arith), "")
s.Serve("tcp", addr)Client
// prepare requests
……
d := client.NewPeer2PeerDiscovery("tcp@"+addr, "")
xclient := client.NewXClient("Arith", client.Failtry, client.RandomSelect, d, client.DefaultOption)
defer xclient.Close()
err := xclient.Call(context.Background(), "Mul", args, reply, nil)see contributors.
Welcome to contribute:
- submit issues or requirements
- send PRs
- write projects to use rpcx
- write tutorials or articles to introduce rpcx
Apache License, Version 2.0



