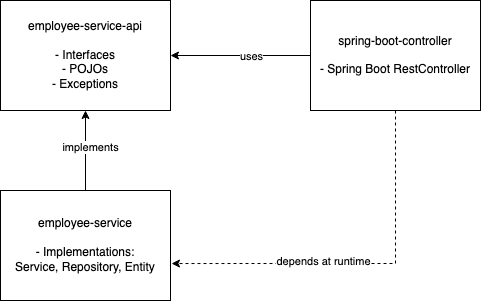
This project contains an application(employee-service), its API(employee-service-api) and a Spring Boot application(spring-boot-controller) that uses the API.
The "employee-service" implements the interfaces and uses the data classes from "employee-service-api". The "employee-service-api" dependency can be used by other applications and libraries without coupling them to the implementation project, "employee-service".
The "employee-service-api" contains only the interfaces, and the data classes, not any behavior. Also, it does not have any dependencies.
The "spring-boot-controller" project can be replaced with any other technology stack at any given time. Therefore, we can think the "spring-boot-controller" as the distributed interface layer of the "employee-service" application.
"employee-service", by design should contain all the implementation details, such as the service and repository implementations, entities and all sorts of tests.
"employee-service" should be considered as a complete application, its API and the Spring Boot applications do not / should not contain any business logic.
"employee-service" implements the "EmployeeServiceFactory" interface (abstract factory) with its "DefaultEmployeeServiceFactory". Currently, this is the only implementation, but other factories can easily be implemented.
If you look into the "employee-service" project's "src/main/resources/META-INF/services/com.example.employee.external.factory.EmployeeServiceFactory" file, you can find that "com.example.employee.internal.factory.DefaultEmployeeServiceFactory" is provided from this project as an implementation for the "EmployeeServiceFactory" interface.
There is no dependency in the "employee-service-api" project, it finds all the "EmployeeServiceFactory" implementations using Java's internal "java.util.ServiceLoader" facility.
The default factory is used by the "AppConfig" class in the "spring-boot-controller". This way, there is no direct or transient dependency between "spring-boot-controller" and the "employee-service".
You need to run mvn clean install on the "employee-service-api", "employee-service" and "spring-boot-controller" projects.
After that, you can run the "spring-boot-controller" as a regular Spring Boot Project usin "DemoApplication" class.
You need to run the docker-compose -f postgres-docker-compose.yml up if you want to use the "JDBC" type EmployeeService.
If you look at the "EmployeeServiceType" enum in the "employee-service-api" project, you can see that there are three implementations you can use, JDBC, NO_OP and IN_MEMORY. You can simply change the "employeeService.type=JDBC" in the "spring-boot-controller" project's "application.properties" file, and use another implementation.