Note: CVEScan is not supported - instead it is recommended to use Ubuntu OVAL data.
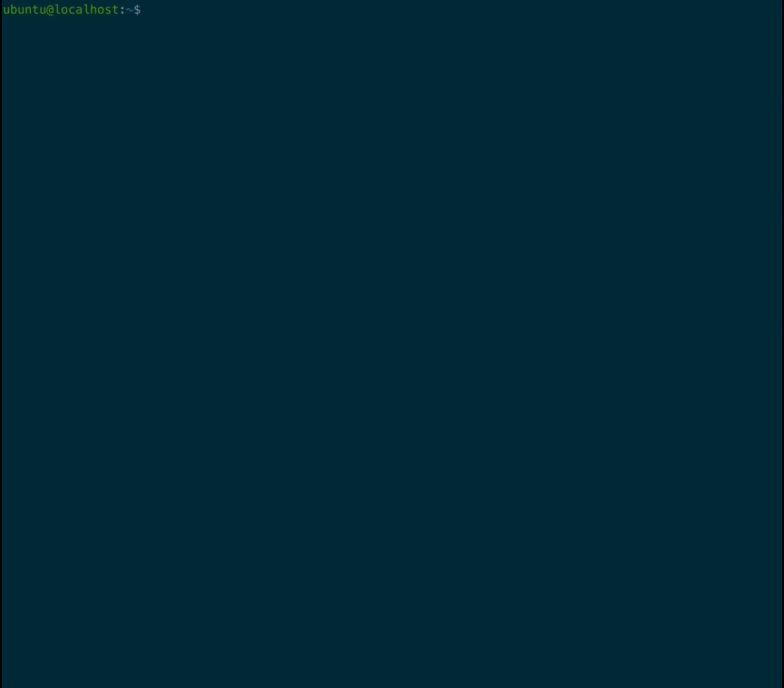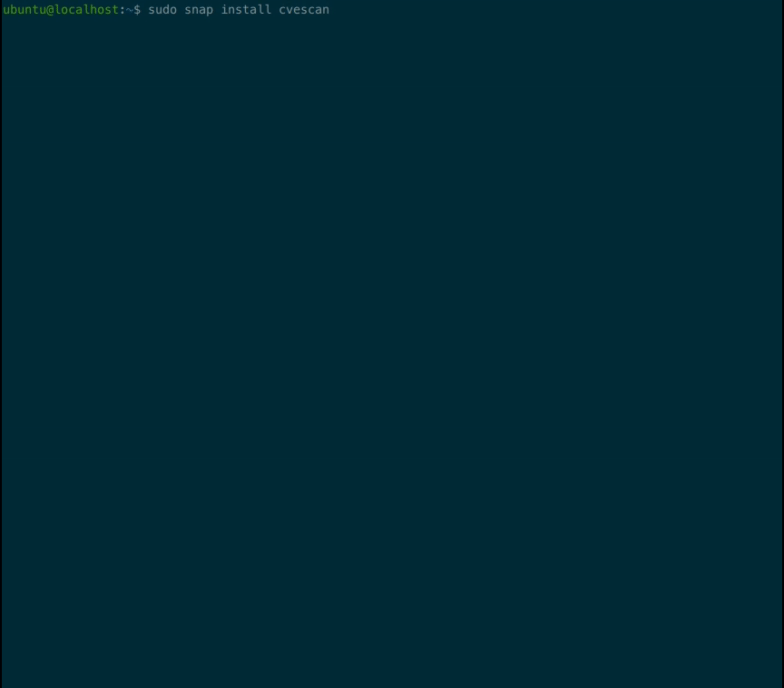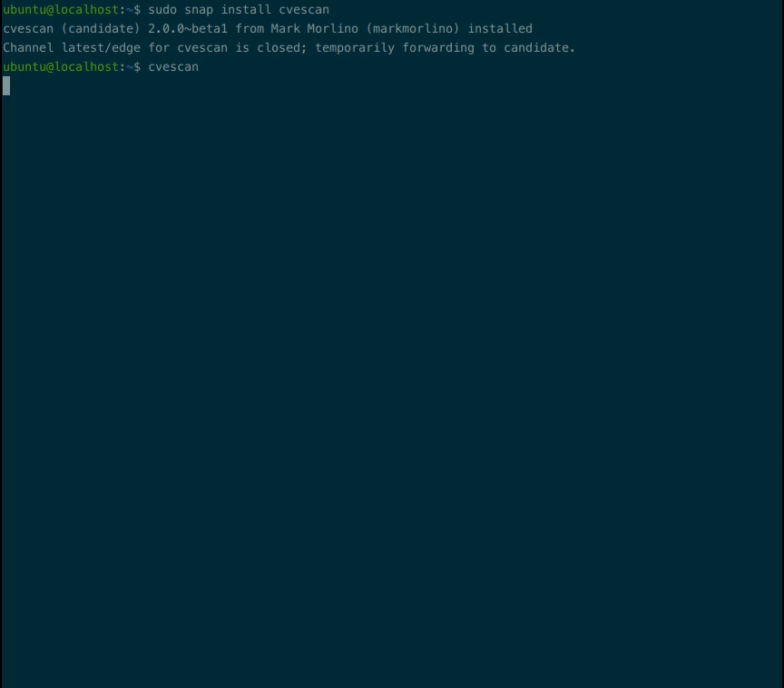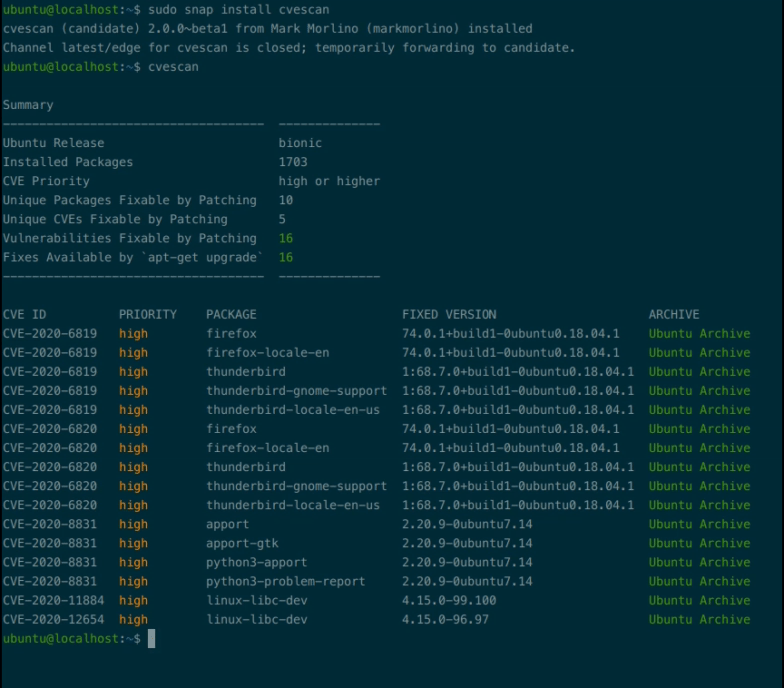
CVEScan analyzes an Ubuntu system to check whether all available security patches have been installed. CVEScan produces a clear, concise report that tells you which, if any, security patches an Ubuntu system may be missing.
In addition to scanning a local system, CVEScan can scan a package manifest file. This is useful in environments where CVEScan cannot be installed on every system.
The Ubuntu Security Team at Canonical regularly publishes a JSON file
containing information about security updates for .deb packages. The source of
the information is the Ubuntu CVE
Tracker. The information
contained in the JSON file is similar to the information published in the
Ubuntu OVAL files, but
the format is designed specifically for use by CVEScan.
v2.0.0 is a complete rewrite of CVEScan. It boasts a clear, concise reporting format and a 10x performance improvement over v1.0.10. Additionally, this rewrite will allow developers to add new features and capabilities more quickly.
As might be expected with the release of a new major version, certain options
and features included with v1.0.10 may no longer be available or may not
function as they use to. If you absolutely must have the old version of
CVEScan, you can install the snap and run cvescan.sh. This will run the
deprecated v1.0.10 of CVEScan.
WARNING: v2.5.0 of CVEScan is the last version that will include the v1.0.10
bash implementation. If you are still using cvescan.sh, please move over to
v2.5.0 of cvescan.
For more information about how v2.0.0 differs from v1.0.10, see the CHANGELOG.
CVEScan provides a number of options. See cvescan -h for more details.
usage: cvescan [-h] [--version] [-v] [-p {critical,high,medium,all}]
[--db UBUNTU_DB_FILE] [-m MANIFEST_FILE] [--csv] [--json]
[--syslog HOST:PORT] [--syslog-light HOST:PORT] [--show-links]
[--unresolved] [-x] [-n] [-c CVE-IDENTIFIER] [-s]
Scan an Ubuntu system for known vulnerabilities
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version Show CVEScan's version number and exit
-v, --verbose enable verbose messages
-p {critical,high,medium,all}, --priority {critical,high,medium,all}
filter output by CVE priority
--db UBUNTU_DB_FILE Specify an Ubuntu vulnerability database file to use instead
of downloading the latest from people.canonical.com.
-m MANIFEST_FILE, --manifest MANIFEST_FILE
scan a package manifest file instead of the local system
--csv format output as CSV
--json format output as JSON
--syslog HOST:PORT send JSON formatted output to a syslog server specified by
<host>:<port>
--syslog-light HOST:PORT
send a simple log message to a syslog server specified by
<host>:<port>
--show-links include links to the Ubuntu CVE Tracker in the output
--unresolved include CVEs that have not yet been resolved in the output
-x, --experimental for users of Ubuntu Advantage, include eXperimental (also
called "alpha") in the output
-n, --nagios format output for use with Nagios NRPE
-c CVE-IDENTIFIER, --cve CVE-IDENTIFIER
report whether or not this system is vulnerable to a
specific CVE.
-s, --silent do not print any output (only used with --cve)
In general, CVEScan's return codes indicate the following:
| Return Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | The scan was successful and no CVEs affect this system. |
| 1 | An error occurred. |
| 2 | Invalid CLI options were specified. |
| 3 | The system is vulnerable to one or more CVEs. |
| 4 | The system is vulnerable to one or more CVEs and one or more patches are available. |
When the --nagios option is specified, CVEScan's return codes indicate the following:
| Return Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | The scan was successful and no CVEs affect this system. |
| 1 | The system is vulnerable to one or more CVEs. |
| 2 | The system is vulnerable to one or more CVEs and one or more patches are available OR invalid CLI options were specified. |
| 3 | An error occurred. |
A package manifest file can be generated by running
dpkg-query -W > manifest.txt on any Ubuntu system. The manifest file can be
copied to any system where CVEScan is installed. CVEScan can then generate
a report based on the manifest file instead of the local system: cvescan -m manifest.txt
The recommended way to install CVEScan is with sudo snap install cvescan
The following commands will install and run CVEScan from source:
$> sudo apt install python3-apt python3-pip
$> git clone https://github.com/canonical/sec-cvescan
$> pip3 install --user sec-cvescan/
$> ~/.local/bin/cvescan
The following commands will install and run CVEScan from source in a virtualenv:
$> sudo apt build-dep python3-apt
$> sudo apt install python3-pip git
$> pip3 install --user virtualenv
$> git clone https://github.com/canonical/sec-cvescan
$> ~/.local/bin/virtualenv -p python3 venv
$> source venv/bin/activate
$> pip3 install -e ./sec-cvescan[apt]
$> venv/bin/cvescan
CVEScan can be run from the source code with python3 -m cvescan
To install the precommit hooks, run
pip3 install --user pre-commit
~/.local/bin/pre-commit install
You can run the automated test suite by running
python3 setup.py test
An HTML code coverage report will be generated at ./htmlcov. You can view
this with any web browser (e.g. firefox ./htmlcov/index.html).
This project adheres to Semantic Versioning.
The version number used by the setup.py, snapcraft.yaml, and cvescan --version argument is stored in cvescan/version.py and
must be updated manually when a new version of CVEScan is released.