The project is about building an HTML & CSS project for a social network site, based on a design idea by Vlad Ermakov on Dribbble .
The original design specification can be found here Swipex @Behance.net
The original design considers a dating social network. I have used the initial design requirement and followed the capstone project challenge to redefine the social network for my solution.
In my project, I considered the concept of servicing a charity branch in a private organization (Rayces), that offers educational services and medical therapy for children patients with learning disabilities. My novel idea is that also, the organization creates a charity branch that gives free treatment to a small number of children using funds from the private company itself but also funds rising campaigns organized by the company. This social network targets families an individuals that want to donate money to support children's patients a full year as well as partial treatment, enabling in this way a small crowdsourcing network. The network gives the donors a chance to get in touch with the children's tutors and receive information about the treatment progress, health checkup updates, and chat messaging. This network could also be applied to private patients to benefit from a centralized system for tutors to get information about their children's treatment progress.
Follow this link for my project's video presentation
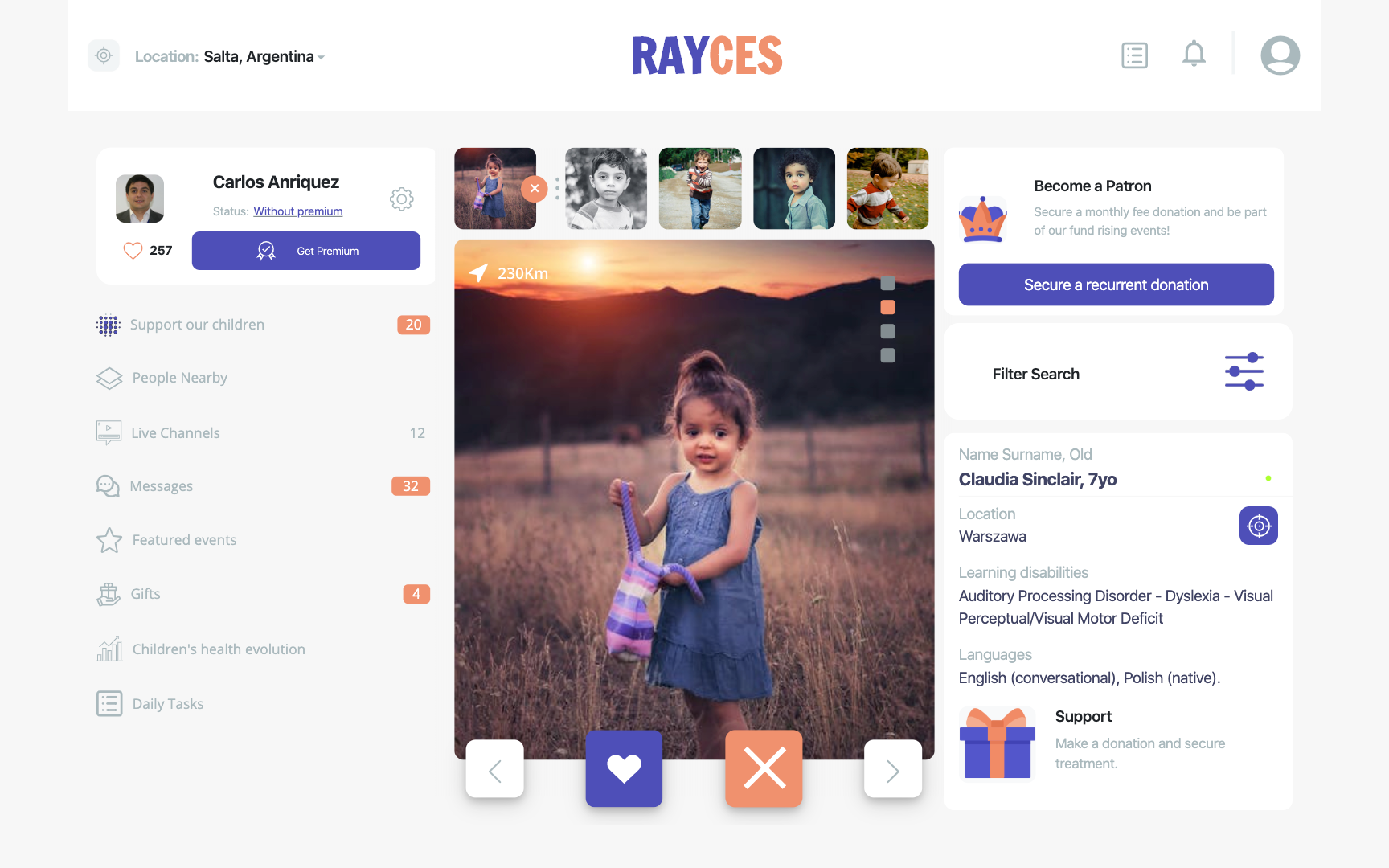
Main Page responsive strategy.
- The main page has a navbar and footer and a modal box with the user information for all mobile screens up to 767px displays. For this solution, I have used a flexbox with a column direction, ensuring 100% of the viewport gets utilized, avoiding undesired overflow. (see Using Full-Screen Height)
- For screens bigger than 768, the screen would lose its modal box, footprint, and the "scroll menu" would appear at the bottom of the image, absolute positioned relative to the main image container.
Main page's film reel
- The main page has a film reel with pictures that shows on all mobile screens. Here, I have used a flexbox to adjust the bases of each element according to the available space. Each picture has little padding left and right that ensures a visible gap between them.
- The small cancel icon shown for the image in focus has been build with pseudocode after the image wrap, and absolute positioned relative to the in-focus image wrap. The top and bottom parameters are adjusted depending on the screen sizes.
- For screens less than 320 px, an in-focus image is shown and an additional three pictures.
- From 320 px to 499 px, in-focus image plus 4 additional pictures.
- From 768 px screens onwards, in-focus image, and an additional six pictures in the film reel.
Using Full-Screen Height
Problem: How to reproduce a typical mobile app UX, where each mobile page design utilizes 100% of the view port's height with no overflow?
For this problem, the solution applied was, using 100% of the view port's height using a flexbox.
- I defined a container, with a display type flex with column direction, using a height of 100vh, and making sure I use no margins top or bottom in the container. Any margin at all would create an overflow that would break the container 100vh definition.
- This solution allows for any sub-container to be aligned using flex properties and making sure all the content would fit in the current viewport's size.
Main hero image on user pages
Problem: How to position the hero image by utilizing more than 50% of the screen's height, showing the modal box (detail person information), and avoiding breaking when we switch to smaller screens?
Solution:
- Initially, I was trying to set up a relative image height using a %vh value. Although the solution partially worked, it was complicated to maintain without adding excessive media queries to avoid overflow on smaller screens.
- The final solution was to fix the header and footer size of the main page, using the right icon sizes and padding, while letting the flex container adjust the hero image (main image). Also, I needed to fix the modal height, so its relative container does not get shrink when screen size reduces in height for different screen sizes.
- To create the modal effect displacement, moving on top of the hero image, I have defined "position=relative" for the container, allowing it to render with the normal page flow, and also, included a little percentage of its hight as a bottom offset, to create the displacement effect.
- This solution is simple enough to maintain and does not require additional code at different media sizes.
Organizing the messages page for media >1024px
- To make the messages page scroll inside the container while in media bigger or equal to 1024px, I needed to assign to the main page inside the section, a specific size of 62vh (considering the nab-var height).
- Inside the messages container (msg-frame class), I included the property overflow-y to enable the scroll effect.
- Finally, I work all the height parameters in each modal-message (modal-msg) to "auto," so, in that way, there is no fixed height, and the msg-frame would have all messages placed in order and with the same size one after the other.
- With this solution, the complete frame would then overflow from the main-page section (msg-frame) container, achieving the scroll effect.
- Finally, I positioned the footer and the menu relative to its parent container. So, it gets rendered in continuation to the main page section with a little 2% offset to compensate for the required margin-top and bottom to align the icons.
Basic Demo Navigability
- I used Java Script to organize a basic click navigation solution between pages.
- In mobile, the main page shows when we click the chat icon on the main page.
- From the message page, we could come back to the main page by clicking the engage icon.
- We can go to the detailed chat page by clicking any message group on the message page. Currently, we go to the same page.
- We go back from the chat page to the messages page by clicking the back arrow.
- For screens bigger than 768px, I use a grid as the primary placing solution and, the main-page and user page take each 50% of the screen width.
- For screens greater or equal to 1024 px, three grid columns organize Menu-bar, main-page, and user page from left to right.
- If we click the chat option in the menu, a small Javascript code will change the display property to "none" (display=none) for the main page and the user page. Additionally, it will display as a block (display = block) both the messages page and chat page. With this solution, the messages page and chat detail page should render in the corresponding grid columns 2 and 3 for the big screen sizes.
- When the user clicks on the "support our children" icon on the menu-bar, the process the inverse one. I use Javascript to disable (display=none) the messages page and chat detail page and enable the display (display=flex) for the main-page and user-page.
- From PC to mobile: (only for demo purposes) Messages page and chat page gests disabled for display (display=none) in the basic mobile view.
Key grid solution to switch from user-layout to message-layout on big screens
Problem: How to manage different layout "grid-column-size" configuration by using the same media query configuration?
General navigability solution:
- When the screen is >1024, using javascript, a click in any of the links "support our children" or "messages" at the menu-bar, will add the classes "layout-message-page" and "layout-user-page" to the #general-layout container wrap.
- These classes will modify the current "grid-template-column" definition to the specific percentage distribution according to the required layout (user layout or message layout).
- Simultaneously, javascript will also disable display (display=none) for all the appropriate section semantics containing the HTML tags for each layout design.
- Using this solution, I have avoided creating different HTML/CSS files for each layout configuration, avoiding multiple link tags to connect additional CSS files.
- HTML5, CSS3, Java Script
- Bootstrap (only containers)
- Visual Code
- This project is the final project requirement for the HTML_CSS module @Microverse Program.
To get a local copy up and running, follow these simple example steps.
-
Clone the repository in your local machine
-
enjoy
👤 Carlos Anriquez
- Github: @canriquez
- Twitter: @cranriquez
- Linkedin: linkedin
Contributions, issues, and feature requests are welcome!
Feel free to check the issues page.
Give a ⭐️ if you like this project!
- The Corgis @Microverse
- My family
This project is MIT licensed.