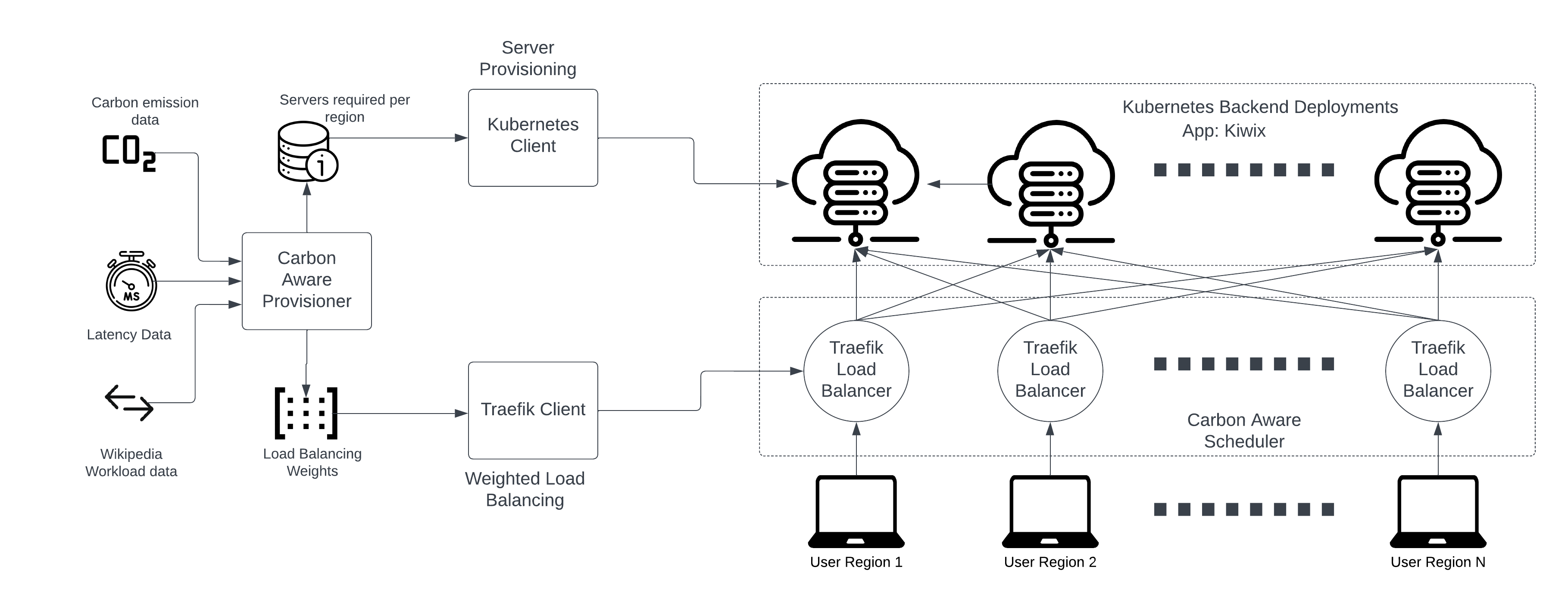
This repository contains information about setting and running CASPER: Carbon-Aware Scheduling and Provisioning for Distributed Web Services. CASPER runs as a Kubernetes Load-balancer. More information can be found on the paper.
Shruti Jasoria, Basundhara Chakrabarty, Abel Souza
- Docker
To install docker follow the official documentation. - kubectl
To install k8s follow the official documentation. - metrics-server
metrics-server can be directly applied to the k8s cluster. The steps are present in the following sections. - kubeadm and kubelet
Follow the official documentation. - Flannel
Flannel can be directly applied to the k8s cluster. - Traefik
Download the latest traefik binaries in the kasper directory. Add all the traefik yml config files in the traefik directory.
kasper
| - ...
| - traefik
| | CHANGELOG.md
| | LICENSE.md
| | traefik
| | ALL THE YAML FILES SHOULD BE AT THIS DIRECTORY LEVEL
| - ...
- Prometheus
Download the latest prometheus binaries in the kasper directory. Add all the prometheus yml config files in the traefik directory.
kasper
| - ...
| - prometheus
| | - prometheus-2.44.0-rc.1.linux-amd64
| | LICENSE
| | console_libraries
| | ALL THE YAML FILES SHOULD BE AT THIS DIRECTORY LEVEL
| - ...
| - ...
Use Python 3.x to run the simulation. Required packages are mentioned in the requirements.txt file and can be installed by running the commad:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
We assume a Kubernetes setup with a master node and two worker nodes. kubectl, kubelet, kubeadm and flannel need to be present in the system
kubeadm setup: https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/install-kubeadm/
- Disable swap in all the machines. This is required to use kubelet and kubeadm. Once disable, this command need not be run again on the machine.
sudo swapoff -a
- Kubelete and docker services should be running before you init kubeadm
sudo service docker start
sudo systemctl start kubelet
- Initialise kubeadm Run the following command in the master node.
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 --cri-socket=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Output of the above command:
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join <MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:6443 --token ugo1bg.kl76ibmcw8zu4p2v \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:2a0e87954353e2a74a5f318672bb3cb974a6dc153e92e1db6f056404903c7a65 \
--cri-socket=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
In the above output, make note of two things:
- Remember to replace <MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP> with the IP address of your master node
- Commands to setup kube configs in home directory
- Command to add worker nodes to the cluster
- Install Flannel
Run the following command on the node with control plane.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
- Join the first and second nodes as worker nodes
sudo kubeadm join <MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:6443 --token ugo1bg.kl76ibmcw8zu4p2v \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:2a0e87954353e2a74a5f318672bb3cb974a6dc153e92e1db6f056404903c7a65 \
--cri-socket=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
- Untaint the control plane node by running:
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl taint nodes <MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP> node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane=:NoSchedule-
node/<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP> untainted
Metallb provides the pod network for the kubernetes services to get an IP address. We have used MetalLb version 0.13.9:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metallb/metallb/v0.13.9/config/manifests/metallb-native.yaml
kubectl apply -f metallb-configmap.yaml
To verify if metallb was deployed successfully:
kubectl get pod -n metallb-system
For eg. :-
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl get pod -n metallb-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
controller-68bf958bf9-f8kkh 1/1 Running 0 49m
speaker-rmdls 1/1 Running 0 49m
speaker-s576d 1/1 Running 0 49m
speaker-sfrzv 1/1 Running 0 49m
To debug any issues with metallb, check the logs of the controller, .i.e.,
kubectl logs controller-68bf958bf9-f8kkh -n
Metrics Server allows for monitoring of CPU/Memory usage of the Pods
- Apply the metrics server manifest:
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl apply -f metrics-server.yaml
serviceaccount/metrics-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
service/metrics-server created
deployment.apps/metrics-server created
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io created
- Verify that metrics-server is running:
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-787d4945fb-2lbgw 1/1 Running 0 107m
coredns-787d4945fb-8c55z 1/1 Running 0 107m
etcd-master_node 1/1 Running 17 107m
kube-apiserver-master_node 1/1 Running 8 107m
kube-controller-manager-master_node 1/1 Running 8 107m
kube-proxy-62kj5 1/1 Running 0 107m
kube-proxy-9f5tt 1/1 Running 0 101m
kube-proxy-p4jxt 1/1 Running 0 102m
kube-scheduler-master_node 1/1 Running 8 107m
metrics-server-75b6f9b4fd-9vttd 0/1 Running 0 9s
- The CPU and Memory usage of pods can now be obtained as follows:
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-594844fc8f-qr65r 1m 3Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-6d485c577f-btsmh 1m 3Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5677c8479f-7p6tc 1m 3Mi
- Preflight fatal error in kubeadm init [ERROR CRI]: container runtime is not running solution: containerd/containerd#4581
Now that we have the cluster running, we need to create the Kubernetes setup (deployments, services, etc) Run the python script "python3 deploy.py" to create the deployment. Or call the method create_kubernetes_setup() from within simulation.py. CAP/deploy.py contains crucial functions for deployment/ service creation/ destruction.
Each pod in the Kubernetes deployment runs a Kiwix application image. Check the Dockerfile, build the Kiwix container and push it to DockerHub such that Kubernetes can use it. Then, update the registry details in line 217 of CAP/deploy.py with your own credentials:
registry = {
"username": "USERNAME",
"password": "TOKEN",
"email": "YOUR@EMAIL.COM",
"registry": "https://index.docker.io/v1/"
}
Should you choose to run other images, fix the image specification in lines 199-223. In our experiments, the image was named kiwix-serve (under casperumass/casper:casper-kiwix) has been uploaded to a private repo on Docker Hub, we recommend doing the same.
Container stuck in Container Creating and kubectl describe shows:
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kiwix-serve-us-central-594844fc8f-vmlrd 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 6m22s
kiwix-serve-us-east-6d485c577f-wff75 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 6m23s
kiwix-serve-us-west-5677c8479f-klwgx 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
Warning FailedCreatePodSandBox 79s (x17 over 4m46s) kubelet (combined from similar events): Failed to create pod sandbox: rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to setup network for sandbox "55873a24810e6f7bd1c4239b674574e17ab4777bc596d34c92c1d5621f95b33d": plugin type="flannel" failed (add): failed to delegate add: failed to set bridge addr: "cni0" already has an IP address different from 10.244.1.1/24
This bug is referenced in this [Stackoverflow post](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61373366/networkplugin-cni-failed-to-set-up-pod-xxxxx-network-failed-to-set-bridge-add
To fix it, check whether the cn01 network interfaces and the flannel.1 IPs match (Use ifconfig on the workers). If not, run the following commands on the workers:
ip link set cni0 down && ip link set flannel.1 down
ip link delete cni0 && ip link delete flannel.1
systemctl restart docker && systemctl restart kubelet
The script simulation.py runs the end-to-end simulation.
Call initialize followed by run() to run a complete end to end simulation:
def main():
_initialize()
_run()
_print_and_save_metrics()
The resulting dataframes are saved in the dataframes/ directory and can be exported for analysis.
There are several moving parts in the simulation. We describe them below:
Traefik is a free load balancer that has been used to perform weighted load balancing between the Kubernetes backend services residing on the workers, each representing a region. Every region has its own traefik endpoint. The traefik codes are in CAP/deploy.py.
Trafik has two main configuration files:
- Static Configuration: Contains the entrypoint on which the trafik router listens, and any additional entrypoints for Prometheus, etc. Each region has its own static config in traefik/traefik_{region}.yaml
entryPoints:
web:
address: "<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:3001"
metrics:
address: "<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4001"
For instance, in our internal configuration it contains:
entryPoints:
web:
address: "192.168.245.71:3001"
metrics:
address: "192.168.245.71:4001"
- Dynamic Configuration: Contains the router rules (what HTTP traffic to filter) and endpoint config (which services to route traffic to and their weights):
services:
ap-southeast-2:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: http://<WORKER_NODE-1_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:30001
.
.
app:
weighted:
services:
- name: ap-southeast-2
weight: '6'
.
.
- Note that the
simulation.pyscript automatically starts traefik and stops it after every execution interval. You will be able to see traefik running processes for each region upon runningsimulation.py:
username@master_node:~/casper$ ps -ef | grep traefik
root 6925 1 0 May22 ? 00:02:10 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-ap-southeast-2.yaml
root 6926 1 0 May22 ? 00:02:20 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-eu-central-1.yaml
root 6931 1 0 May22 ? 00:01:37 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-eu-west-3.yaml
root 6941 1 0 May22 ? 00:02:29 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-us-east-1.yaml
root 6946 1 0 May22 ? 00:01:21 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-us-east-2.yaml
root 6955 1 0 May22 ? 00:01:20 ./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-us-west-1.yaml
- If you need to start traefik manually, the command is:
./traefik/traefik --configFile traefik/traefik-ap-southeast-2.yaml
-
Prometheus is a metrics collector that interfaces with the traefik endpoints after every set of HTTP requests is sent, and aggregates them. It provides easy integration with traefik and provides a seamless python API to observe the metrics. The metric collection and aggregation code is located in CAP/metrics.py
-
The prometheus config is simple; just add the traefik endpoints to scrape for metrics:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "prometheus"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4001","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4002","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4003","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4004","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4005","<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:4006"]
For instance, in our internal configuration we have:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "prometheus"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090","192.168.245.71:4001","192.168.245.71:4002","192.168.245.71:4003","192.168.245.71:4004","192.168.245.71:4005","192.168.245.71:4006"]
-
The exported metrics and their descriptions are available on : https://doc.traefik.io/traefik/observability/metrics/overview/
-
Code to start/stop prometheus is present in
CAP/deploy.py
httpmon is used to henerate trafic to run the experiments.
- To run:
./httpmon --url http://<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:3000 --thinktime 1 --open --concurrency 1700
Instructions to setup httpmon are present on its github page. Once the setup is complete, copy the files
- client/http-mon-client.sh
- client/concurrency.out
to httpmon's directory.
- concurrency.out has number of requests that have to be sent per second.
- Sleep time between request rate updation can be changed by updating the variable
SLEEP_TIMEon line 14 of http-mon-client.sh. - If more request rates are added to concurrency.out, update the variable
Non line 16 of http-mon-client.sh.
- Future work: A template autoscaler code is located in autoscaler.py. This code has been tested independently but not during our simulations.
Other load-balancers may be used. We have tested GoBetWeen, but haven't proceeded with it due to issues in the load-balancer's weight updates not being performant. If you want to test it, use the below configurations:
- Config Files are in
casper/gobetween/config update_weights_python.pyshould calculate and update the weights to be used by gobetween- Start gobetween :
gobetween -c gobetween/config/gobetween.toml
root@master_node:~/casper/gobetween# gobetween -c config/gobetween.toml
2023/04/22 01:37:47 gobetween v0.8.0
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (manager): Initializing...
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (server): Creating 'sample': <MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:3000 roundrobin exec none
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (scheduler): Starting scheduler sample
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (execFetch): Fetching [~/casper/gobetween/config/update_weights_python.py]
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (manager): Initialized
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (metrics): Metrics disabled
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (api): API disabled
2023-04-22 01:37:47 [INFO ] (execFetch): Fetched [{<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:31460 p=1,w=1,l=true,a=0} {<WORKER_NODE-1_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:30897 p=1,w=2,l=true,a=0} {<WORKER_NODE-2_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:32049 p=1,w=2,l=true,a=0}]
- curl http://<MASTER_NODE_INTERNAL_NETWORK_IP>:3000 from any node will load balance to the backends:
username@master_node:~$ curl http://192.168.245.71:3000
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1" />
<link type="root" href="">
<title>Welcome to Kiwix Server</title>
<link
type="text/css"
href="/skin/index.css?cacheid=0f9ba34e"
rel="Stylesheet"
/>
@inproceedings{souza2023casper,
title={CASPER: Carbon-Aware Scheduling and Provisioning for Distributed Web Services},
author={Souza, Abel and Jasoria, Shruti and Chakrabarty, Basundhara and Bridgwater, Alexander and Lundberg, Axel and Skogh, Filip and Ali-Eldin, Ahmed and Irwin, David and Shenoy, Prashant},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 14th International Green and Sustainable Computing Conference (IGSC), Toronto, ON, Canada},
pages={67--73},
year={2023}
}
- The bottleneck on the server end is CPU cores, the CPU cores reach a max usage (~1 core) much faster than memory does
- Keeping a max of 100 servers/region, let's set 1/100 = 0.01 core/server
- We assign 0.01 core/pod and limit of 0.1 core/pod, set up 6 pods (one for each region), use equal weights for load balancing, and notice that max usage (90+) is reached with 600 requests/sec, or when each pod is getting 100 requests/sec
- Therefore, we can assume that with limit of 0.1 core/pod, the capacity is 100 requests/second
- For 0.01 core/pod as limit, the capacity should be 10 requests/pod/second or 60 requests/sec. This is consistent with our observation:
time=1682471572.984567 latency=1:2:2:2:2:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=2ms requests=55 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=55rps ql=0 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=2133 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:2:2:2:8:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=2ms accOpenQueuing=3 accErrors=0
username@master_node:~/casper# kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-ap-southeast-2-5fc4767cdd-gj6pz 9m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-eu-central-1-6f66f84858-mhcx2 10m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-eu-west-3-7f944b6df4-4k5j2 10m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-1-64dd6cd7bb-75hz7 10m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-2-6f7c4c66c4-r9ql5 10m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-1-57879cd54b-stpxx 9m 4Mi
- So, for each pod each server limit = 0.01 core/pod, let base=0.009/pod
- If CAP's servers matrix= [ 5 0 34 0 15 3], CAP should create 6 deployments, with the following CPU resource limits: 0.05,0,0.34,0,0.15,0.03
2023-04-30 22:02:44,640 INFO [INFO] Servers/ Region: [ 8 0 74 28 0 5] 2023-04-30 22:02:44,686 INFO [INFO] server_deployments: {'ap-southeast-2': 8, 'eu-central-1': 0, 'eu-west-3': 74, 'us-east-1': 28, 'us-east-2': 0, 'us-west-1': 5}
username@master_node:~$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kiwix-serve-ap-southeast-2 LoadBalancer 10.108.248.2 192.168.245.75 8086:30738/TCP 4d16h
kiwix-serve-eu-central-1 LoadBalancer 10.105.134.209 192.168.245.71 8081:31997/TCP 4d16h
kiwix-serve-eu-west-3 LoadBalancer 10.108.43.23 192.168.245.71 8082:30543/TCP 4d16h
kiwix-serve-us-east-1 LoadBalancer 10.103.37.232 192.168.245.74 8083:31159/TCP 4d16h
kiwix-serve-us-east-2 LoadBalancer 10.99.227.233 192.168.245.74 8084:32535/TCP 4d16h
kiwix-serve-us-west-1 LoadBalancer 10.105.157.66 192.168.245.75 8085:31930/TCP 4d16h
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8d
Requests Redirected:
([Region(ap-southeast-2), Region(eu-central-1), Region(eu-west-3), Region(us-east-1), Region(us-east-2), Region(us-west-1)],)
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.081
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.001
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.741
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.281
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.001
[INFO] Verifying update: CPU Limit: 0.051000000000000004
servers_per_region [ 8 0 74 28 0 5]
[[ 79 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 500 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 231 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 224 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 56 0 0]
Running 1700/sec
time=1682135682.356059 latency=1:2:2:2:4:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=2ms requests=1823 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=1730rps ql=1 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=143140 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:2:2:2:9:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=3ms accOpenQueuing=233 accErrors=0
Usage is <=500 mCPU
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 502m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 455m 5Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 488m 5Mi
Running 2000/sec
0.00% accRequests=192552 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:2:22:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=3ms accOpenQueuing=315 accErrors=0
time=1682135842.526689 latency=1:1:2:2:5:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=3ms requests=2197 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=2080rps ql=2 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=194749 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:2:22:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=3ms accOpenQueuing=317 accErrors=0
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 579m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 527m 5Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 547m 5Mi
Running 2500/sec
time=1682135893.068578 latency=1:1:2:2:5:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=2ms requests=2569 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=2525rps ql=4 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=48300 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:2:20:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=4ms accOpenQueuing=85 accErrors=0
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 711m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 648m 5Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 635m 5Mi
Running 3000/sec:
time=1682295940.682874 latency=1:1:2:2:11:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=4ms requests=3132 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=3056rps ql=4 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=64092 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:2:26:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=4ms accOpenQueuing=103 accErrors=0
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 855m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 780m 5Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 713m 5Mi
Running 3500/sec
time=1682295739.191462 latency=1:1:2:2:49:(5)ms latency95=25ms latency99=35ms requests=3625 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=3577rps ql=6 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=39629 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:2:51:(4)ms accLatency95=22ms accLatency99=34ms accOpenQueuing=161 accErrors=0
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 901m 4Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 894m 5Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 790m 5Mi
Running 4000/sec: Excess: Errors show up:
0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:12:111:(9)ms accLatency95=38ms accLatency99=47ms accOpenQueuing=1034 accErrors=0
time=1682296288.557899 latency=1:1:2:12:55:(8)ms latency95=34ms latency99=43ms requests=4180 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=3956rps ql=3 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=120174 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:12:111:(9)ms accLatency95=38ms accLatency99=47ms accOpenQueuing=1066 accErrors=0
time=1682296289.632032 latency=1:1:2:18:61:(11)ms latency95=43ms latency99=51ms requests=4190 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=3901rps ql=135 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=124364 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:12:111:(9)ms accLatency95=38ms accLatency99=47ms accOpenQueuing=1103 accErrors=0
time=1682296294.967543 latency=1:89:482:1224:4828:(790)ms latency95=2589ms latency99=3587ms requests=17181 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=3220rps ql=1895 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=141545 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:23:4828:(104)ms accLatency95=715ms accLatency99=2199ms accOpenQueuing=7269 accErrors=0
time=1682296296.760530 latency=1:83:368:1378:5590:(888)ms latency95=3214ms latency99=4437ms requests=9535 option1=0 option2=0 errors=451 throughput=5066rps ql=989 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=151080 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:1:2:29:5590:(151)ms accLatency95=1128ms accLatency99=2705ms accOpenQueuing=12071 accErrors=451
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 872m 20Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 873m 20Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 826m 21Mi
At 500/sec:
time=1682316008.392951 latency=1:2:2:2:4:(2)ms latency95=2ms latency99=2ms requests=532 option1=0 option2=0 errors=0 throughput=529rps ql=1 rr=0.00% cr=0.00% accRequests=16601 accOption1=0 accOption2=0 accLatency=1:2:2:2:30:(2)ms accLatency95=2ms accLatency99=3ms
username@master_node:~/casper$ kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
kiwix-serve-us-central-6865bb9cdc-fvrpz 134m 21Mi
kiwix-serve-us-east-579cbfd99c-626p5 133m 21Mi
kiwix-serve-us-west-5d9975ffc-448nf 136m 21Mi