Streaming Logs from CloudWatch to Scalyr
In order to send logs to Scalyr in near-real-time, there are two steps involved:
- Create an AWS Lambda Function that receives CloudWatch log events, transforms them to a Scalyr-compatible message, and posts that to a Scalyr API.
- Set up your CloudWatch Log Group(s) with a subscription filter that will stream CloudWatch log data to that lambda function.
If you haven’t set up a "cloudwatch2scalyr" lambda function yet, both of these steps will be taken care of in the Lambda Function creation wizard as described below.
NOTE: At some point (later in the instructions) you'll be asked to upload a ZIP file to Amazon. You can find the latest pre-built copy here, or you can build your own locally using the make_distribution.sh shell script.
Start the Lambda Function creation wizard
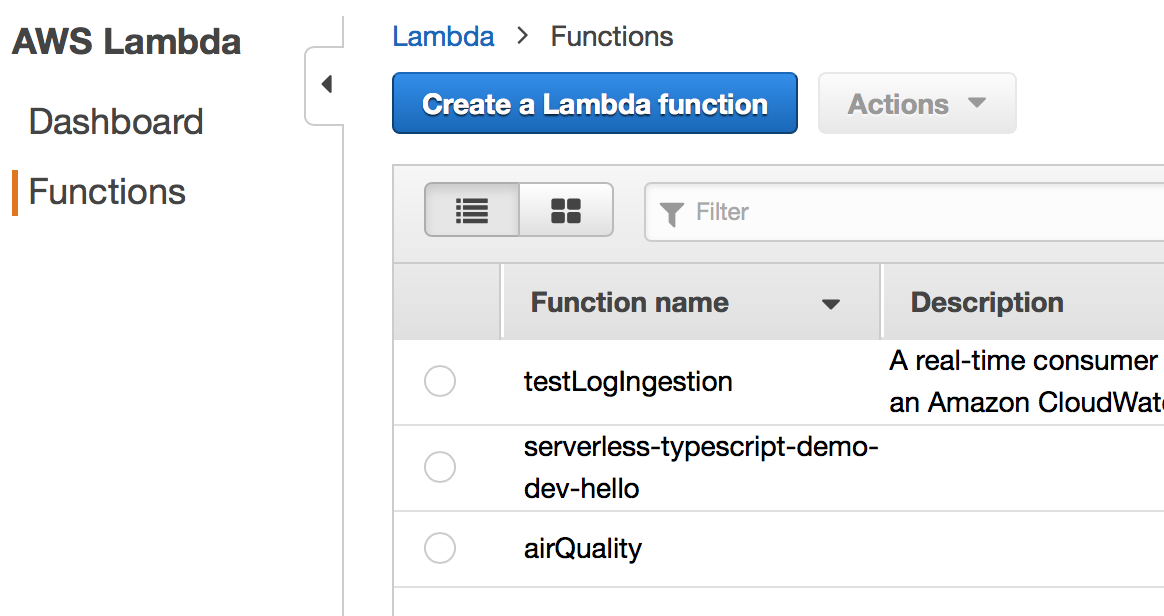
First, go to the Lambda Management Console in AWS. For us-east-1, the link is https://console.aws.amazon.com/lambda/home?region=us-east-1#/functions?display=list – if you’re in a different region, you can substitute that region for "us-east-1" in the URL above.
Once you navigate to that page, you should see something like this:
Click "Create a Lambda function" - this will start the wizard.
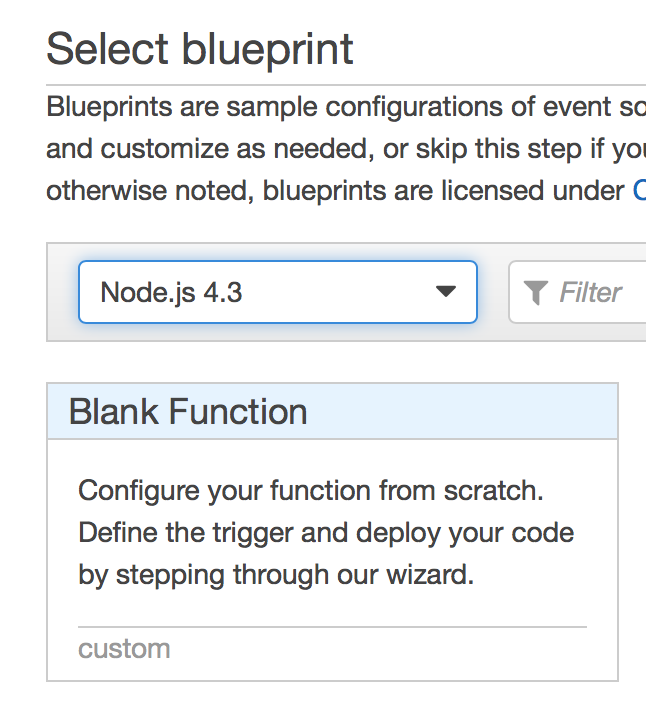
Pick runtime and function blueprint
On the next page, you’ll need to pick a "runtime" and a function “blueprint”. Choose “Node.js 4.3” for the runtime and click on “Blank Function” for the blueprint, as shown below:
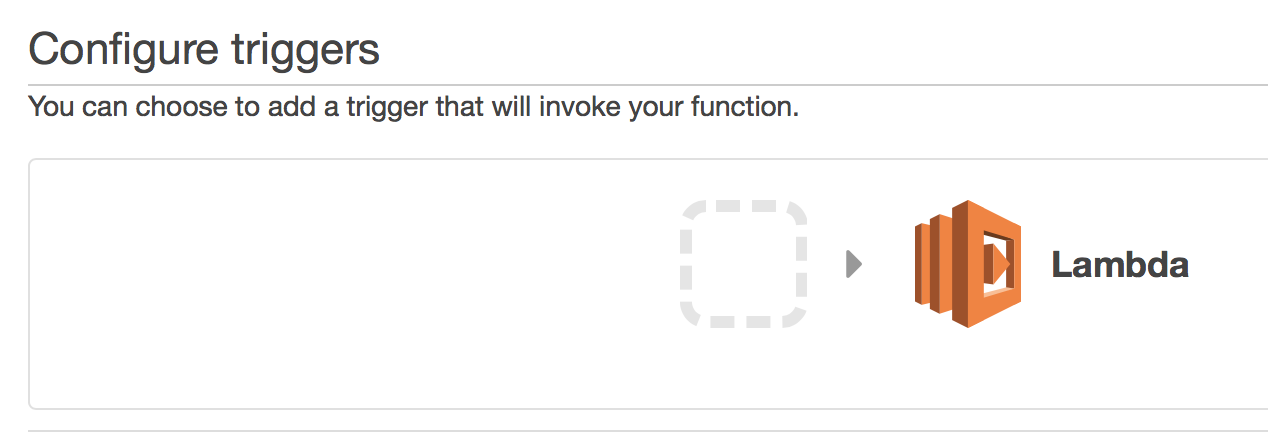
Configure trigger
On the next page, you’ll configure a trigger to invoke the function. Click on the rounded dashed-line rectangle to do this and then select "CloudWatch Logs" from the dropdown that appears:
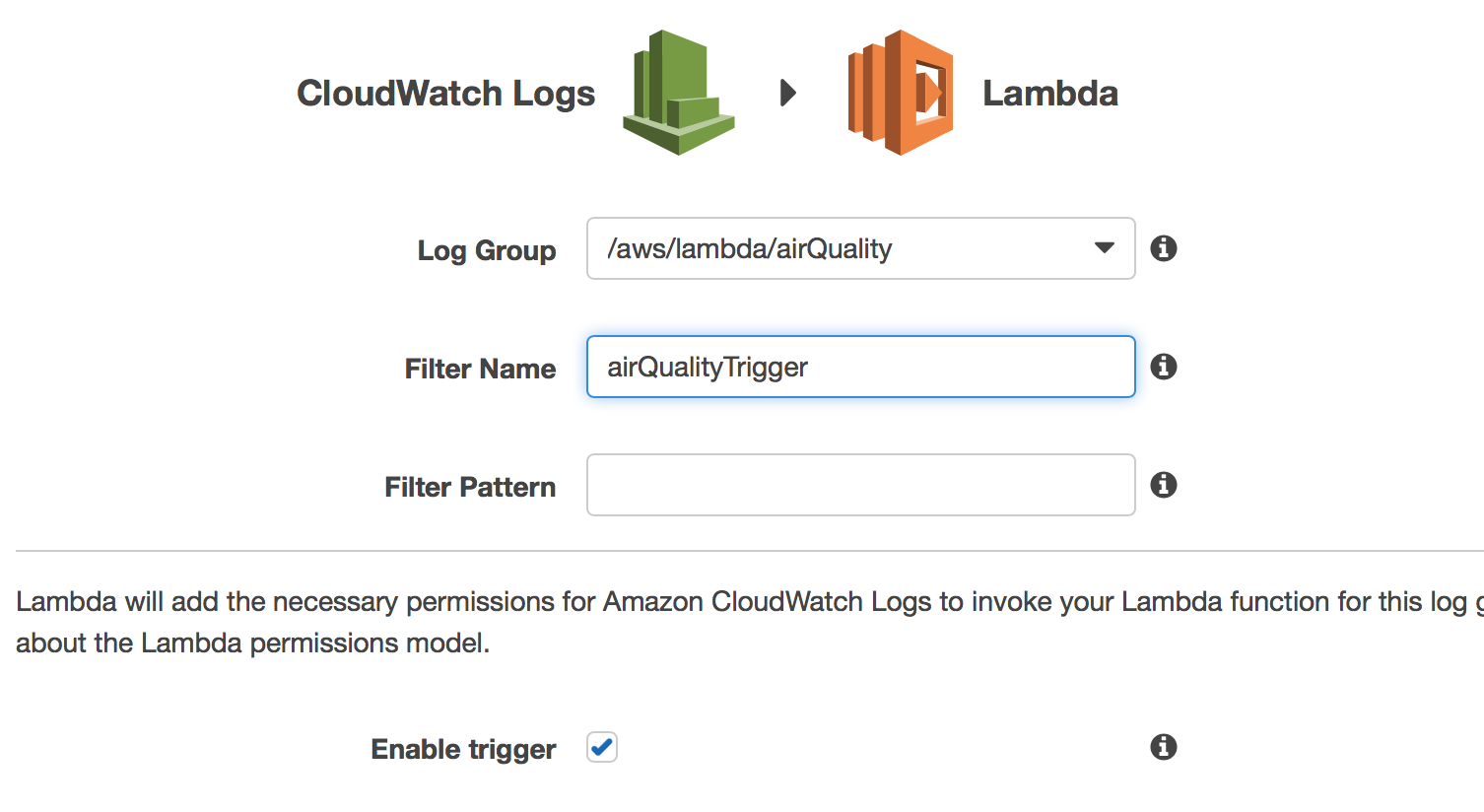
At this point, you’ll need to select a Log Group and provide a Filter Name (which can be anything, but it is required). Also, check the "Enable trigger" checkbox:
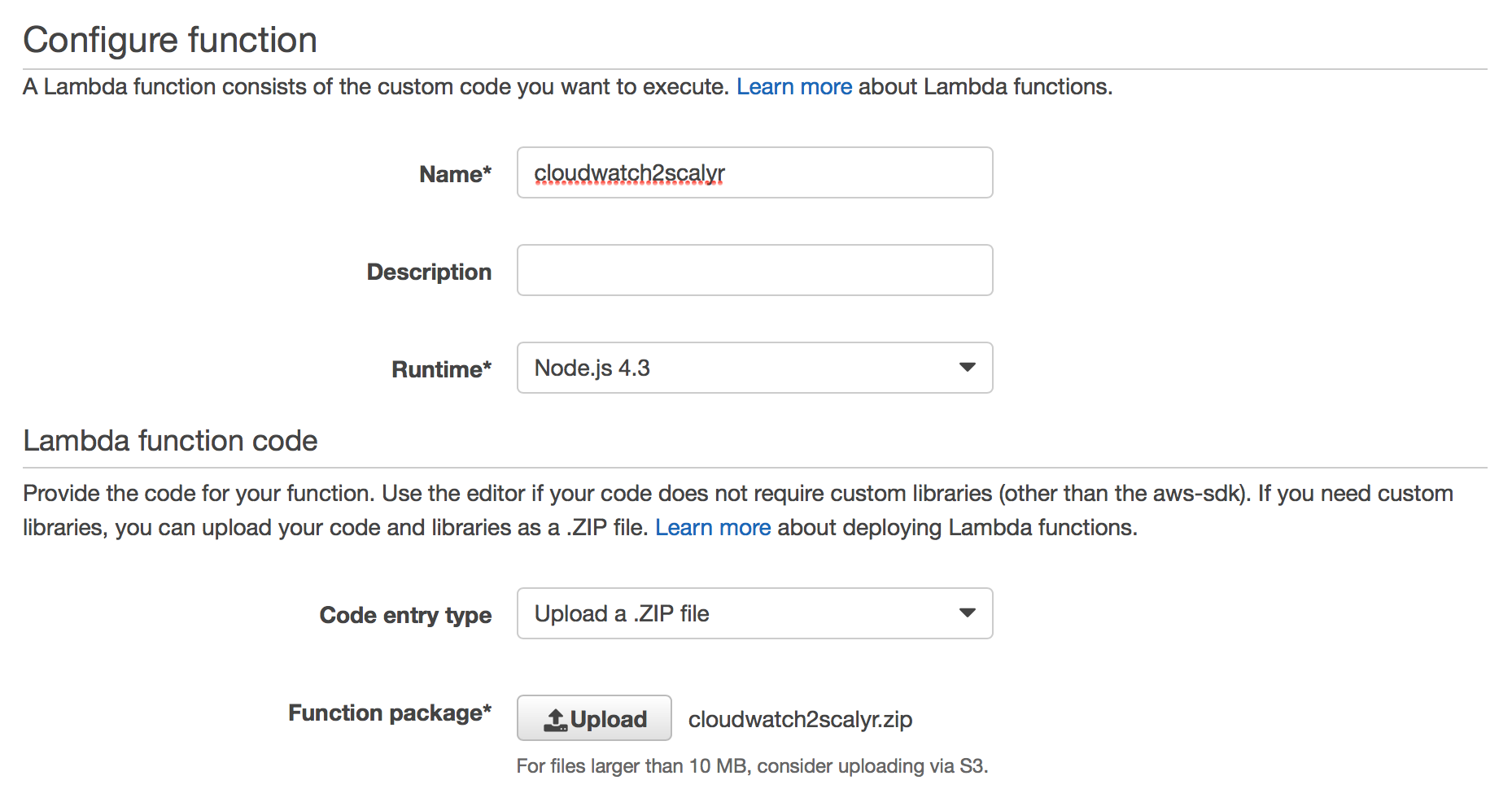
Supply function name and upload code
On the next screen, you’ll need to supply a function name and an optional description, as well as upload the lambda function code (which is in cloudwatch2scalyr.zip):
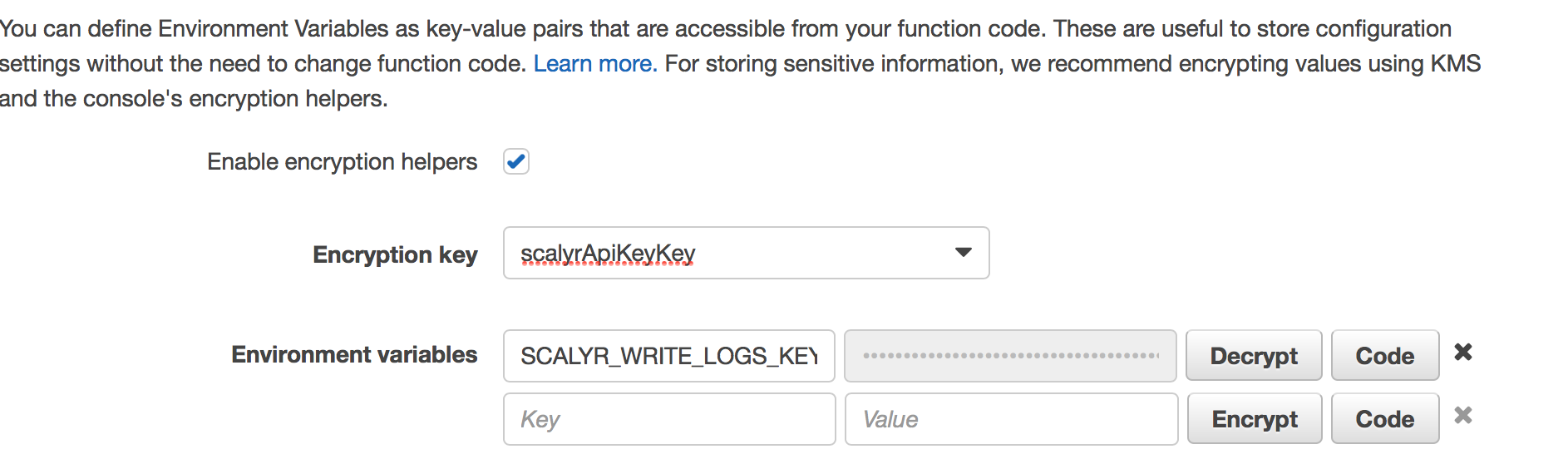
Supply environment variables
You’ll need to specify your Scalyr "Write Logs" API key as an environment variable on this screen (scroll down a bit). In order to do this, you’ll need to create a KMS encryption key if you don’t have one in your account already (beyond the scope of this document). Select your encryption key and enter an environment variable:
- Enter "SCALYR_WRITE_LOGS_KEY" in the first column (no quotes)
- Provide your account’s actual Scalyr "Write Logs" API Key in the second column.
- Click "Encrypt".
Once you’ve done this, you should see something like:
There are a couple of additional environment variables you can pass to the code - USE_ADD_EVENTS_API, PARSER_NAME, and SCALYR_BASE_URL. (These should not be encrypted.)
- In general,
USE_ADD_EVENTS_APIshould be false (and you don’t actually need to specify it unless you want it to be true). PARSER_NAMEis optional as well and refers to a specific custom parser defined using the Scalyr UI - if not specified, the default parser is used.SCALYR_BASE_URLdefaults tohttps://www.scalyr.comand selects the Scalyr region to which you want to upload your logs, such ashttps://upload.eu.scalyr.com. Note: If this parameter is configured incorrectly, you will not get error messages from Scalyr during log upload; AWS logs of this Lambda function will look as if everything is working, but the logs won't show in Scalyr.
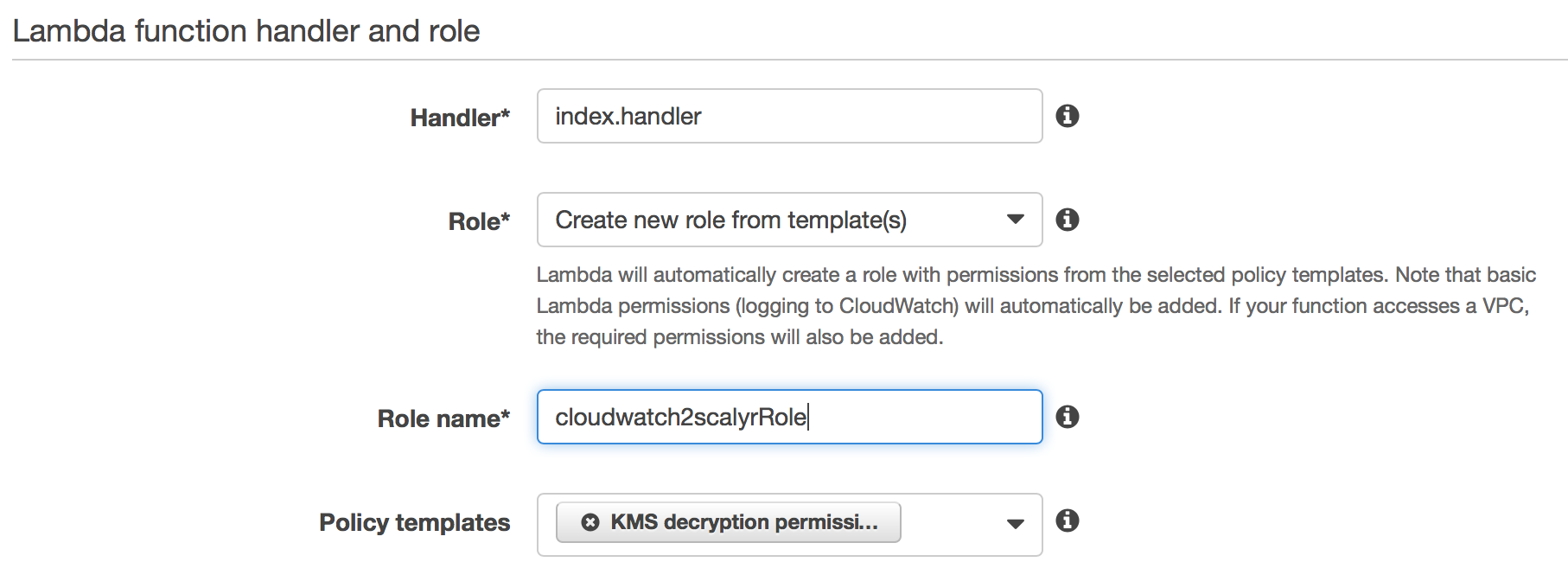
Define a role for your function
The last step on this page is to define a role for your function. In the next section of the page, choose "Create new role from template(s)" from the Role dropdown, give the role a name, and choose “KMS decryption permissions” from the Policy Templates dropdown:
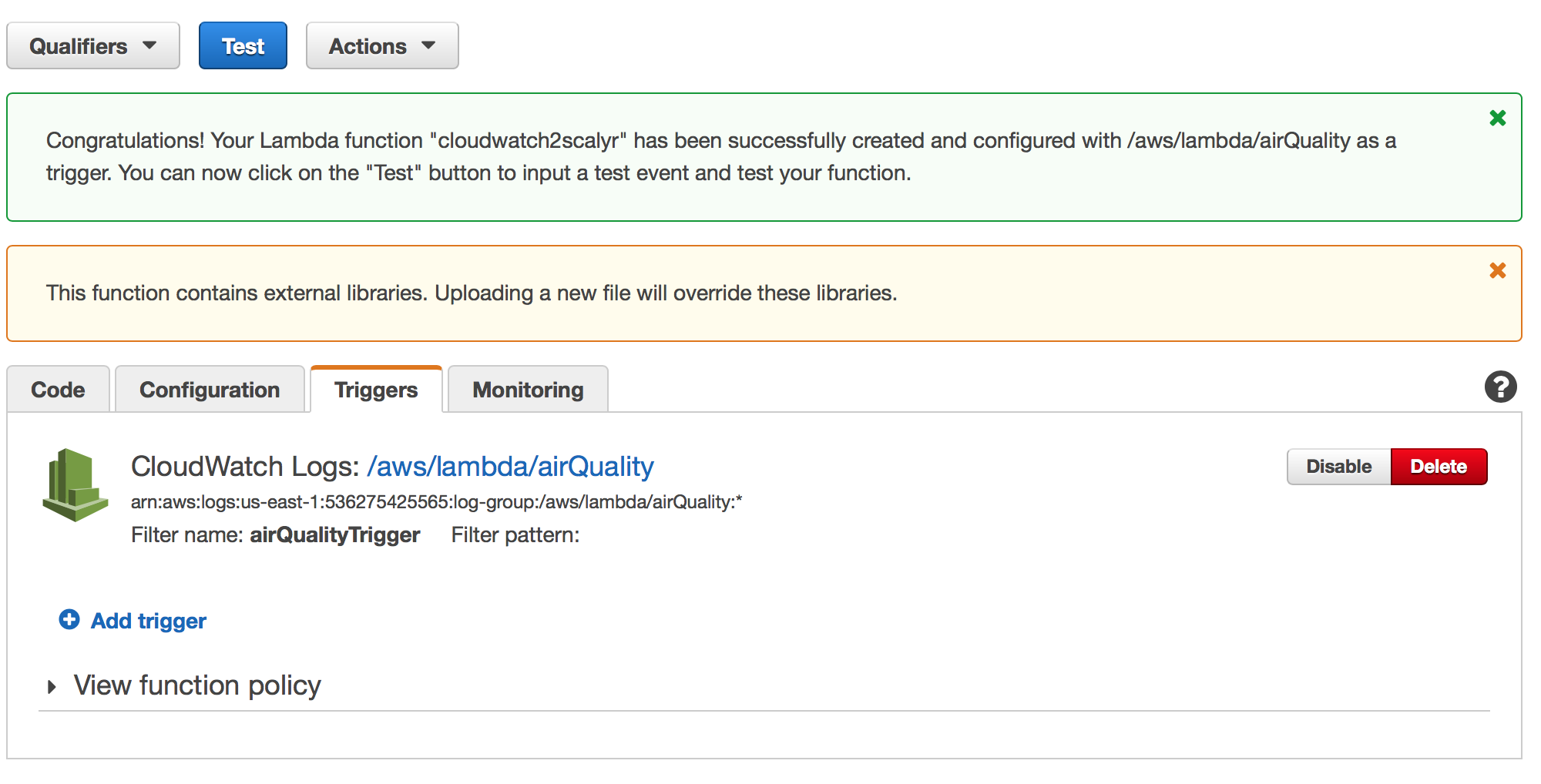
Finalize the installation
Now, click "Next". On the next page, click “Create Function”. You should see a screen like:
At this point, you’re done!
Try it out
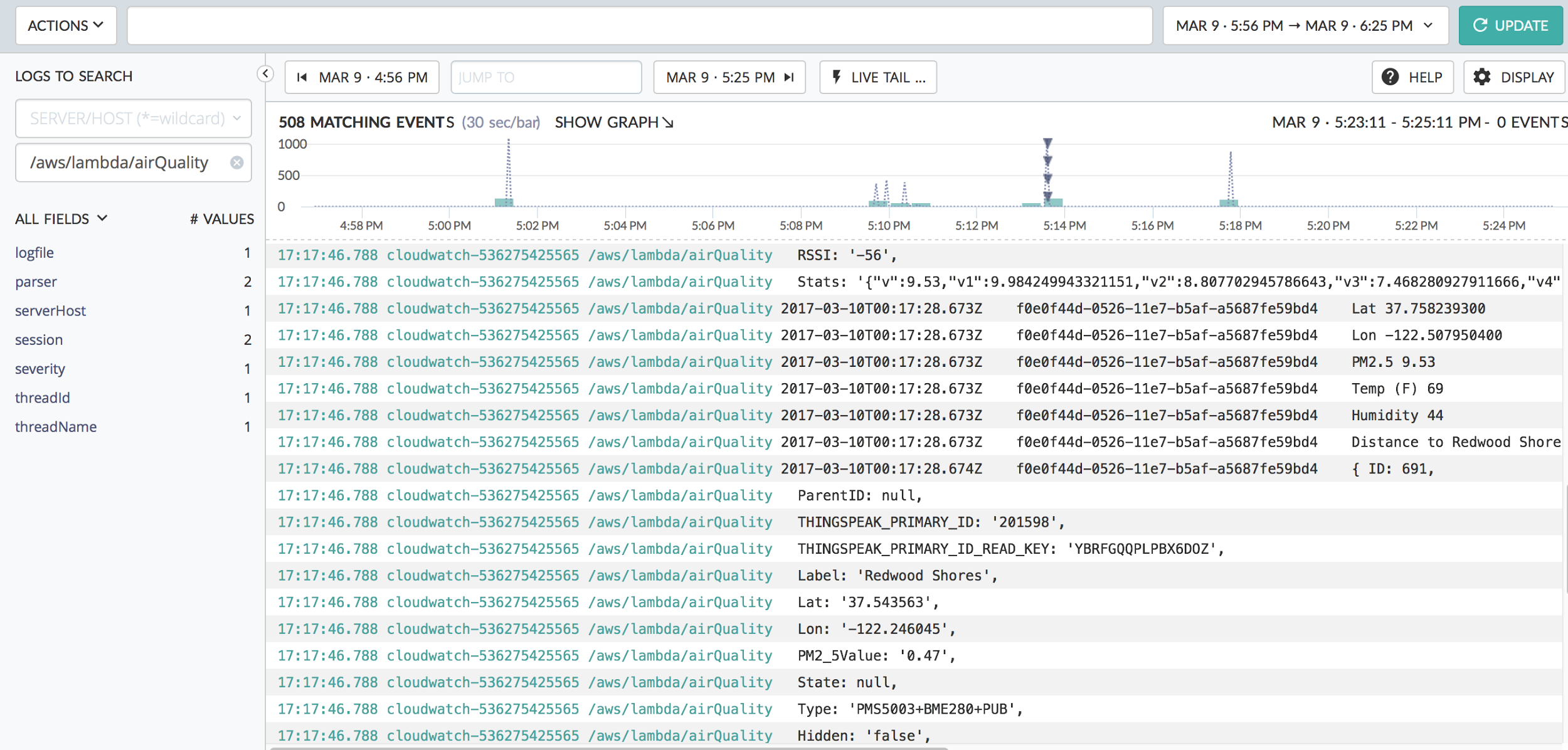
Try it out by triggering some kind of action that will generate CloudWatch logs. This should cause events to be streamed to Scalyr (it may take a few seconds for them to show up):
As you’ll notice, the log messages that show up in Scalyr are identical to those you would see in CloudWatch. Also note the serverHost field ("cloudwatch-536….") and logfile field (“/aws/lambda/airQuality”). You can set up a custom parser in Scalyr based on the log file name (it should match your PARSER_NAME environment variable). You can also customize the serverHost field via the SERVER_HOST environment variable.
A bit about the addEvents transformation code (experimental)
This is an experimental feature that allows you to do some parsing in AWS Lambda itself by modifying the code in cloudwatch2scalyr.
You can also customize the serverHost, logfile, and parser on a per-log-group basis by setting an environment variable, LOG_GROUP_OPTIONS.
The cloudwatch2scalyr.zip file contains one main file (index.js) as well as supporting Node.js libraries. If you wish to pre-parse interesting fields from the logs, you’ll probably be most interested in the transformToAddEventsMessage function, which is responsible for translating from CloudWatch-speak to Scalyr-speak. Note: at this time, we don’t recommend using the addEvents API from Amazon Lambda (use uploadLogs, the default, instead).
To use LOG_GROUP_OPTIONS, set the variable to a JSON string with log group names as keys, e.g.:
{
"API-Gateway-Execution-Logs_abcdef12345/production": {
"serverHost": "API-Gateway",
"logfile": "My-Friendly-Api-Name",
"parser": "myGatewayParser"
},
"API-Gateway-Execution-Logs_12345abcdef/production": {
"serverHost": "API-Gateway",
"logfile": "My-Other-Api"
}
}Defaults are used for any omitted fields.
For more information about the format Scalyr expects, see this link: https://www.scalyr.com/help/api#addEvents
The function can be found here.