Project, 02456 Deep Learning, Technical University of Denmark
Christina Bligaard Pedersen (s134891), Dea Steenstrup (s123870), Emma Christine Jappe (s102240) & Rasa Audange Muktupavela (s161197)
This project revolved around making a deep learning model for prediction of protein transmembrane helices. The overall goal was to create a model that takes an amino acid sequence as an input and predicts the protein topology (i.e. which amino acid residues are positioned where relative to the membrane).
There are five categories for each residue:
- Membrane in-out
- Membrane out-in
- Signal peptide
- Inside
- Outside
Furthermore, the outputs a prediction of the protein type.
- Signal peptide + globular (SP+Glob)
- Signal peptide + transmembrane (SP+TM)
- Transmembrane (TM)
- Globular (Glob)
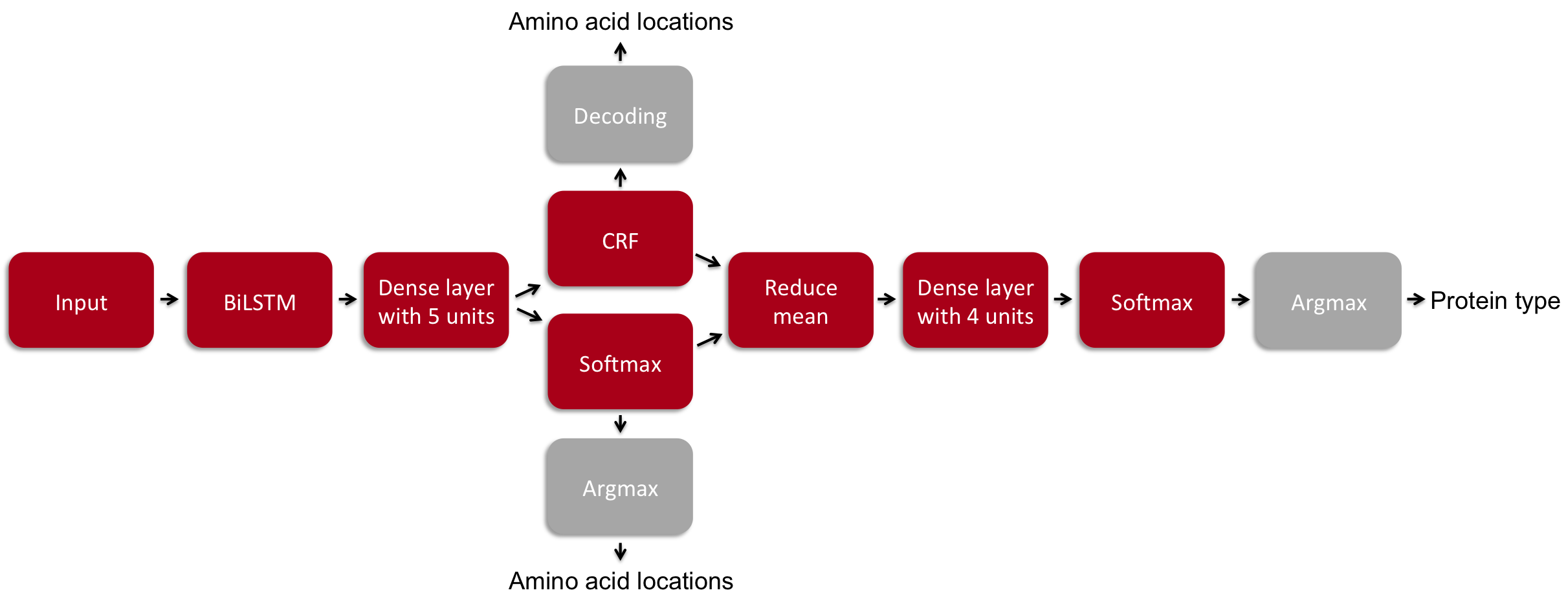
The model of choice for this problem was a bidirectional recurrent neural network (RNN) with a long short-term memory (LSTM) cell followed by a dense layer and either a conditional random field (CRF) or simply a softmax function followed by an argmax. This part of the model is used for predicting the location of each amino acid. On top of this model, we average the probabilities of each category over the entire amino acid sequence length and have a dense layer, and finally we use the softmax and argmax functions to predict the protein type.
The loss function for the first part of the prediction (amino acid locations) is '-log likelihood' if the CRF is used, and the 'weighted cross-entropy loss for a sequence of logits' if not. The loss function for the second part of the prediction (protein type) is the 'sparse softmax cross entropy'. In the end, the two losses are summed and the ADAM algorithm is used as the optimizer to minimize the loss.
The data used for this project was the TOPCONS2-data downloaded from here. The data consisted of 6,856 proteins, but to ensure computational efficiency, we removed proteins longer than 2,000 amino acids (n = 123), and as a result we have a dataset of 6,733 proteins in total. These were divided into five partitions maintaining the same proportion of each class and the same length distribution as the full dataset. Proteins with more than 30 % homology were placed within a single partition (homology partitioning). The full dataset contained 2,171 SP+Glob-proteins, 718 SP+TM, 313 TM and 3,531 Glob.
For training, validating and testing the model, a setup was made in which 3 partitions were used for training, 1 was used for validation, and 1 was used for testing. During training, which typically ran for 1,000 epochs, the model was validated every 10 epochs - and each time the validation loss decreased, the model was saved.
Initial tests showed that using 60 units in the LSTM cells and relu as an activation function for the type-prediction, yielded good results. These settings were fixed and a grid search was performed for the following hyper-parameter value combinations (a total of 64 runs):
- With and without the CRF
- Batch size = 16, 32, 64 or 128
- Learning rate = 0.01, 0.005, 0.002, 0.001, 0.0005, 0.0001, 0.00005, 0.00001
After training, the model with the lowest validation loss was selected for runs with and without the CRF, and these models were tested on the test partition.
- data_tm.npz
The data file contains 7 matrices: 1) BLOSUM62-encoded proteins (matrix size 6733x2000x23), 2) Protein labels per amino acid (matrix size 6733x2000), the labels are: Membrane in → out, Membrane out → in, Signal peptide, Inside, Outside, 3) Protein lengths (size 6733), 4) Sequence mask - padding for all proteins shorter than 2000 amino acids (matrix size 6733x2000), 1 for positions within the protein length and 0 for padded positions, 5) Protein type (size 6733), the types are: Globular with signal peptide, TM with signal peptide, TM, and globular, 6) Partitioning fold (size 6733), values from 0 to 4, and 7) Protein id numbers (size 6733).
- training.py
- model.py
- minibatches.py
- confidence_plot.py
- conf_matrix.py
- plots.py
- crf.py
- marginal_probabilities.py
- testing_model.ipynb (Jupyter notebook file for recreating the main results of this study)
- lr_0.001_crf_False_batch_16_model
- lr_0.01_crf_True_batch_32_model