Welcome! In this repository you'll find a set of custom nodes for ComfyUI that allows you to use Core ML models in your ComfyUI workflows. These models are designed to leverage the Apple Neural Engine (ANE) on Apple Silicon (M1/M2) machines, thereby enhancing your workflows and improving performance.
If you're not sure how to obtain these models, you can download them here or convert your own models using coremltools.
In simple terms, think of Core ML models as a tool that can help your ComfyUI work faster and more efficiently. For instance, during my tests on an M2 Pro 32GB machine, the use of Core ML models sped up the generation of 512x512 images by a factor of approximately 1.5 to 2 times.
To start using custom nodes in your ComfyUI, follow these simple steps:
- Clone or download this repository: You can do this directly into the custom_nodes directory of your ComfyUI.
- Install the dependencies: You'll need to use a package manager like pip to do this.
That's it! You're now ready to start enhancing your ComfyUI workflows with Core ML models.
- Check Installation for more details on installation.
- Check How to use for more details on how to use the custom nodes.
- Check Example Workflows for some example workflows.
- Core ML: A machine learning framework developed by Apple. It's used to run machine learning models on Apple devices.
- Core ML Model: A machine learning model that can be run on Apple devices using Core ML.
- mlmodelc: A compiled Core ML model. This is the recommended format for Core ML models.
- mlpackage: A Core ML model packaged in a directory. This is the default format for Core ML models.
- ANE: Apple Neural Engine. A hardware accelerator for machine learning tasks on Apple devices.
- Compute Unit: A Core ML option that allows you to specify the hardware on which the model should run.
- CPU_AND_ANE: A Core ML compute unit option that allows the model to run on both the CPU and ANE. This is the default option.
- CPU_AND_GPU: A Core ML compute unit option that allows the model to run on both the CPU and GPU.
- CPU_ONLY: A Core ML compute unit option that allows the model to run on the CPU only.
- ALL: A Core ML compute unit option that allows the model to run on all available hardware.
- CLIP: Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training. A model that learns visual concepts from natural language supervision. It's used as a text encoder in Stable Diffusion.
- VAE: Variational Autoencoder. A model that learns a latent representation of images. It's used as a prior in Stable Diffusion.
- Checkpoint: A file that contains the weights of a model. It's used to load models in Stable Diffusion.
- LCM: Latent Consistency Model. A type of model designed to generate images with as few steps as possible.
Note
Note on Compute Units:
For the model to run on the ANE, the model must be converted with the --attention-implementation SPLIT_EINSUM
option.
Models converted with --attention-implementation ORIGINAL will run on GPU instead of ANE.
These custom nodes come with a host of features, including:
- Loading Core ML Unet models
- Support for ControlNet
- Support for ANE (Apple Neural Engine)
- Support for CPU and GPU
- Support for
mlmodelcandmlpackagefiles - Support for SDXL models
- Support for LCM models
- Support for LoRAs
- SD1.5 -> Core ML conversion
- SDXL -> Core ML conversion
- LCM -> Core ML conversion
Note
Please note that using Core ML models can take a bit longer to load initially. For the best experience, I recommend using the compiled models (.mlmodelc files) instead of the .mlpackage files.
Note
This repository will continue to be updated with more nodes and features over time.
The easiest way to install the custom nodes is to use the ComfyUI-Manager. You can find the installation instructions here. Once you've installed the ComfyUI-Manager, you can install the custom nodes by following these steps:
- Open the ComfyUI-Manager by clicking the
Managerbutton in the ComfyUI toolbar. - Click the
Install Custom Nodesbutton. - Search for
Core MLand click theInstallbutton. - Restart ComfyUI.
-
Clone this repository into the custom_nodes directory of your ComfyUI. If you're not sure how to do this, you can download the repository as a zip file and extract it into the same directory.
cd /path/to/comfyui/custom_nodes git clone https://github.com/aszc-dev/ComfyUI-CoreMLSuite.git -
Next, install the required dependencies using pip or another package manager:
cd /path/to/comfyui/custom_nodes/ComfyUI-CoreMLSuite pip install -r requirements.txt
Once you've installed the custom nodes, you can start using them in your ComfyUI workflows.
To do this, you need to add the nodes to your workflow. You can do this by right-clicking on the workflow canvas and
selecting the nodes from the list of available nodes (the nodes are in the Core ML Suite category).
You can also double-click the canvas and use the search bar to find the nodes. The list of available nodes is given
below.
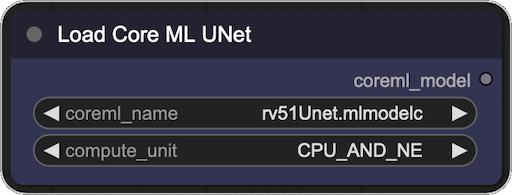
This node allows you to load a Core ML UNet model and use it in your ComfyUI workflow. Place the converted
.mlpackage or .mlmodelc file in ComfyUI's models/unet directory and use the node to load the model. The output of the
node is a coreml_model object that can be used with the Core ML Sampler.
- Inputs:
- model_name: The name of the model to load. This should be the name of the .mlpackage or .mlmodelc file.
- compute_unit: The hardware on which the model should run. This can be one of the following:
CPU_AND_ANE: The model will run on both the CPU and ANE. This is the default option. It works best with models converted with--attention-implementation SPLIT_EINSUMor--attention-implementation SPLIT_EINSUM_V2.CPU_AND_GPU: The model will run on both the CPU and GPU. It works best with models converted with--attention-implementation ORIGINAL.CPU_ONLY: The model will run on the CPU only.ALL: The model will run on all available hardware.
- Outputs:
- coreml_model: A Core ML model that can be used with the Core ML Sampler.
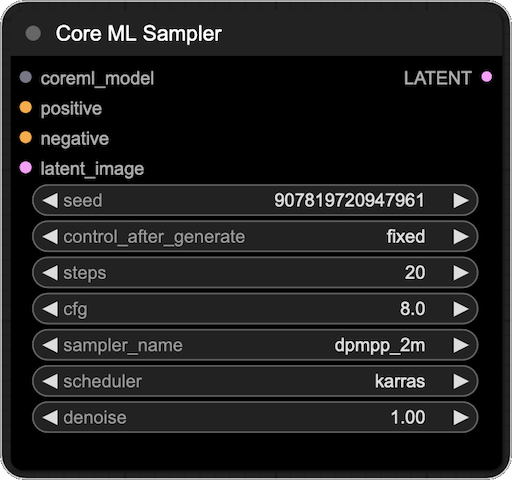
This node allows you to generate images using a Core ML model. The node takes a Core ML model as input and outputs a latent image similar to the latent image output by the KSampler. This means that you can use the resulting latent as you normally would in your workflow.
- Inputs:
- coreml_model: The Core ML model to use for sampling. This should be the output of the Core ML UNet Loader.
- latent_image [optional]: The latent image to use for sampling. If provided, should be of the same size as the input of the Core ML model. If not provided, the node will create a latent suitable for the Core ML model used. Useful in img2img workflows.
- ... (the rest of the inputs are the same as the KSampler)
- Outputs:
- LATENT: The latent image output by the Core ML model. This can be decoded using a VAE Decoder or used as input to the next node in your workflow.
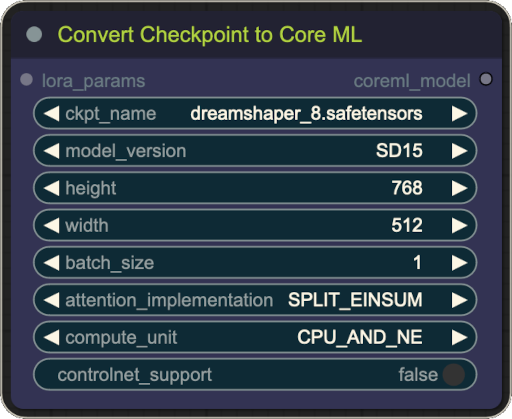
You can use this node to convert any SD1.5 based checkpoint to a Core ML model. The converted model is stored in the
models/unet directory and can be used with the Core ML UNet Loader. The conversion parameters are encoded in
the node name, so if the model already exists, the node will not convert it again.
- Inputs:
- ckpt_name: The name of the checkpoint to convert. This should be the name of the checkpoint file stored in the
models/checkpointsdirectory. - model_version: Whether the model is based on SD1.5 or SDXL.
- height: The desired height of the image generated by the model. The default is 512. Must be a multiple of 8.
- width: The desired width of the image generated by the model. The default is 512. Must be a multiple of 8.
- batch_size: The batch size of generated images. If you're planning to generate batches of images, you can try increasing this value to speed up the generation process. The default is 1.
- attention_implementation: The attention implementation used when converting the model. Choose SPLIT_EINSUM or SPLIT_EINSUM_V2 for better ANE support. Choose ORIGINAL for better GPU support.
- compute_unit: The hardware on which the model should run. This is used only when loading the model and doesn't affect the conversion process.
- controlnet_support: For the model to support ControlNet, it must be converted with this option set to True. The default is False.
- lora_params [optional]: Optional LoRA names and weights. If provided, the model will be converted with LoRA(s) baked in. More on loading LoRAs below.
- ckpt_name: The name of the checkpoint to convert. This should be the name of the checkpoint file stored in the
- Outputs:
- coreml_model: The converted Core ML model that can be used with Core ML Sampler.
Note
Some models use a custom config .yaml file. If you're using such a model, you'll need to place the config file in the
models/configs directory. The config file should be named the same as the checkpoint file. For example, if the
checkpoint file is named juggernaut_aftermath.safetensors, the config file should be
named juggernaut_aftermath.yaml.
The config file will be automatically loaded during conversion.
Note
For now, the converter relies heavilty on the model name to determine the conversion parameters. This means that if you change the model name, the node will convert the model again. Other than that, if you find the name too long or confusing, you can change it to anything you want.
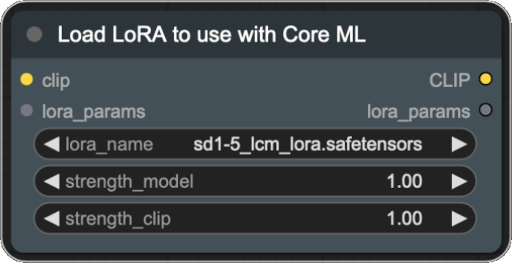
This node allows you to load LoRAs and bake them into a model. Since this is a workaround (as model weights can't be modified after conversion), there are a few caveats to keep in mind:
-
The LoRA weights and strength_model parameter are baked into the model. This means that you can't change them after conversion. This also means that you need to convert the model again if you want to change the LoRA weights.
-
Loading LoRA affects CLIP, which is not a part of Core ML workflow, so you'll need to load CLIP separately, either using
CLIPLoaderorCheckpointLoaderSimple. (See example workflows for more details.) -
After conversion, if you want to load the model using
CoreMLUnetLoader, you'll need to apply the same LoRAs to CLIP manually. (See example workflows for more details.) -
The LoRA names are encoded in the model name. This means that if you change the name of the LoRA file, you'll need to change the model name as well, or the node will convert the model again. (Model strength is not encoded, so if you want to change it, you'll need to delete the converted model manually)
-
strength_clip parameter only affects the CLIP model and is not baked into the converted model. This means that you can change it after conversion.
-
Inputs:
- lora_name: The name of the LoRA to load.
- strength_model: The strength of the LoRA model.
- strength_clip: The strength of the LoRA CLIP.
- lora_params [optional]: Optional output from other LoRA Loaders.
- clip: The CLIP model to use with the LoRA. This can be either output of the
CLIPLoader/CheckpointLoaderSimpleor other LoRA Loaders.
-
Outputs:
- lora_params: The LoRA parameters that can be passed to the Core ML Converter or other LoRA Loaders.
- CLIP: The CLIP model with LoRA applied.
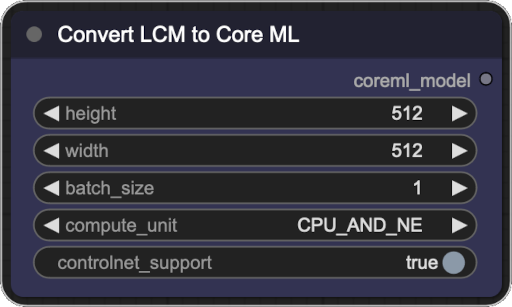
This node converts SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7 model to Core
ML. The converted model is stored in the models/unet directory and can be used with the Core ML UNet Loader. The
conversion parameteres are encoded in the node name, so if the model already exists, the node will not convert it again.
- Inputs:
- height: The desired height of the image generated by the model. The default is 512. Must be a multiple of 8.
- width: The desired width of the image generated by the model. The default is 512. Must be a multiple of 8.
- batch_size: The batch size of generated images. If you're planning to generate batches of images, you can try increasing this value to speed up the generation process. The default is 1.
- compute_unit: The hardware on which the model should run. This is used only when loading the model and doesn't affect the conversion process.
- controlnet_support: For the model to support ControlNet, it must be converted with this option set to True. The default is False.
Note
The conversion process can take a while, so please be patient.
Note
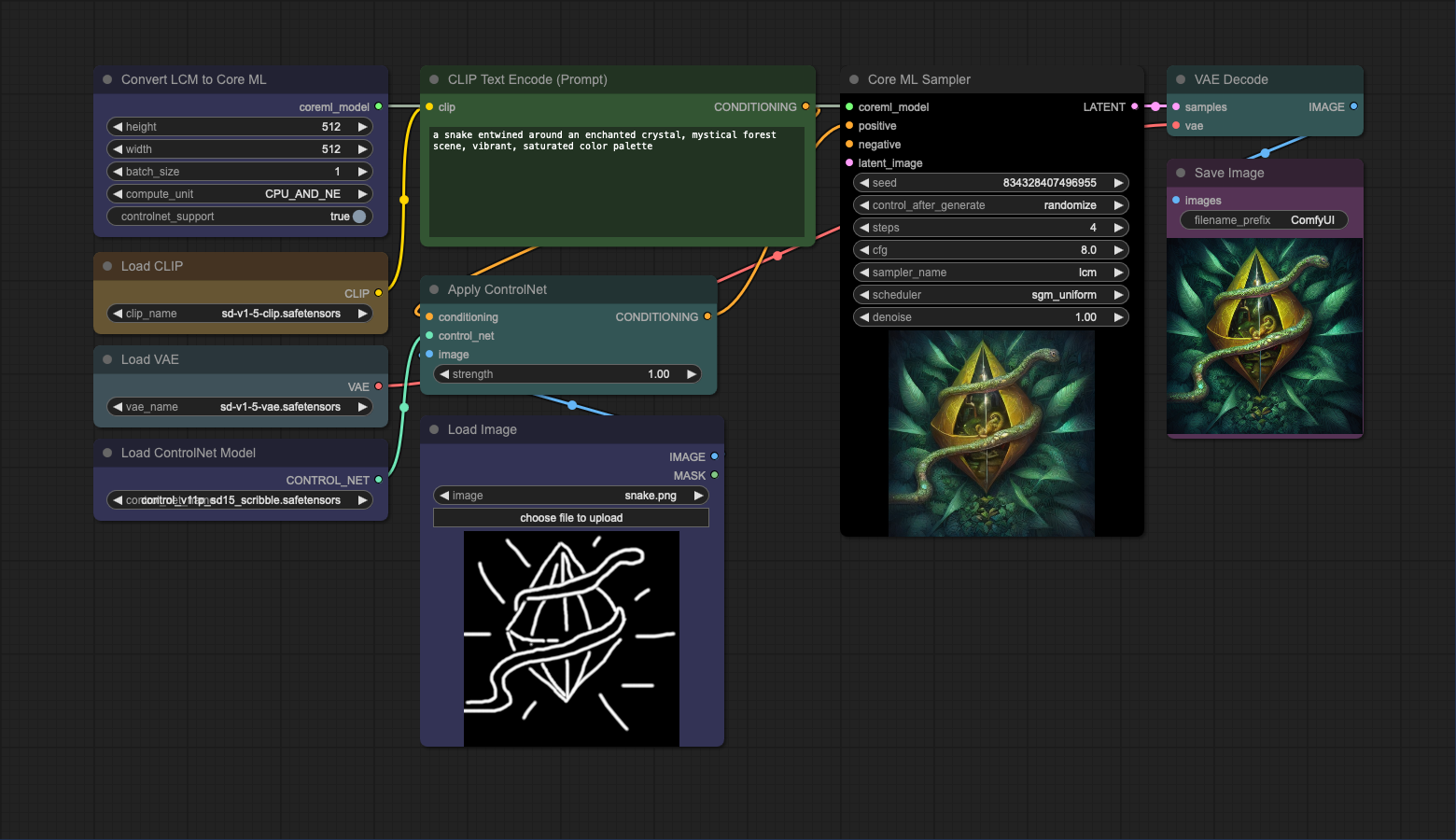
When using the LCM model with Core ML Sampler, please set sampler_name to lcm and scheduler to sgm_uniform.
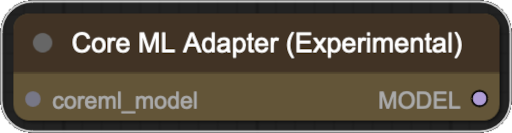
This node allows you to use a Core ML as a standard ComfyUI model. This is an experimental node and may not work with all models and nodes. Please use with caution and pay attention to the expected inputs of the model.
- Input:
- coreml_model: The Core ML model to use as a ComfyUI model.
- Output:
- MODEL: The Core ML model wrapped in a ComfyUI model.
Note
While this approach allows you to use Core ML models with many ComfyUI nodes (both standard and custom), the expected inputs of the model will not be checked, which may cause errors. Please make sure to use a model compatible with the expected parameters.
Note
The models used are just an example. Feel free to experiment with different models and see what works best for you.
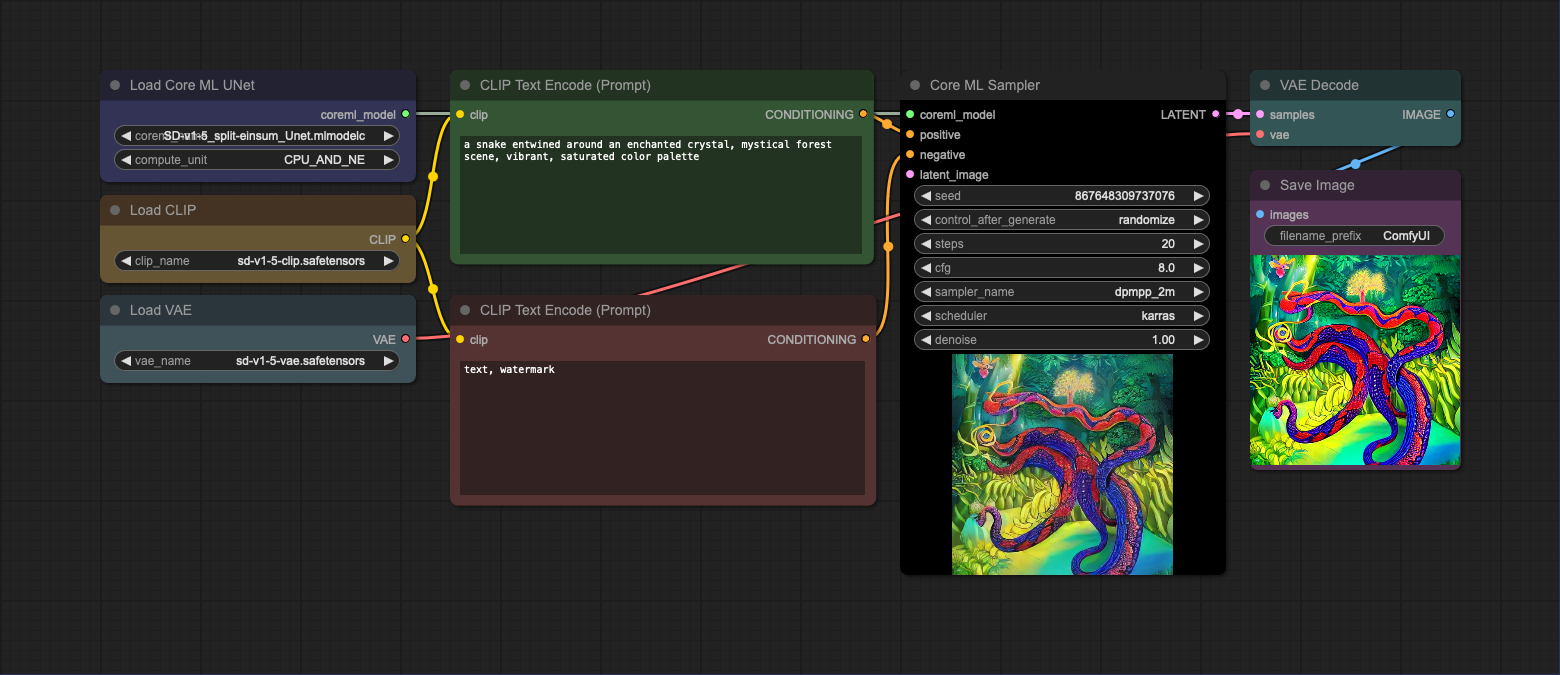
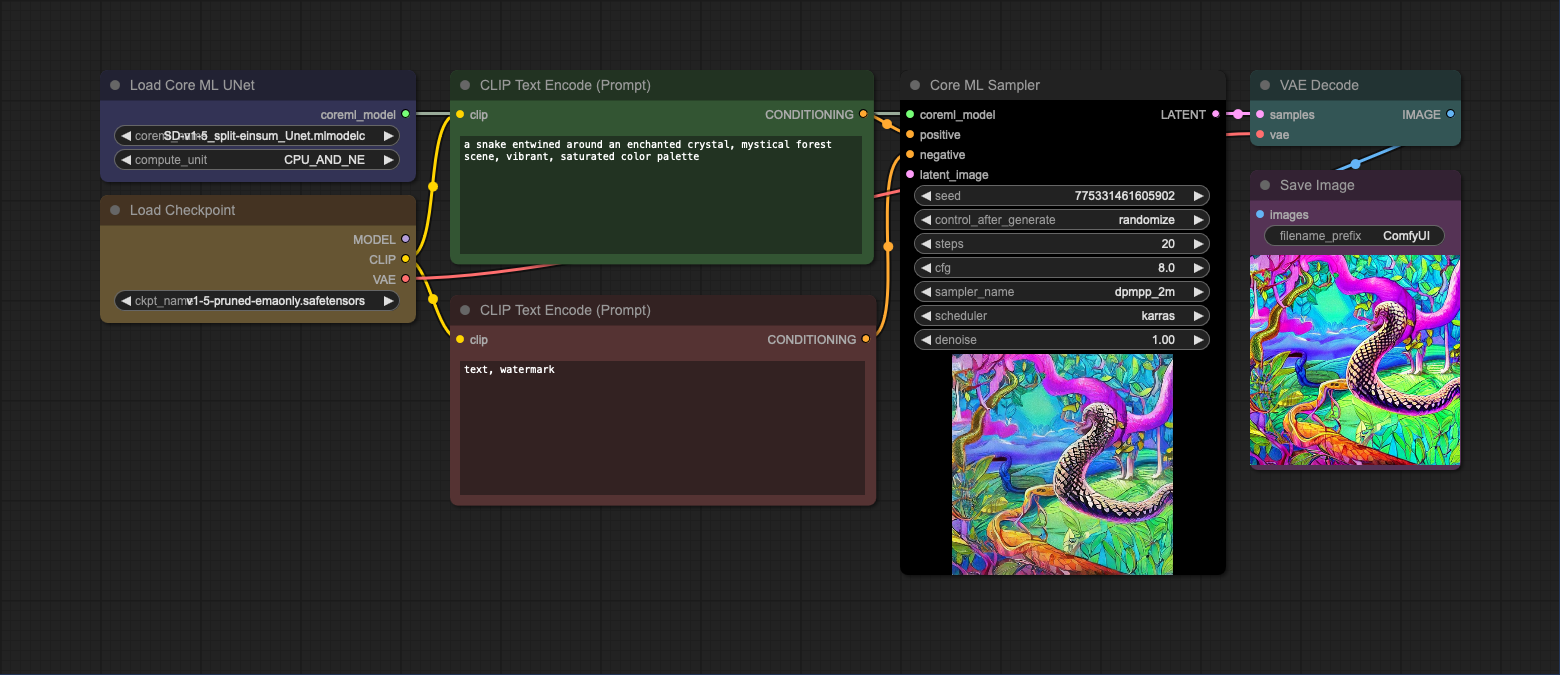
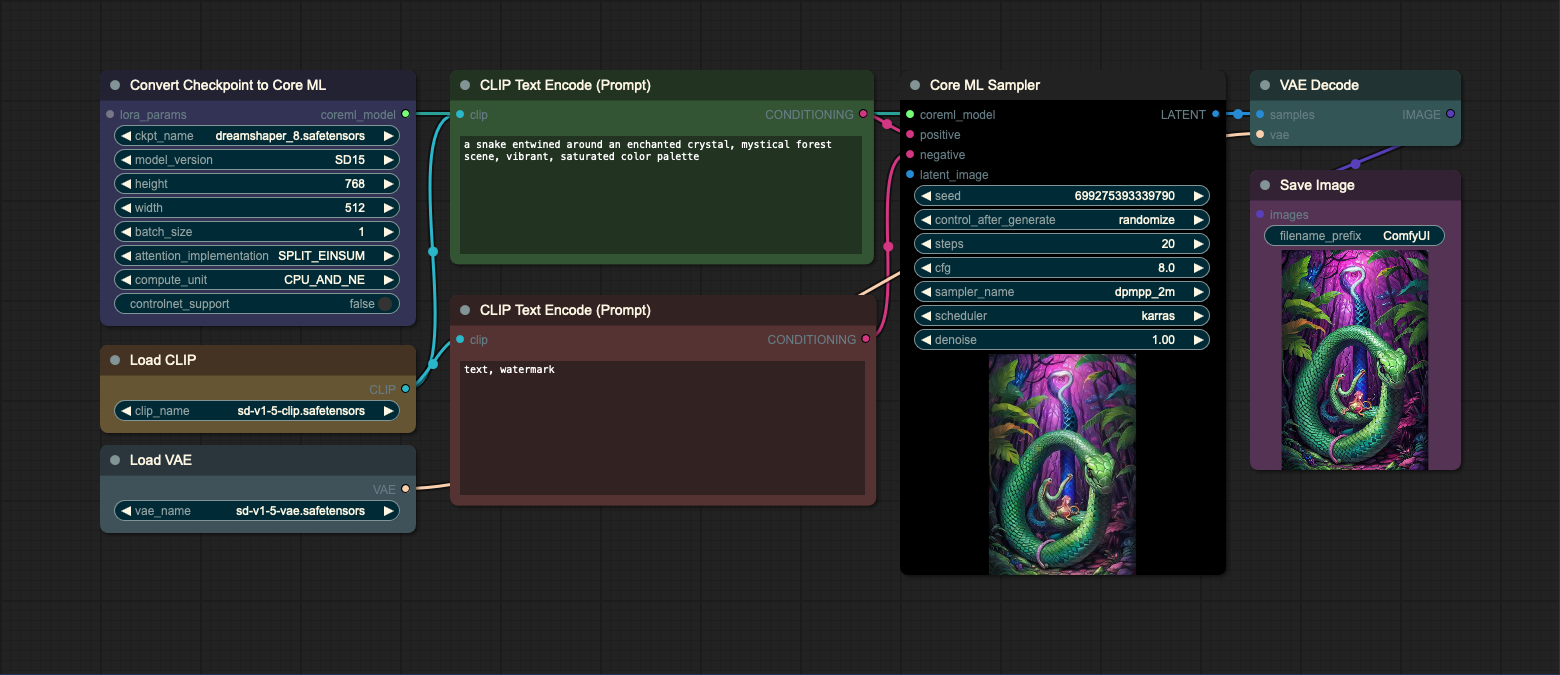
This is a basic txt2img workflow that uses the Core ML UNet loader to load a model. The CLIP and VAE models are loaded using the standard ComfyUI nodes. In the first example, the text encoder (CLIP) and VAE models are loaded separately. In the second example, the text encoder and VAE models are loaded from the checkpoint file. Note that you can use any CLIP or VAE model as long as it's compatible with Stable Diffusion v1.5.
- Loading text encoder (CLIP) and VAE models separately
- Loading text encoder (CLIP) and VAE models from checkpoint file
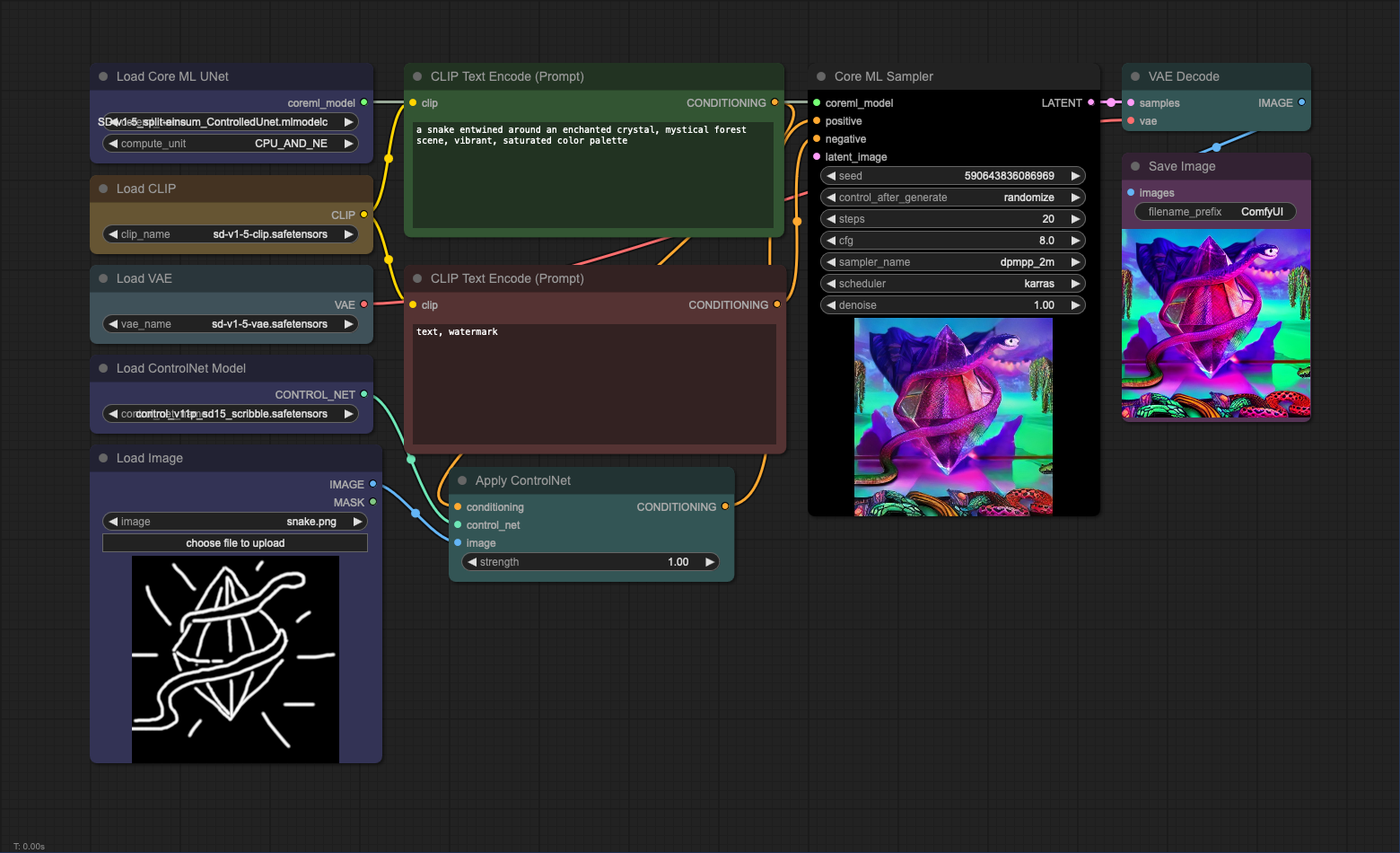
This workflow uses the Core ML UNet loader to load a Core ML UNet model that supports ControlNet. The ControlNet is
being loaded using the standard ComfyUI nodes. Please refer to
the basic txt2img workflow for more details on how to load the CLIP and VAE
models.
The ControlNet model used in this workflow is available
here.
Once downloaded, place the model in the models/controlnet directory.
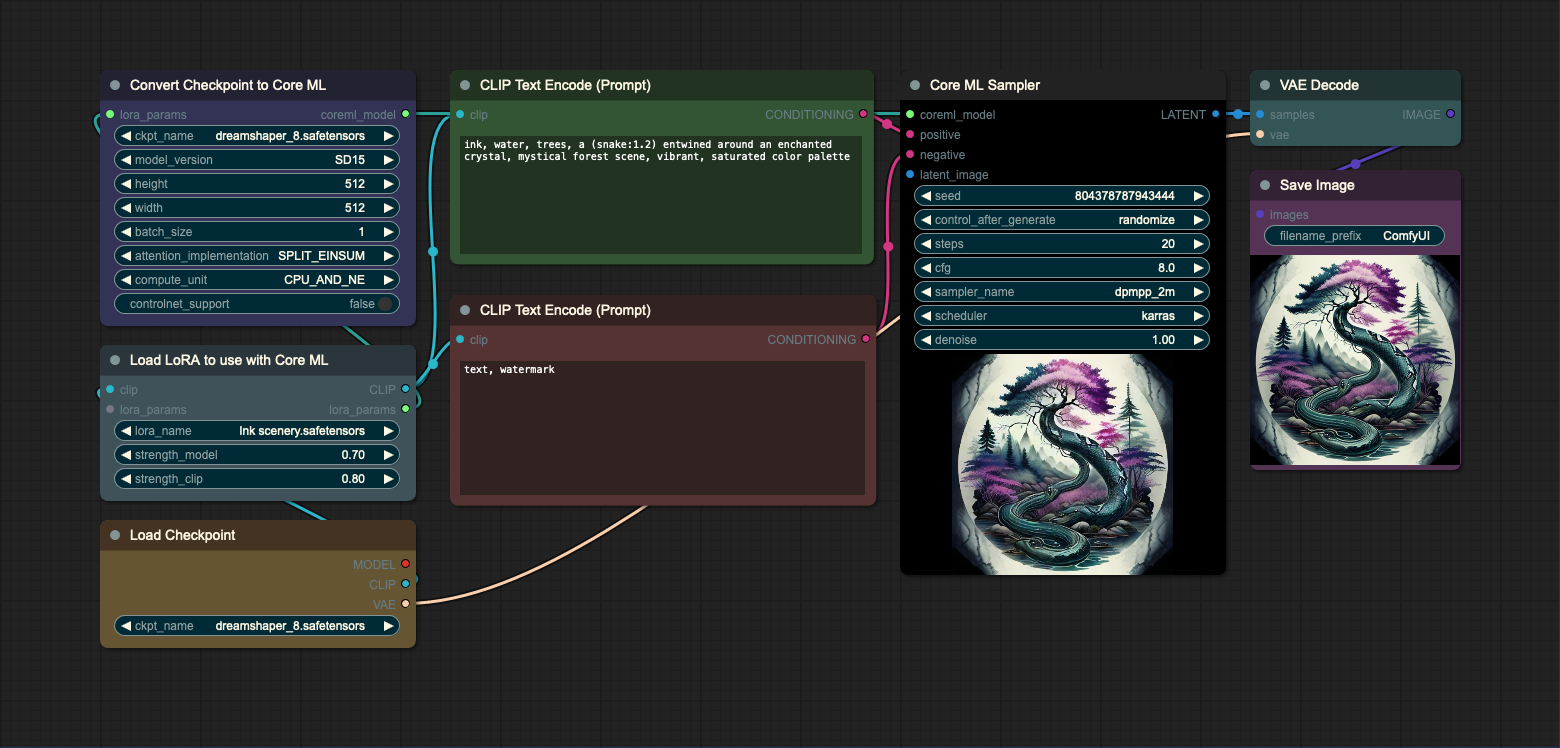
This workflow uses the Checkpoint Converter to convert the checkpoint file. See Checkpoint Converter description for more details.
This workflow uses the Checkpoint Converter to convert the checkpoint file with LoRA. See LoRA Loader description to read more about the caveats of using LoRA.
Please note that you can use multiple LoRAs with the same model. To do this, you'll need to use multiple LoRA Loaders.
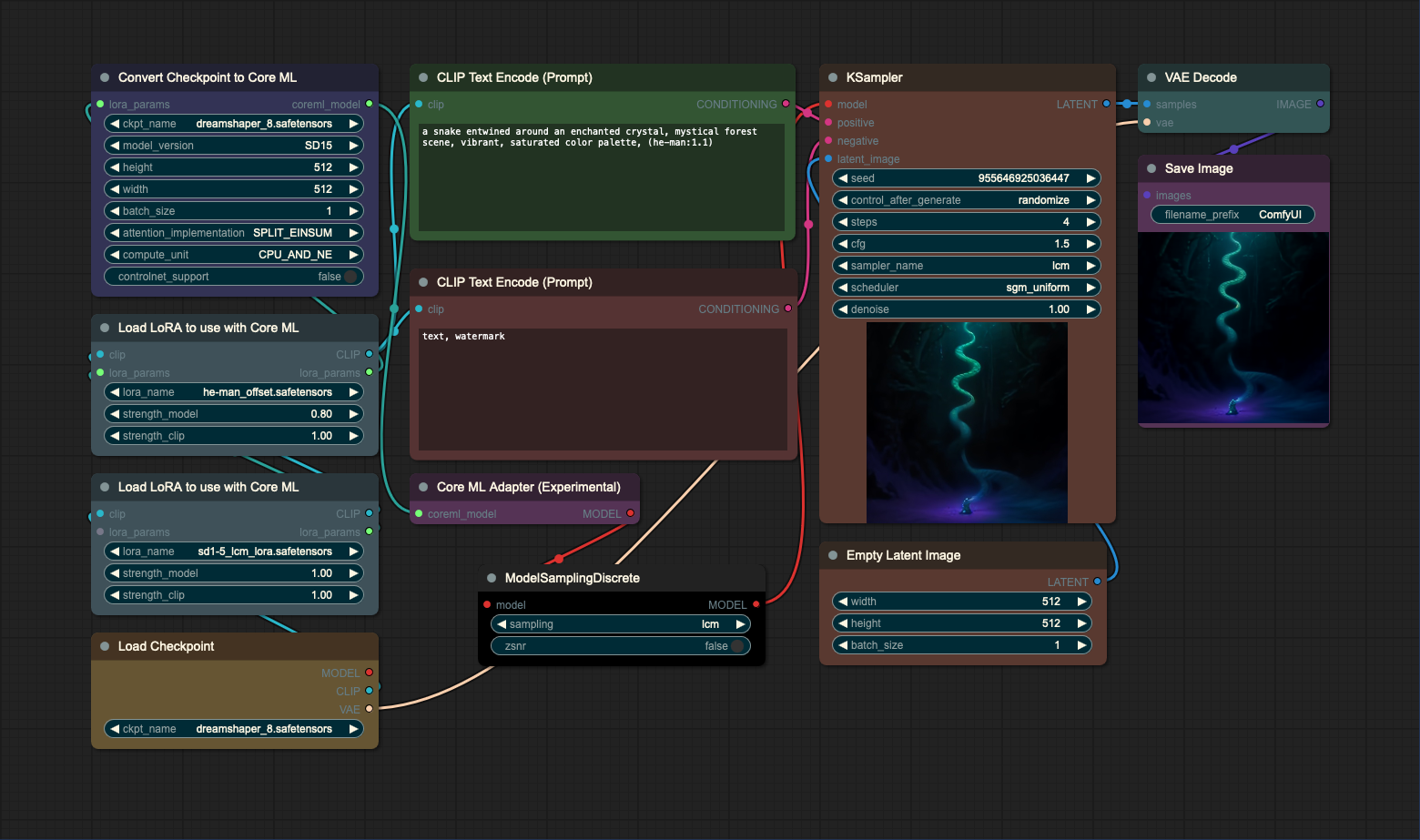
Important
In this example, the model is passed through the adapter and ModelSamplingDiscrete nodes to a standard ComfyUI's
KSampler (not Core ML Sampler). ModelSamplingDiscrete needs to be used to sample models with LCM LoRAs properly.
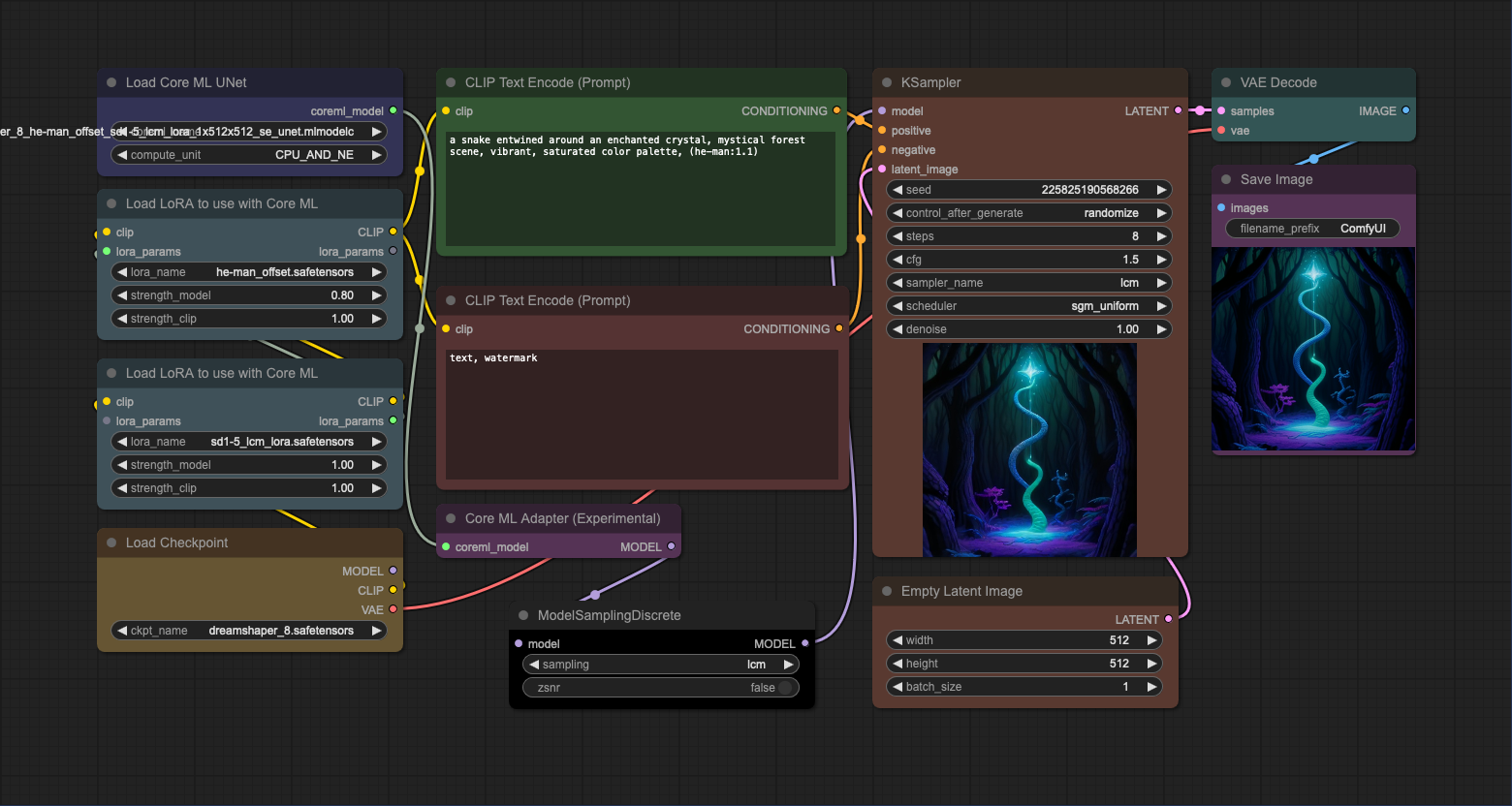
This workflow uses the Core ML UNet Loader to load a model with LoRAs. The CLIP must be loaded separately and passed through the same LoRA nodes as during conversion. See LoRA Loader description to read more about the caveats of using LoRA. Since lora_name and strength_model are baked into the model, it is not necessary to pass them as inputs to the loader.
Important
In this example, the model is passed through the adapter and ModelSamplingDiscrete nodes to a standard ComfyUI's
KSampler (not Core ML Sampler). ModelSamplingDiscrete needs to be used to sample models with LCM LoRAs properly.
This workflow uses LCM converter to
convert SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7
model to Core ML. The converted model can then be used with or without ControlNet to generate images.
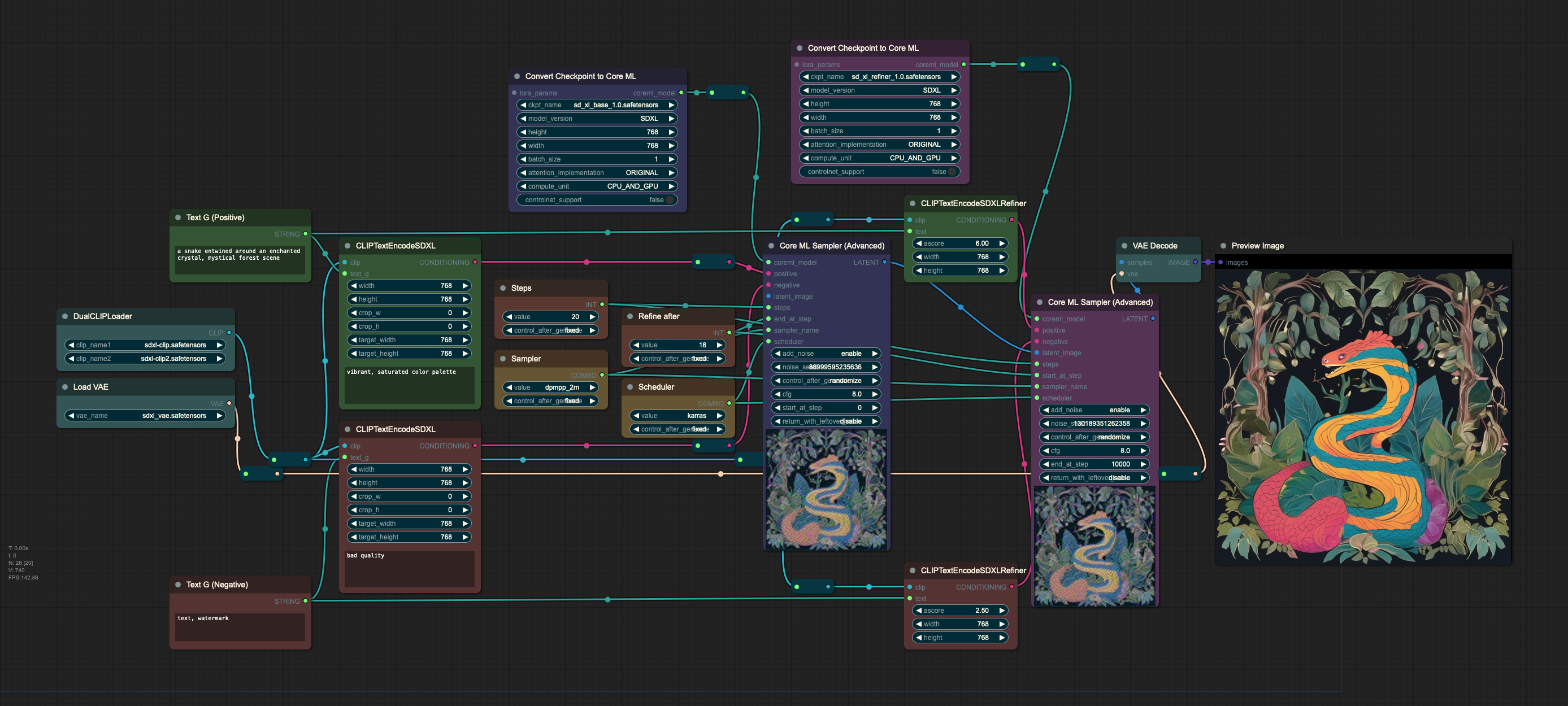
This is a basic workflow for SDXL. You add LoRAs and ControlNets the same way as in the previous examples. You can also skip the refiner step.
The models used in this workflow are available at the following links:
Important
SDXL on ANE is not supported. If loading of the model gets stuck, please try using CPU_AND_GPU or CPU_ONLY.
For best results, use ORIGINAL attention implementation.
- Core ML models are fixed in terms of their inputs and outputs. This means you'll need to use latent images of the same size as the input of the model (512x512 is the default for SD1.5). However, you can convert the model to a different input size using tools available in the apple/ml-stable-diffusion repository.
- SD2.1 models are not supported.
Unless EnumeratedShapes is used during conversion. Needs more testing.
I'm here to help! If you have any questions or suggestions, don't hesitate to open an issue and I'll do my best to assist you.