This guide walks you through the process of creating a server application that can receive HTTP multi-part file uploads.
What You Will Build
You will create a Spring Boot web application that accepts file uploads. You will also build a simple HTML interface to upload a test file.
What You Need
Starting with Spring Initializr
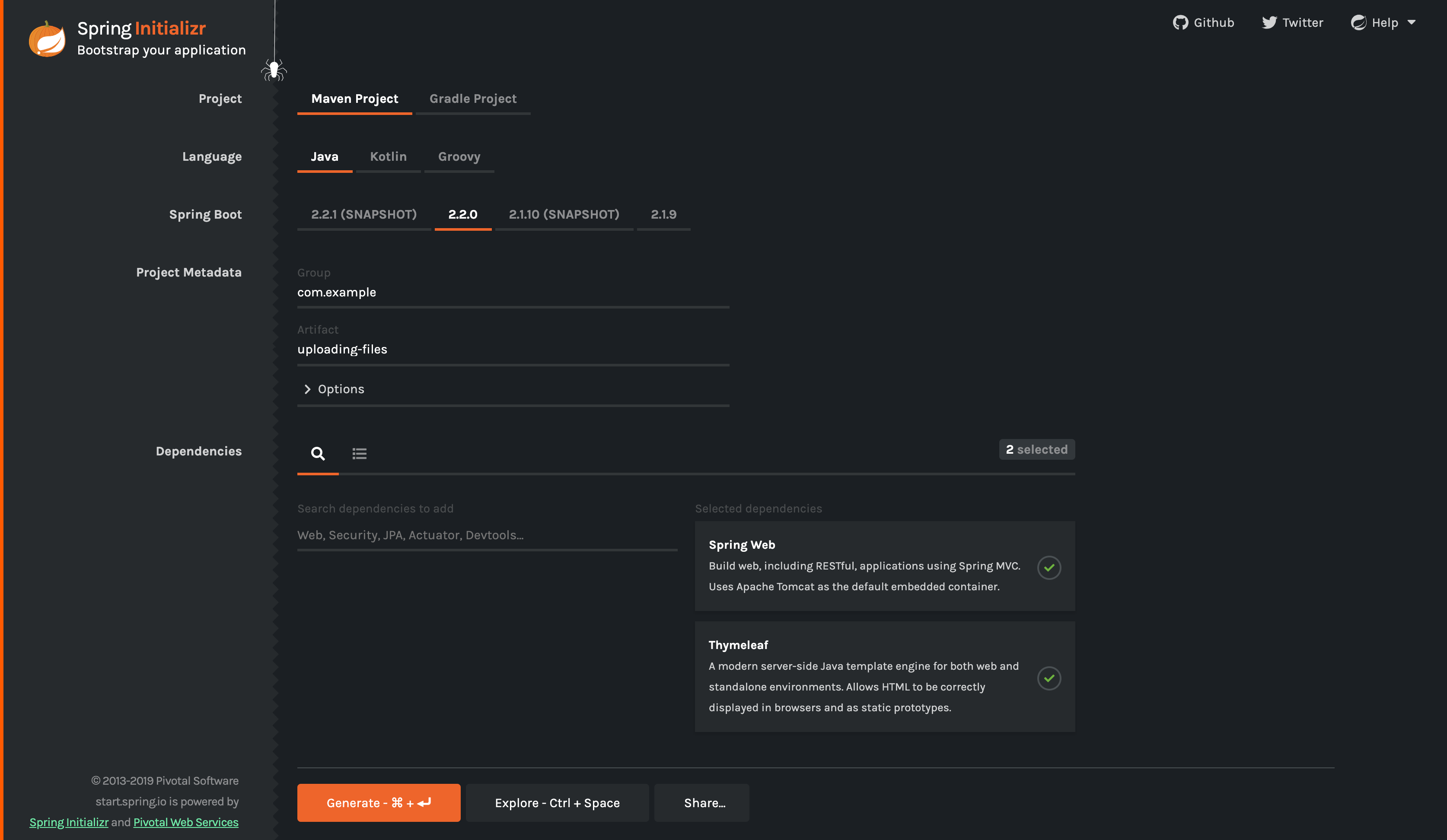
For all Spring applications, you should start with the Spring Initializr. The Initializr offers a fast way to pull in all the dependencies you need for an application and does a lot of the setup for you. This example needs the Spring Web and Thymeleaf dependencies. The following image shows the Initializr set up for this sample project:
|
Note
|
The preceding image shows the Initializr with Maven chosen as the build tool. You
can also use Gradle. It also shows values of com.example and uploading-files as the
Group and Artifact, respectively. You will use those values throughout the rest of this
sample.
|
The following listing shows the pom.xml file that is created when you choose Maven:
link:initial/pom.xml[]The following listing shows the build.gradle file that is created when you choose Gradle:
link:initial/build.gradle[]Create an Application Class
To start a Spring Boot MVC application, you first need a starter. In this sample,
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf and spring-boot-starter-web are already added as
dependencies. To upload files with Servlet containers, you need to register a
MultipartConfigElement class (which would be <multipart-config> in web.xml). Thanks to
Spring Boot, everything is auto-configured for you!
All you need to get started with this application is the following
UploadingFilesApplication class (from
src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/UploadingFilesApplication.java):
link:initial/src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/UploadingFilesApplication.java[]As part of auto-configuring Spring MVC, Spring Boot will create a MultipartConfigElement
bean and make itself ready for file uploads.
Create a File Upload Controller
The initial application already contains a few classes to deal with storing and loading
the uploaded files on disk. They are all located in the
com.example.uploadingfiles.storage package. You will use those in your new
FileUploadController. The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/FileUploadController.java) shows the file
upload controller:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/FileUploadController.java[]The FileUploadController class is annotated with @Controller so that Spring MVC can
pick it up and look for routes. Each method is tagged with @GetMapping or @PostMapping
to tie the path and the HTTP action to a particular controller action.
In this case:
-
GET /: Looks up the current list of uploaded files from theStorageServiceand loads it into a Thymeleaf template. It calculates a link to the actual resource by usingMvcUriComponentsBuilder. -
GET /files/{filename}: Loads the resource (if it exists) and sends it to the browser to download by using aContent-Dispositionresponse header. -
POST /: Handles a multi-part messagefileand gives it to theStorageServicefor saving.
|
Note
|
In a production scenario, you more likely would store the files in a temporary location, a database, or perhaps a NoSQL store (such as Mongo’s GridFS). It is best to NOT load up the file system of your application with content. |
You will need to provide a StorageService so that the controller can interact with a
storage layer (such as a file system). The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/storage/StorageService.java) shows that
interface:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles//storage/StorageService.java[]Creating an HTML Template
The following Thymeleaf template (from src/main/resources/templates/uploadForm.html)
shows an example of how to upload files and show what has been uploaded:
link:complete/src/main/resources/templates/uploadForm.html[]This template has three parts:
-
An optional message at the top where Spring MVC writes a flash-scoped message.
-
A form that lets the user upload files.
-
A list of files supplied from the backend.
Tuning File Upload Limits
When configuring file uploads, it is often useful to set limits on the size of files.
Imagine trying to handle a 5GB file upload! With Spring Boot, we can tune its
auto-configured MultipartConfigElement with some property settings.
Add the following properties to your existing properties settings (in
src/main/resources/application.properties):
link:complete/src/main/resources/application.properties[]The multipart settings are constrained as follows:
-
spring.http.multipart.max-file-sizeis set to 128KB, meaning total file size cannot exceed 128KB. -
spring.http.multipart.max-request-sizeis set to 128KB, meaning total request size for amultipart/form-datacannot exceed 128KB.
Run the Application
You want a target folder to which to upload files, so you need to enhance the basic
UploadingFilesApplication class that Spring Initializr created and add a Boot
CommandLineRunner to delete and re-create that folder at startup. The following listing
(from src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/UploadingFilesApplication.java) shows how
to do so:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/UploadingFilesApplication.java[]https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-guides/getting-started-macros/master/build_an_executable_jar_subhead.adoc https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-guides/getting-started-macros/master/build_an_executable_jar_with_both.adoc
That runs the server-side piece that receives file uploads. Logging output is displayed. The service should be up and running within a few seconds.
With the server running, you need to open a browser and visit http://localhost:8080/ to
see the upload form. Pick a (small) file and press Upload. You should see the success
page from the controller. If you choose a file that is too large, you will get an ugly
error page.
You should then see a line resembling the following in your browser window:
“You successfully uploaded <name of your file>!”
Testing Your Application
There are multiple ways to test this particular feature in our application. The following
listing (from src/test/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/FileUploadTests.java) shows one
example that uses MockMvc so that it does not require starting the servlet container:
link:complete/src/test/java/com/example/uploadingfiles/FileUploadTests.java[]In those tests, you use various mocks to set up the interactions with your controller and
the StorageService but also with the Servlet container itself by using
MockMultipartFile.
For an example of an integration test, see the FileUploadIntegrationTests class (which
is in src/test/java/com/example/uploadingfiles).
Summary
Congratulations! You have just written a web application that uses Spring to handle file uploads.