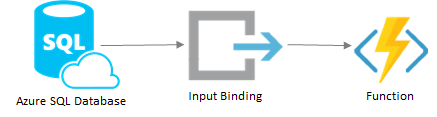
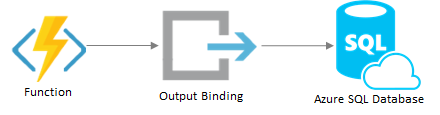
This is a binding for Azure Functions for Azure SQL Database. With it, cloud developers who use SQL Database can enjoy the same benefits that other binding users enjoy, includining minimal function code. blog post
This project builds SQLBindingExtension.dll which defines a new [SQLDatabase] binding attribute.
This binding is for the Azure Functions v1 runtime (.NET Framework).
For building and deployment instructions, see Deployment further down.
To use the SQL Database binding, just add a [SQLDatabase] attribute to your functions.
[FunctionName("genre")]
public static HttpResponseMessage title(HttpRequestMessage req,
[HttpTrigger] TitleRequest parameters,
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", SQLQuery = "SELECT * FROM Book WHERE Genre={genre}")] DataTable table,
TraceWriter log)
{
// Convert data table to JSON string
var objType = JArray.FromObject(table, JsonSerializer.CreateDefault(new JsonSerializerSettings { NullValueHandling = NullValueHandling.Ignore })); //.FirstOrDefault(); // Get the first row
var js = objType.ToString();
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
StatusCode = HttpStatusCode.OK,
Content = new StringContent("{ \"Data\": " + js + " }", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json")
};
}
For specific details on parameters, see Input Bindings and Output Bindings.
When used as an input binding, the binding executes a query and passes the result to your function--either as a System.Data.DataTable object or the equivalent JSON string.
Two parameters are required for an input binding:
- ConnnectionString: Name of connection string setting (such as "ConnectionString"). The actual connection string should be defined in local.settings.json (if running locally) or Application Settings in the Azure Portal.
local.settings.json
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "",
"AzureWebJobsDashboard": "",
"AzureWebJobs_ExtensionsPath": ".",
"ConnectionString": "Server=my-server.database.windows.net;Database=Books;User ID=my-user;Password=my-password;Trusted_Connection=False;Encrypt=True;"
}
}
- SQLQuery: A T-SQL query to execute. The results will be passed to your function.
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", SQLQuery = "SELECT * FROM Book WHERE Genre={genre}")] DataTable table,
SQLQuery parameters may contain {parameter} names. For example, an HTTP Trigger may pass in a query string parameter named title. If your SQLQuery parameter contains {title} it will be replaced with the incoming parameter value.
Important: The percent sign (%) character cannot be used in the SQLQuery parameter. This is because the Azure Functions binding framework interprets %name% as application setting references. However, there is a work-around. Use CHAR(37) in place of %.
For example,
...WHERE title LIKE CHAR(37) + '{title}' + CHAR(37)
will be interpreted as
...WHERE title LIKE '%{title}%'
Your [SQLDatabase] attribute should be followed by a variable, which can be either of these types:
- DataTable: a System.Data.DataTable. You can enumerate the DataRow collection in the Rows property.
- string: a JSON string - a serialized DataTable (actually a fragment, not complete JSON) in the form
[ { "column1": "value1", "column2": "value2", ... }, { ...record 2...}, ... { ...record N... } ]
Use whichever data type suits your work best.
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", SQLQuery = "SELECT * FROM Book WHERE Genre={genre}")] DataTable table,
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", SQLQuery = "SELECT * FROM Book WHERE Genre={genre}")] string tableJson,
Use the data type that suits you best.
The example below searches books by title. The function uses an HTTP Trigger and a SQL Database input binding. It performs a title search, where title is a URL query string parameter. Matching records are returned in JSON format.
[FunctionName("title")]
public static HttpResponseMessage title(HttpRequestMessage req,
[HttpTrigger] TitleRequest parameters,
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString",
SQLQuery = "SELECT * FROM Book WHERE Title LIKE +CHAR(37)+'{title}'+CHAR(37)")]
DataTable table,
TraceWriter log)
{
log.Info("title|DataTable: C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
// Convert data table to JSON string
var objType = JArray.FromObject(table, JsonSerializer.CreateDefault(new JsonSerializerSettings { NullValueHandling = NullValueHandling.Ignore })); //.FirstOrDefault(); // Get the first row
var js = objType.ToString();
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
StatusCode = HttpStatusCode.OK,
Content = new StringContent("{ \"Data\": " + js + " }", Encoding.UTF8, "application/json")
};
}
When the function is invoked with a URL such as the following,
https://[function-name].azurewebsites.net/api/title?title=world
This is the response:
{
Data: [
{
Title: "Proteus in the Underworld",
Author: "Charles Sheffield",
Yr: "1995",
Genre: "Science Fiction"
},
{
Title: "Quest of the Three Worlds",
Author: "Cordwainer Smith",
Yr: "1966",
Genre: "Science Fiction"
},
{
Title: "Ringworld",
Author: "Larry Niven",
Yr: "1970",
Genre: "Science Fiction"
},
{
Title: "The Ringworld Engineers",
Author: "Larry Niven",
Yr: "1979",
Genre: "Science Fiction"
}
]
}
When used as an output binding, the function passes a dataset (or multiple datasets) and the binding adds the records to a specified database table. SqlBulkCopy is used for rapid insertion. If any of the records already existed, they are not updated and no error is generated.
The binding doesn't perform updates or deletes. For that, you'll need your own function code, for example using .NET's SqlConnection / SqlCommand objects in C#.
Two parameters are required for an output binding:
- IConnector<ConnnectionString>: Name of connection string setting (such as "ConnectionString"). The actual connection string should be defined in local.settings.json (if running locally) or Application Settings in the Azure Portal.
- IConnector<TableName>: Name of the database table to add records to.
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", TableName = "Book", SQLQuery = "")] ICollector<DataTable> output,
Use the data type that suits you best.
Your [SQLDatabase] attribute should be followed by a variable, which can be either of these types:
- ICollector: a System.Data.DataTable containing a DataRow collection.
- ICollector: a JSON string - a serialized DataTable (actually a fragment, not complete JSON) in the form
[ { "column1": "value1", "column2": "value2", ... }, { ...record 2...}, ... { ...record N... } ]
Use whichever data type suits your work best.
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", TableName = "Book", SQLQuery = "")] ICollector<DataTable> output,
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString", TableName = "Book", SQLQuery = "")] ICollector<string> output,
The example below adds book records. The function uses an HTTP Trigger and a SQL Database output binding. It accepts an HTTP POST payload of book objects, turns them into DataRows in a DataTable, and the output binding adds the records.
[FunctionName("addbooks")]
public static HttpResponseMessage addbooks(HttpRequestMessage req,
[HttpTrigger] Book[] books,
[SQLDatabase(ConnectionString = "ConnectionString",
TableName = "Book", SQLQuery = "")] ICollector<DataSet> output, TraceWriter log)
{
// Create data table JSON for output
string json = @"[ ";
if (books != null)
{
int count = 0;
foreach (Book book in books)
{
if (count > 0) json += ",";
json += @"{ ""Title"": """ + book.title + @""", ""Author"": """ + book.author + @""", ""Yr"": """ + book.yr + @""", ""Genre"": """ + book.genre + @""" }";
count++;
}
}
json += "]";
output.Add(json);
return req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.Created);
}
Once you download or clone this repository, it is suggested you proceed as follows:
-
Ensure you can build the solution
-
Try running the sample app locally. To do that, you'll first need to:
- Create an Azure DB for Books
- Run the included SQL script to create a Book table
- Set the ConnectionString parameter value for your books database in the Function App project's local.settings.json file.
-
Reference SQLDatabaseExtension.dll in your Function App project.
-
Add [SQLDatabase] attributes/parameters to your code, and a ConnectionString setting to your function project's local.settings.json file.
-
Run and test/debug locally.
-
Publish to Azure.
-
In Azure Portal, navigate to your function's Application Settings area and add a ConnectionString parameter for your database.