\rōd\ - a line (as of rope or chain) used to attach an anchor to a boat
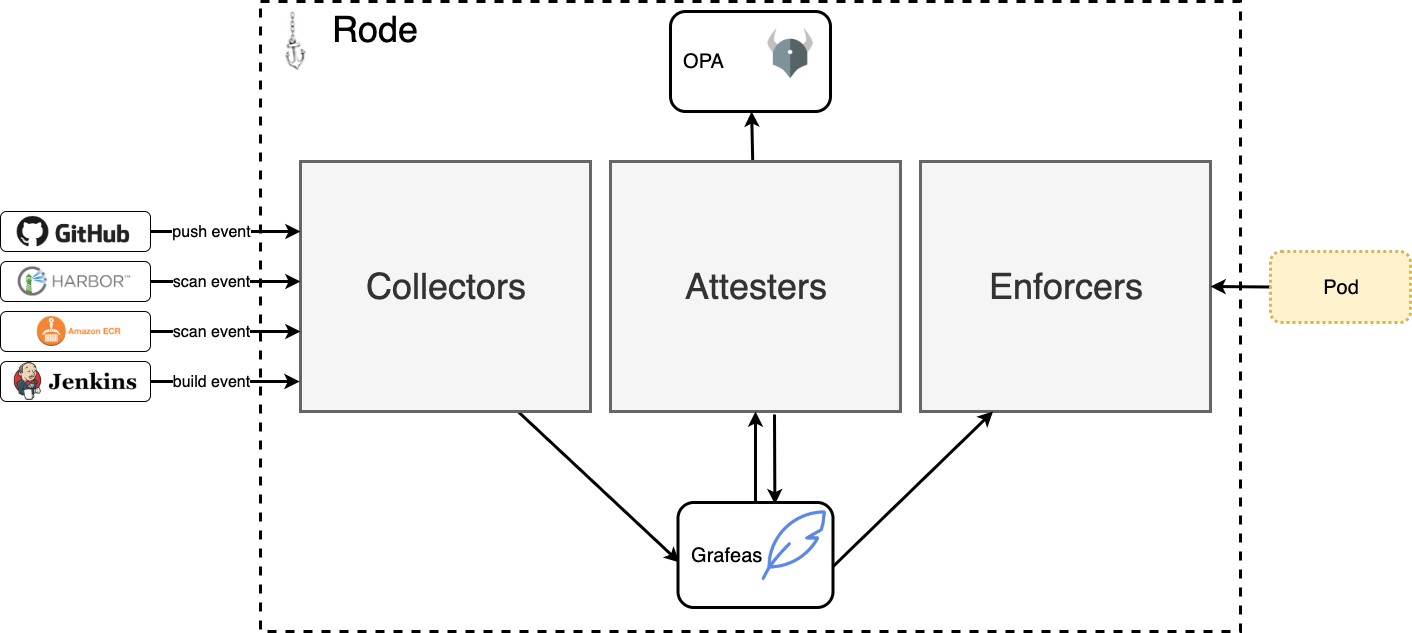
Rode provides the collection, attestation and enforcement of policies in your software supply chain. Watch the demo and slides from DeliveryConf for a quick introduction!
There are 3 primary components in rode: collectors, attesters and enforcers
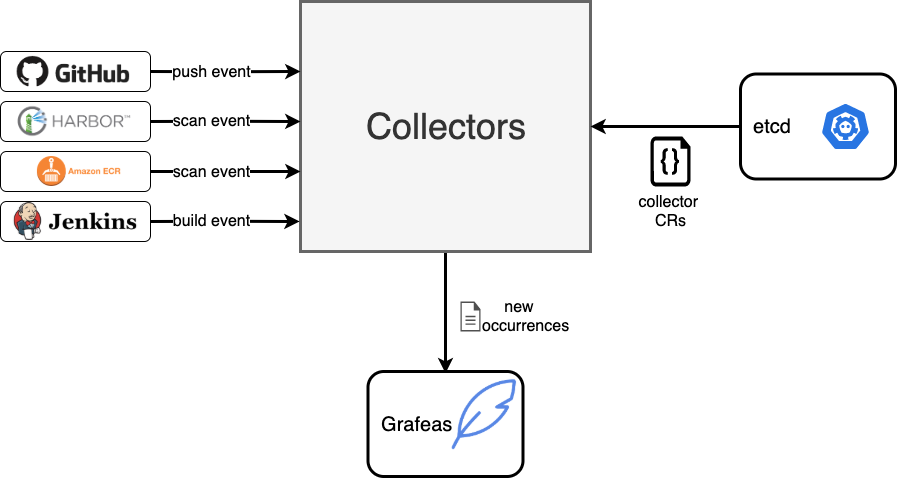
Collectors are responsible for receiving events from external systems and converting them into occurrences in Grafeas.
The list of supported collectors is growing and currently includes:
- ECR Events - image scan events are sent to an SQS queue via CloudWatch event rules. A collector in rode processes the messages from the queue and converts them into discovery and vulnerability occurrences in Grafeas.
- Harbor Events - image scan events are sent to a Rode endpoint. A collector in rode processes the messages from the queue and converts them into discovery and vulnerability occurrences in Grafeas.
Collectors are defined as Collector custom resources. See below for an example:
apiVersion: rode.liatr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Collector
spec:
name: my_collector
type: ecr
queueName: my_ecr_event_queue
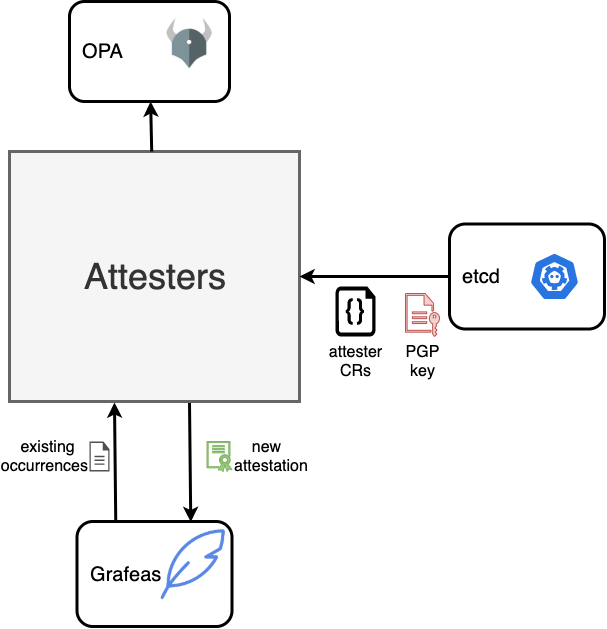
Attesters monitor collectors for new occurrences. Whenever a new occurrence is created on a resource, then all occurrences are loaded for that resource and passed in to Open Policy Agent (OPA) to determine if all necessary occurrences exist for the resource.
If all occurrences exist and comply with the policy, then the attester will use its private PGP key to sign a new attestation for the resource and store the attestation in Grafeas.
Attesters are defined as Attester custom resources. See below for an example:
apiVersion: rode.liatr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Attester
spec:
name: my_collector
pgp-secret: my_secret_name
policy: |
package my_collector
violation[{"msg":"analysis failed"}]{
input.occurrences[_].discovered.discovered.analysisStatus != "FINISHED_SUCCESS"
}
violation[{"msg":"analysis not performed"}]{
analysisStatus := [s | s := input.occurrences[_].discovered.discovered.analysisStatus]
count(analysisStatus) = 0
}
violation[{"msg":"critical vulnerability found"}]{
severityCount("CRITICAL") > 0
}
violation[{"msg":"high vulnerability found"}]{
severityCount("HIGH") > 10
}
severityCount(severity) = cnt {
cnt := count([v | v := input.occurrences[_].vulnerability.severity; v == severity])
}
The PGP key is automatically generated and stored as a Kubernetes secret if it doesn't already exist.
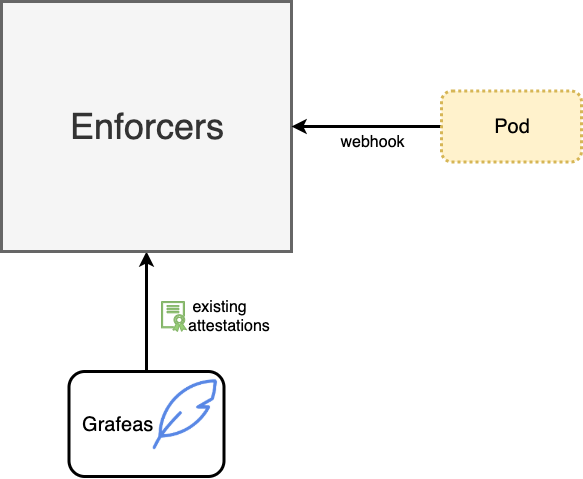
Enforcers are defined as validating admission webhook that ensures the resource defined as an image in the Pod has been properly attested.
Enforcers are configured to ensure the specified attester referenced in the namespace for the pod had successfully created an attestation. The namespace must include a label for enforcement to be activated:
"rode.liatr.io/enforce": true
The easiest way to install rode is via the helm chart:
helm repo add liatrio https://harbor.toolchain.lead.prod.liatr.io/chartrepo/public
helm upgrade -i rode liatrio/rode
Setup collectors, attesters and enforcers through a quickstart:
kubectl apply -f examples/aws-quickstart.yaml
The ECR event collector requires the following IAM policy. Either attach the policy to the EC2 instance or use IRSA and pass the role ARN to Helm:
helm upgrade -i rode liatrio/rode --set rbac.serviceAccountAnnotations."eks\.amazonaws\.com/role-arn"=arn:aws:iam::1234567890:role/RodeServiceAccount
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sqs:CreateQueue"
"sqs:SetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:GetQueueUrl",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:ReceiveMessage",
"sqs:DeleteMessage",
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"events:PutTargets",
"events:PutRule"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
If Harbor is being utilized as a container registry, you can specify harbor as the collector type.
apiVersion: rode.liatr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Collector
spec:
name: my_collector
type: ecr
queueName: my_ecr_event_queue
apiVersion: rode.liatr.io/v1alpha1 kind: Collector metadata: name: harborCollector finalizers:
- collectors.finalizers.rode.liatr.io spec: harbor: harborUrl: "https://example.com" project: "example-project" secret: "default/harbor-harbor-core" type: harbor
# Development
To run locally, install CRDs, then use skaffold with the `local` profile:
To install CRDs (Only needs to be run once):
`make install`
To run controllers:
`skaffold dev --port-forward`
This will also run [localstack](https://github.com/localstack/localstack) to mock services such as SQS.
Setup collectors, attesters and enforcers:
`kubectl apply -f examples/aws-quickstart.yaml`
To create an occurence, use the aws cli to send a test message to localstack:
aws sqs send-message
--endpoint-url http://localhost:30576
--queue-url http://localhost:30576/queue/rode-ecr-event-collector
--message-body file://test/sample_scan_event.json