mProxy is an MQTT proxy.
It is deployed in front of MQTT broker and can be used for authorization, packet inspection and modification, logging and debugging and various other purposes.
go get github.com/cebrains/mproxy
cd $(GOPATH)/github.com/cebrains/mproxy
make
./mproxymProxy starts TCP and WS servers, offering connections to devices. Upon the connection, it establishes a session with a remote MQTT broker. It then pipes packets from devices to MQTT broker, inspecting or modifying them as they flow through proxy.
Here is the flow in more details:
- Device connects to mProxy's TCP server
- mProxy accepts the inbound (IN) connection and estabishes a new session with remote MQTT broker (i.e. it dials out to MQTT broker only once it accepted new connection from a device. This way one device-mProxy connection corresponds to one mProxy-MQTT broker connection.)
- mProxy then spawn 2 goroutines: one that will read incoming packets from device-mProxy socket (INBOUND or UPLINK), inspect them (calling event handlers) and write them to mProxy-broker socket (forwarding them towards the broker) and other that will be reading MQTT broker responses from mProxy-broker socket and writing them towards device, in device-mProxy socket (OUTBOUND or DOWNLINK).
mProxy can parse and understand MQTT packages, and upon their detection it actually calls external event handlers. Event handlers should implement the following interface defined in pkg/mqtt/events.go:
// Event is an interface for mProxy hooks
type Event interface {
// Authorization on client `CONNECT`
// Each of the params are passed by reference, so that it can be changed
AuthConnect(client *Client) error
// Authorization on client `PUBLISH`
// Topic is passed by reference, so that it can be modified
AuthPublish(client *Client, topic *string, payload *[]byte) error
// Authorization on client `SUBSCRIBE`
// Topics are passed by reference, so that they can be modified
AuthSubscribe(client *Client, topics *[]string) error
// After client successfully connected
Connect(client *Client)
// After client successfully published
Publish(client *Client, topic *string, payload *[]byte)
// After client successfully subscribed
Subscribe(client *Client, topics *[]string)
// After client unsubscribed
Unsubscribe(client *Client, topics *[]string)
// Disconnect on connection with client lost
Disconnect(client *Client)
}An example of implementation is given here, alongside with it's main() function.
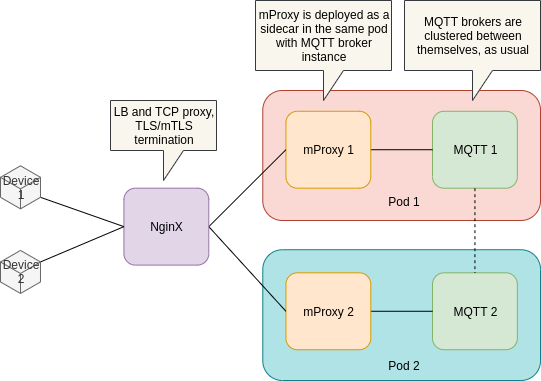
mProxy does not do load balancing - just pure and simple proxying. This is why it should be deployed right in front of it's corresponding MQTT broker instance: one mProxy for each MQTT broker instance in the MQTT cluster.
Usually this is done by deploying mProxy as a side-car in the same Kubernetes pod alongside with MQTT broker instance (MQTT cluster node).
TLS termination and LB tasks can be offloaded to a standard ingress proxy - for example NginX.