warp10r
R client for executing WarpScript on a Warp 10 instance.
Fork
The original package [https://github.com/senx/warp10-r] has been forked to make the package more concilient with current developments of R packages :
- Package has been moved to the root of the git repository
- Dependancies have been added to the DESCRIPTION
- Construct a warp 10 script with helpers function and send them to Warp 10 database
Installation
remotes::install_github("centreon/warp10-r")First steps
Hello World
library(warp10r)
# Create a connection
con <- wrp_connect(endpoint = "https://warp.senx.io/api/v0/exec")
print(con)
#> Warp10 connexion:
#> - endpoint: https://warp.senx.io/api/v0/exec
#> - token: available
#> - stack: empty
# set_script store a script in the connection object.
set_script(con, "'Hello World'")
set_script(con, "NOW")
print(con)
#> Warp10 connexion:
#> - endpoint: https://warp.senx.io/api/v0/exec
#> - token: available
#> - stack: map, map
# We can see the script
cat(get_script(con))
#> 'Hello World'
#> NOW
# Execute the script
wrp_exec(con)
#> [[1]]
#> [1] 1.573809e+15
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "Hello World"Example with Geo Time Series
library(tibble)
df1 <- tibble(ds = 1:10, y = rnorm(10))
df2 <- tibble(ds = 2:11, y = rnorm(10))
con %>%
clear_script() %>%
wrp_new_gts() %>%
wrp_rename("randGTS") %>%
wrp_add_value_df(df1, tick = ds, value = y) %>%
wrp_new_gts() %>%
wrp_add_value_df(df2, tick = ds, value = y) %>%
wrp_rename("nogeoTS") %>%
wrp_exec()
#> [[1]]
#> # A GTS object: 10 x 2
#> # class: nogeoTS
#> timestamp value
#> * <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2 -0.320
#> 2 3 -1.15
#> 3 4 -0.500
#> 4 5 -0.877
#> 5 6 -0.234
#> 6 7 -0.227
#> 7 8 0.569
#> 8 9 -0.514
#> 9 10 2.17
#> 10 11 -1.24
#>
#> [[2]]
#> # A GTS object: 10 x 2
#> # class: randGTS
#> timestamp value
#> * <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 -1.66
#> 2 2 0.632
#> 3 3 0.0918
#> 4 4 -1.78
#> 5 5 -0.0555
#> 6 6 0.132
#> 7 7 -0.784
#> 8 8 -0.447
#> 9 9 -0.435
#> 10 10 0.432Outlier detection
Anomaly detection is already implemented in Warpscript. Let’s take twitter data as an example.
Set up and show data
library(AnomalyDetection)
library(dplyr)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'dplyr'
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter, lag
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
library(ggplot2)
library(hrbrthemes)
#> NOTE: Either Arial Narrow or Roboto Condensed fonts are required to use these themes.
#> Please use hrbrthemes::import_roboto_condensed() to install Roboto Condensed and
#> if Arial Narrow is not on your system, please see http://bit.ly/arialnarrow
library(lubridate)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'lubridate'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> date
library(purrr)
data("raw_data")
raw_data %>%
ggplot(aes(timestamp, count)) +
geom_line() +
theme_ipsum(base_family = "Verdana")Create a subset of the data
Default settings do not authorize more than 1,000 operations for a warpscript. Therefore, let’s take the previous data and concatenate them into 3 hours timespan.
df <- raw_data %>%
group_by(date_hour = ceiling_date(timestamp, "3 hours")) %>%
summarise_at("count", sum)
df %>%
ggplot(aes(date_hour, count)) +
geom_line() +
theme_ipsum(base_family = "Verdana")Lets find some anomalies
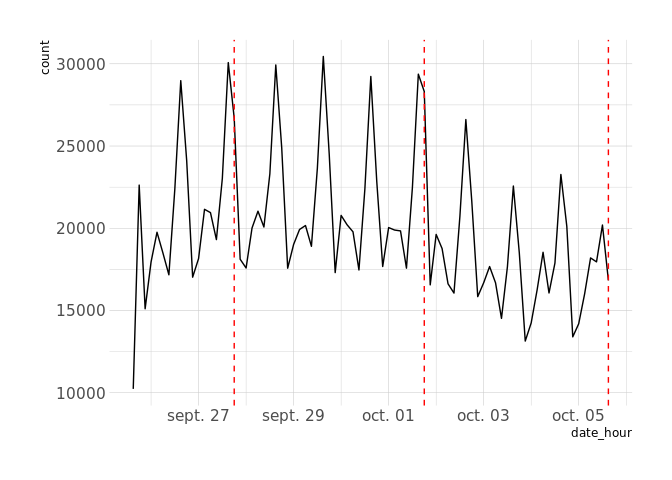
res <- con %>%
wrp_new_gts() %>%
wrp_rename("twitter data") %>%
wrp_add_value_df(df, tick = "date_hour", value = "count") %>%
wrp_bucketize(span = "3 h", bucketizer = "sum") %>%
wrp_hybridtest(period = 8, piece = 4, k = 4) %>%
wrp_exec()
print(res)
#> [[1]]
#> [[1]][[1]]
#> [1] 3.389256e+14
#>
#> [[1]][[2]]
#> [1] 3.392712e+14
#>
#> [[1]][[3]]
#> [1] 3.39606e+14
# Results is a list of abnormal dates in microseconds
res_dbl <- map_dbl(res[[1]], ~ .x / 1e6)
df %>%
ggplot(aes(date_hour, count)) +
geom_line() +
geom_vline(xintercept = res_dbl, linetype = 2, color = "red") +
theme_ipsum(base_family = "Verdana")