This is a sample project for the article Build Reliable Machine Learning Pipelines with Continuous Integration.
Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of continuously merging and testing code changes into a shared repository. In a machine learning project, CI can be very useful for several reasons:
✅ Catching errors early: CI facilitates the early identification of errors by automatically testing any code changes made, enabling timely problem detection during the development phase
✅ Ensuring reproducibility: CI helps ensure reproducibility by establishing clear and consistent testing procedures, making it easier to replicate machine learning project results.
✅ Faster feedback and decision-making: By providing clear metrics and parameters, CI enables faster feedback and decision-making, freeing up reviewer time for more critical tasks.
- Data scientists make changes to the code, creating a new model locally.
- Data scientists push the new model to remote storage.
- Data scientists create a pull request for the changes.
- A CI pipeline is triggered to test the code and model.
- If all tests pass, the changes are merged into the main branch.
- Pull data and model from a remote storage
- Run tests
- Automatically generate metrics report
- DVC: Version data and experiments - article
- CML: Post a comment to the pull request showing the metrics and parameters of an experiment
src: consists of Python scriptsdata: consists of datatests: consists of test filesdvclive: consists of metrics of DVC experiments.dvc/config: consists of locations of the remote storageparams.yaml: consists of parameters for Python scripts.github/workflows: consists of GitHub workflows
To try out this project, first start with cloning the project to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/khuyentran1401/cicd-mlops-demoSet up the environment:
# Go to the project directory
cd cicd-mlops-demo
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Pull data from the remote storage location called read
dvc pull -r readMake changes to any files in the following directories src, tests, params.yaml. To demonstrate, we will make minor changes the file params.yaml:
Create an experiment:
dvc exp runAfter running the experiments, we need to store changes to our data and model remotely. One option is to use an S3 bucket as a remote storage.
Follow these steps to push your data and model to an S3 bucket:
- Create an S3 bucket
- Ensure your S3 credentials are store locally.
- Add the URI of your S3 bucket to the
.dvc/configfile
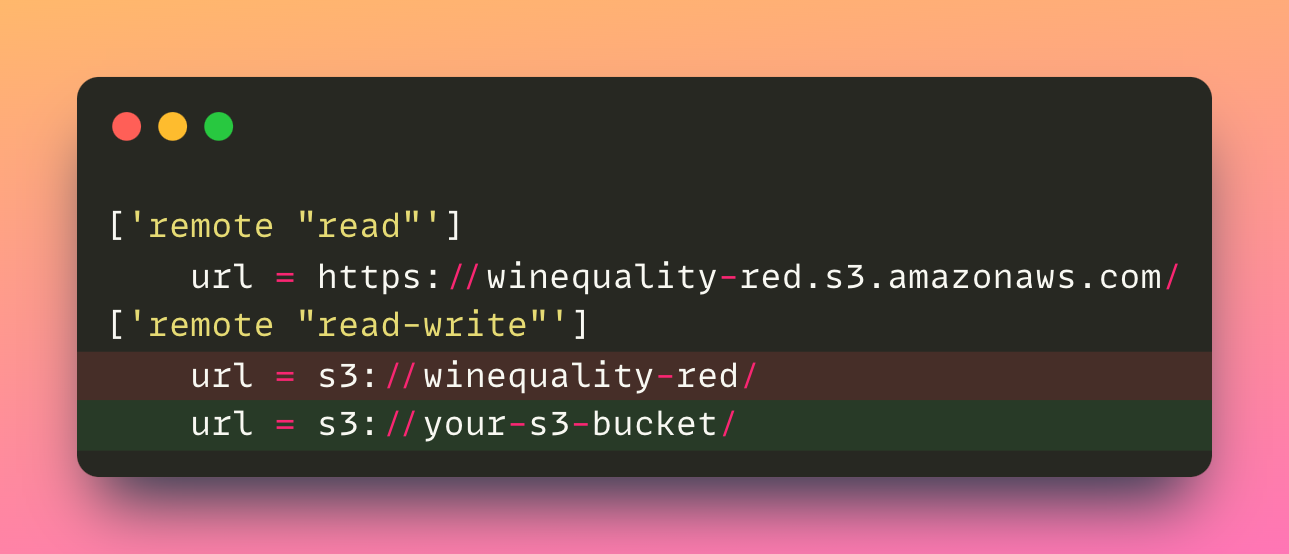 4. Push changes a remote location called
4. Push changes a remote location called read-write using:
dvc push -r read-writeAdd, commit, and push changes to the repository:
git add .
git commit -m 'add 100 for C'
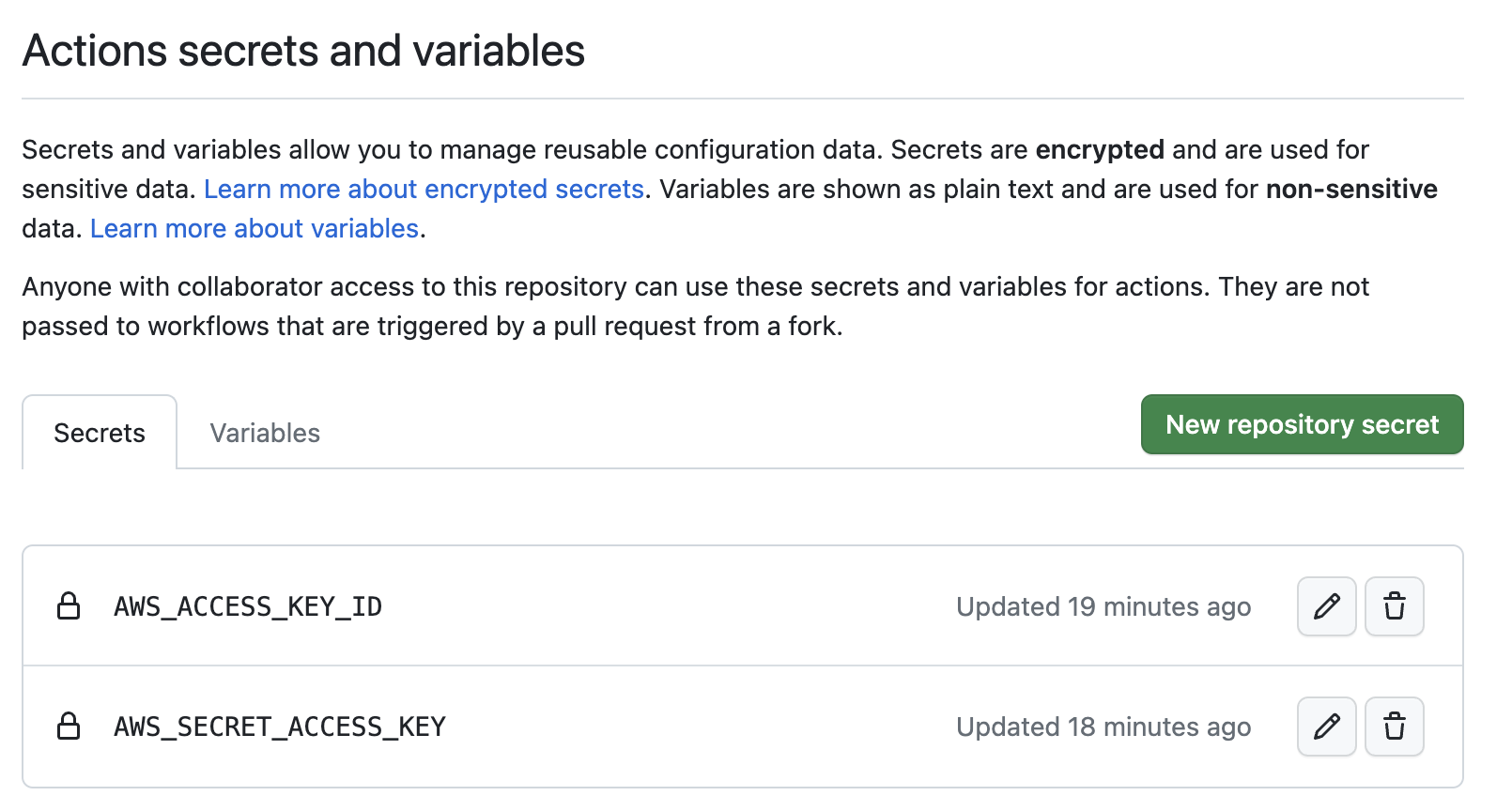
git push origin ci-mainEncrypted secrets allows you to store your sensitive information in your repository. We will use encrypted secrets to make AWS credentials and GitHub token accessible by GitHub Actions.
AWS credentials are necessary to pull data and model from your S3 bucket. Follow this tutorial to add AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY secrets to your repository.
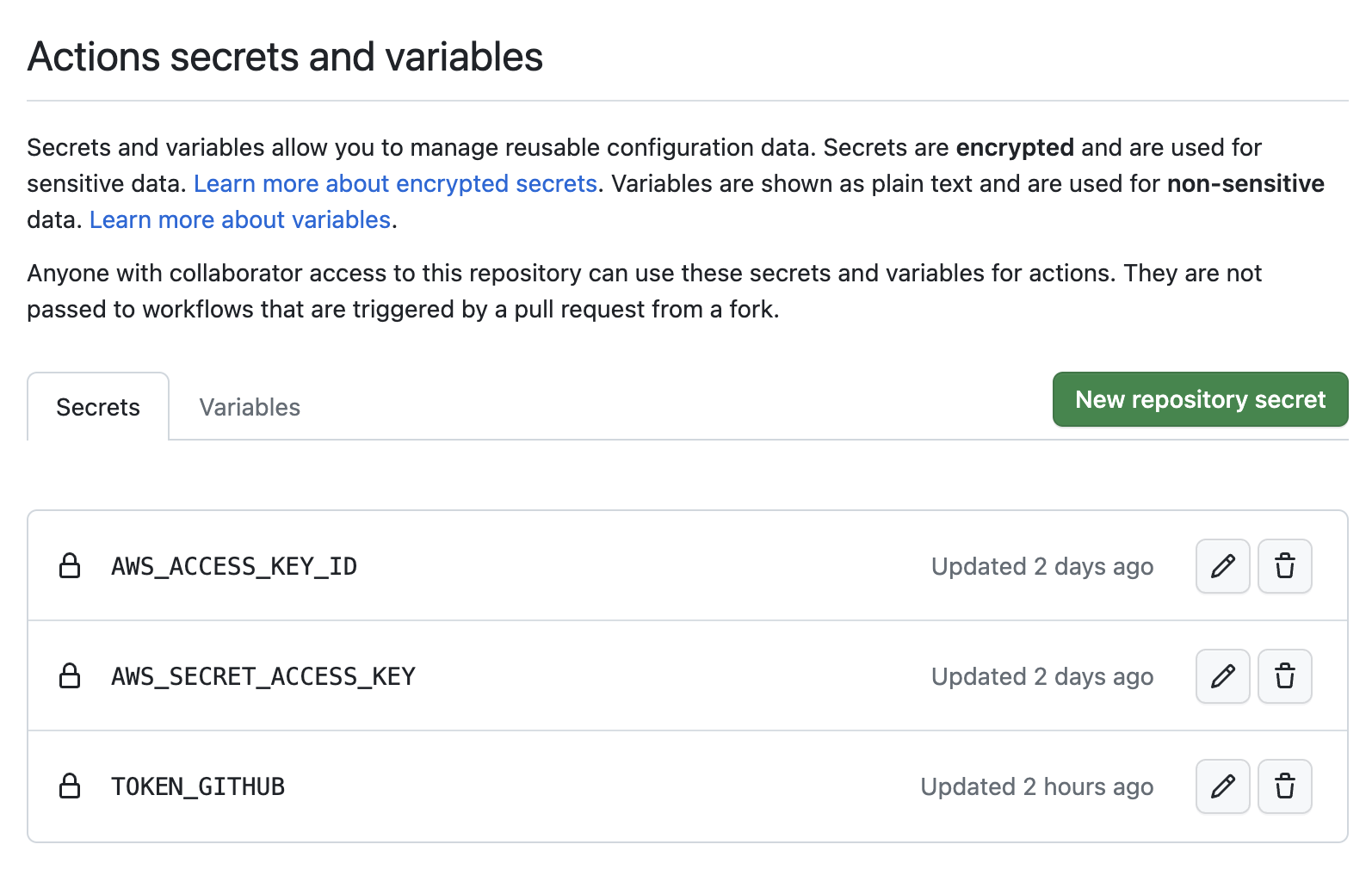
GitHub token is necessary to write metrics and parameters as a comment in your pull request. To use GitHub token as an encrypted secret, follow these steps:
- Create a personal access token
- Create a secret named
TOKEN_GITHUB - In the "Value" field, paste the token that you created in step 1.
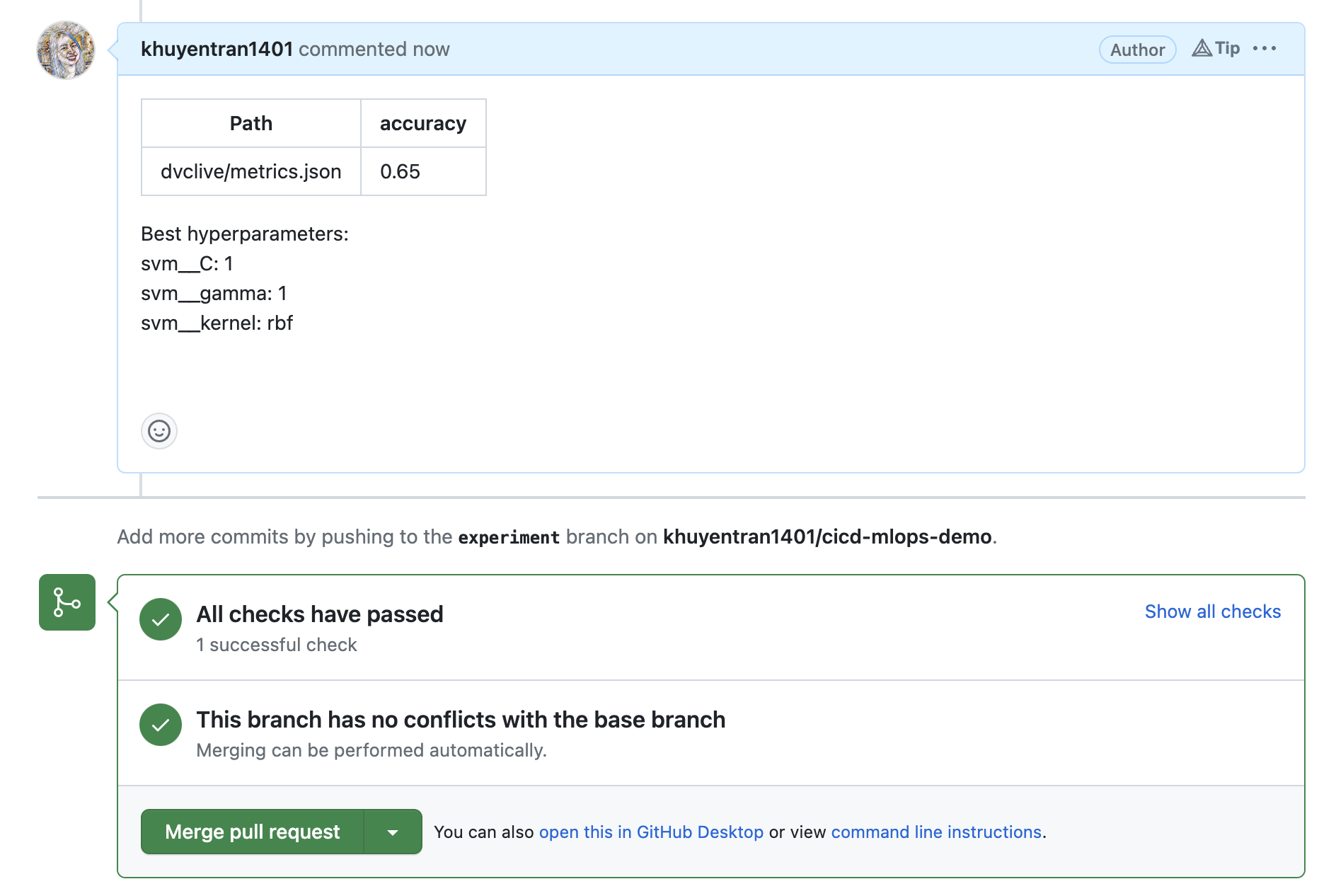
Next, create a pull request
Once creating a PR, a GitHub workflow will start to run tests. Once all tests passed, a comment will appear in the PR with the metrics and parameters of the new experiment.