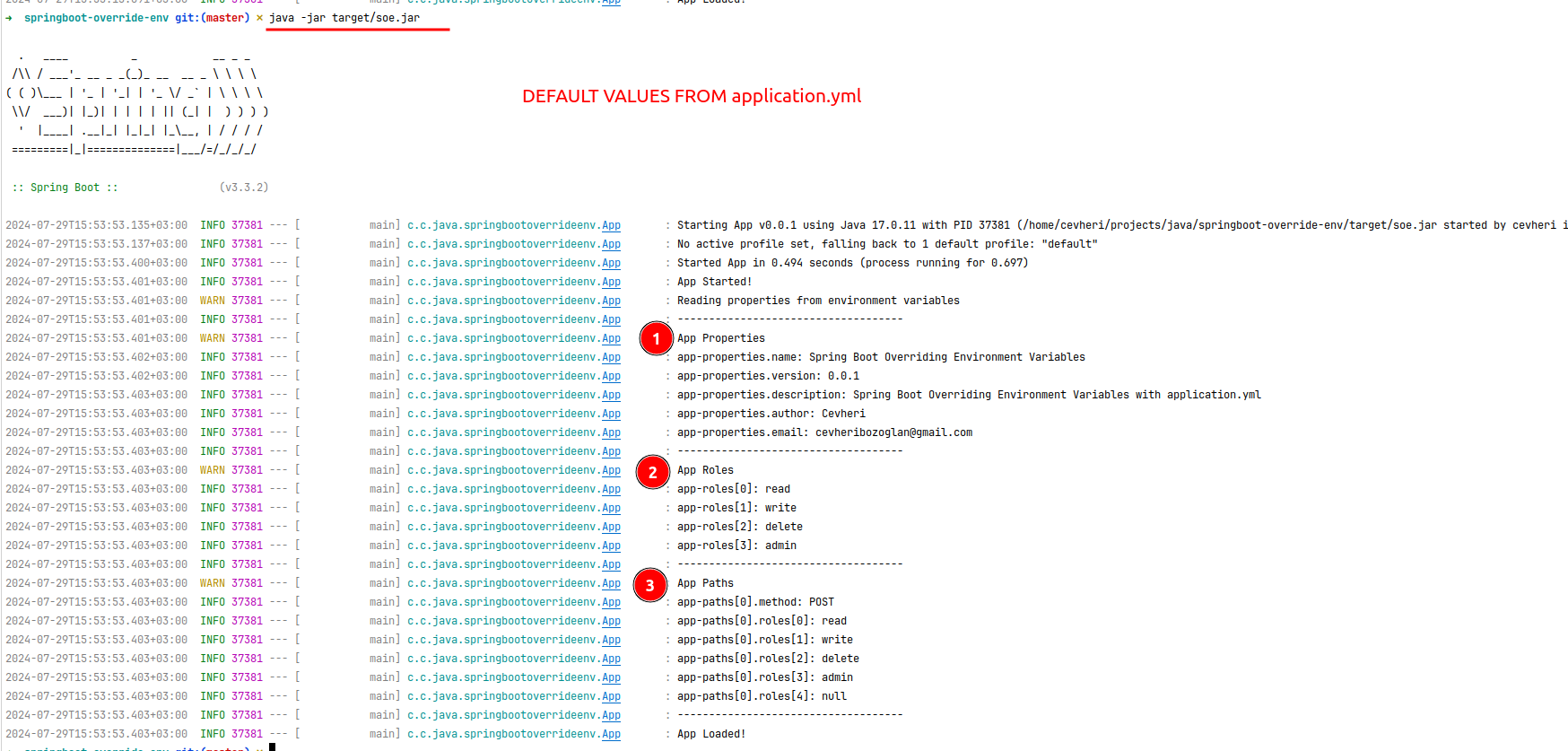
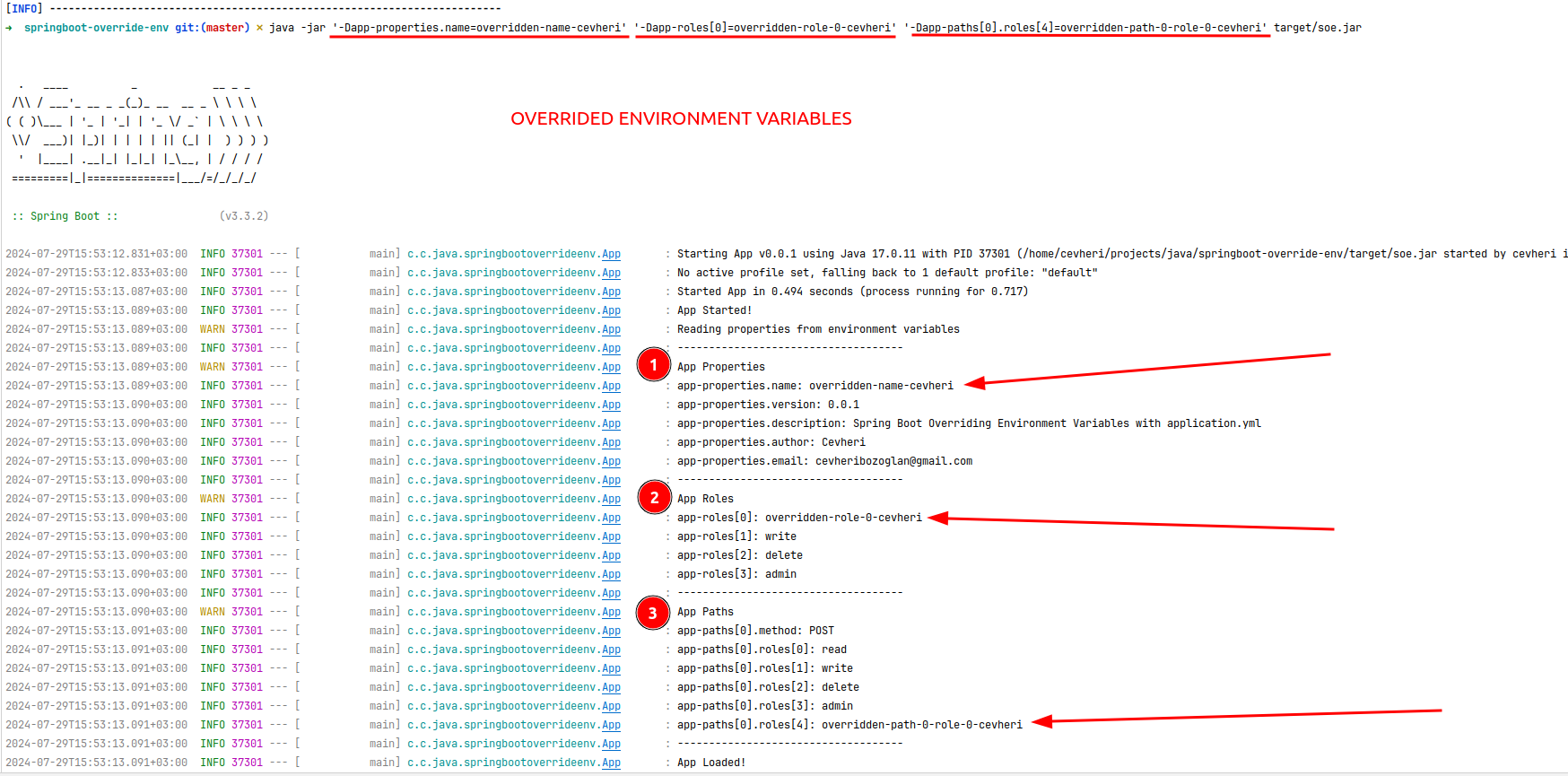
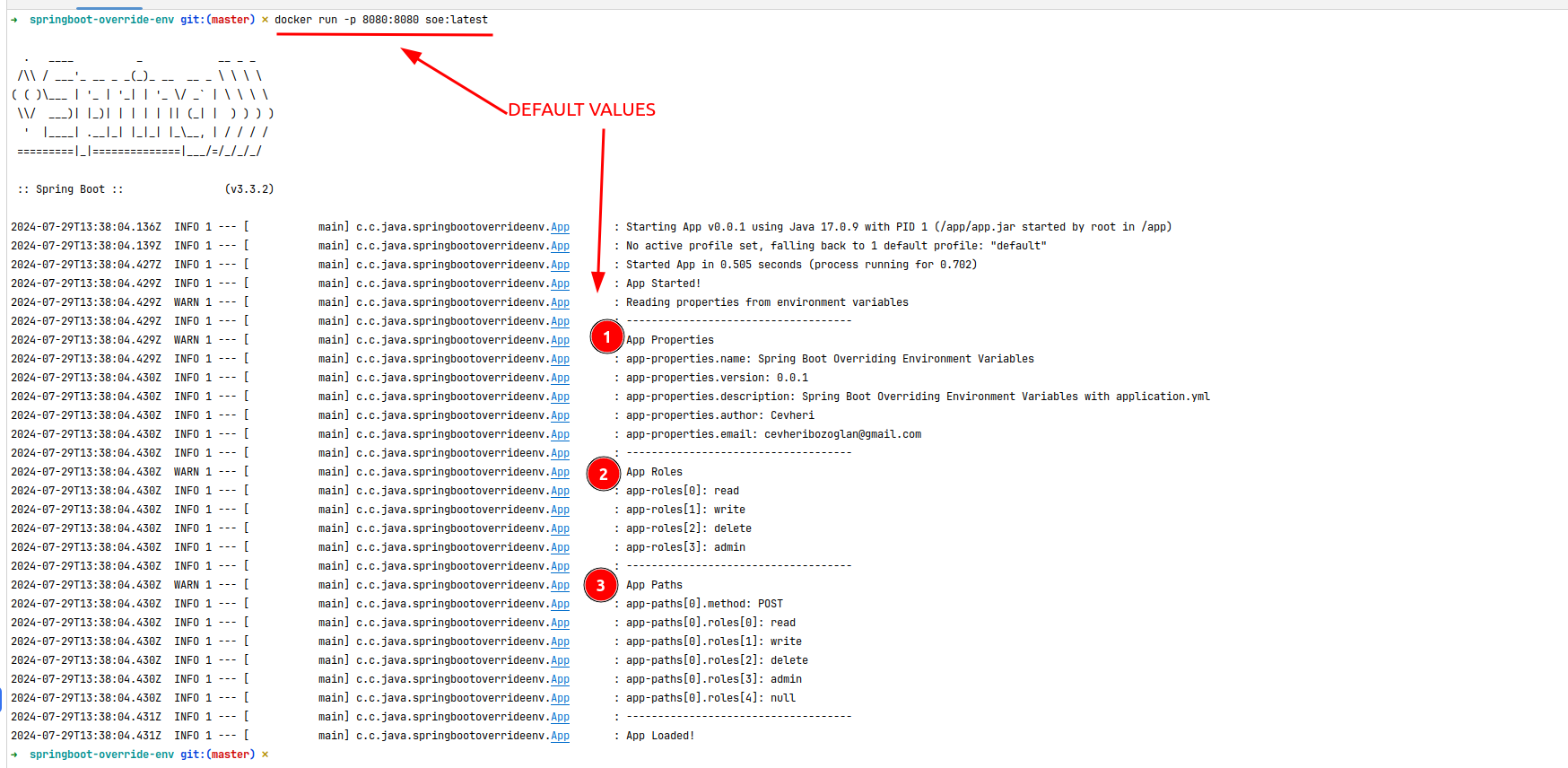
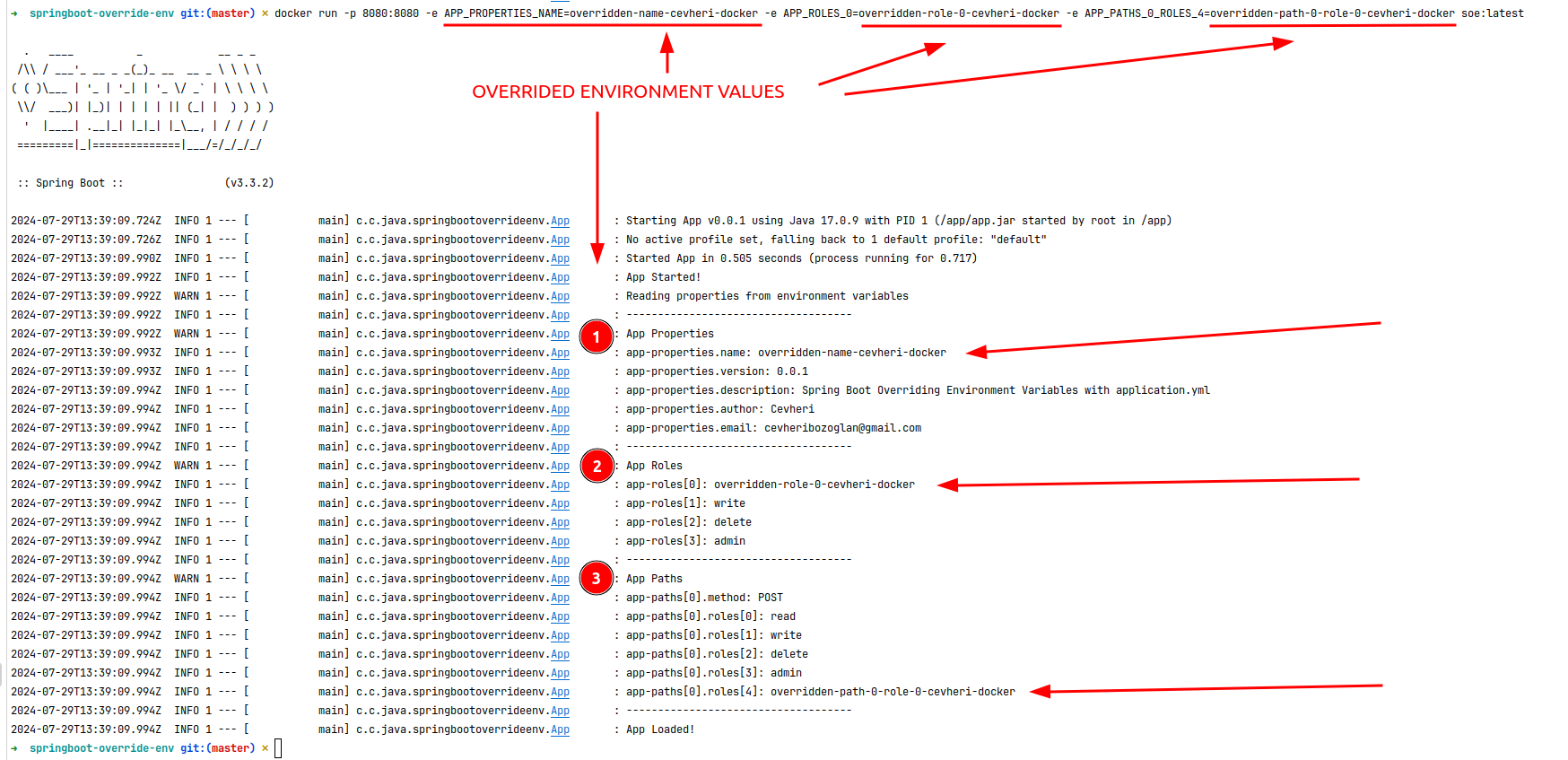
This is an example of overriding the application.yml file with the OS environment variables.
Single or Array environment variables can be overridden.
We talk about many ways to override environment variables in a Spring Boot application. Not autoconfiguration values :(
- Your Spring Boot application has a
application.ymlorapplication.propertiesfile. - The application properties are converted to environment variables when you run the Spring Boot application.
- The environment variables are key-value pairs that are set in the operating system.
- They are used to configure applications and services.
- Many ways to override environment variables in a Spring Boot application.
- This guide will show you how to override environment variables in a Spring Boot application.
- Single and array environment variables will be overridden.
- When you run a Spring Boot application, the application properties are converted to environment variables.
- You can override environment variables using the
-Dflag when java -jar is used. - You can override environment variables using the
-eflag when running a Spring Boot application in a Docker container. - You can override environment variables using ConfigMaps and Secrets when running a Spring Boot application in a Kubernetes cluster.
- You can override environment variables using the
application.ymlfile from git repository with spring cloud config server.
- JDK 17
- Maven 3.9x
- Spring Boot 3x
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/cevheri/java-spring-boot-overriding-environment-variables.git- Change directory
cd java-spring-boot-overriding-environment-variables- Run the Spring Boot application
mvn spring-boot:run 4 and 5 are the most common use cases for overriding environment variables in a Spring Boot application. Maybe next time we can talk about the Kubernetes and Spring Cloud Config Server use cases.
4 and 5 are the most common use cases for overriding environment variables in a Spring Boot application. Maybe next time we can talk about the Kubernetes and Spring Cloud Config Server use cases.
When you run a Spring Boot application, the application properties are converted to environment variable like UPPER_CASE with underscores.
- application.yml file
app-object:
name: "Spring Boot Overriding Environment Variables"
version: "0.0.1"
description: "Spring Boot Overriding Environment Variables with application.yml"
author: "Cevheri"
email: "cevheribozoglan@gmail.com"- OS Environment Variable
APP_OBJECT_NAME=overridden-name
APP_OBJECT_VERSION=overridden-version
APP_OBJECT_DESCRIPTION=overridden-description
APP_OBJECT_AUTHOR=overridden-author
APP_OBJECT_EMAIL=overridden-emailEnvironment variables are key-value pairs that are set in the operating system. They are used to configure applications and services.
When you run a Spring Boot application using the java -jar command, you can override environment variables using the -D flag.
When you run a Spring Boot application in a Docker container, you can override environment variables using the -e flag.
mvn clean installdocker build -t soe:latest .Run the Spring Boot application using the java -jar command.
java -jar target/soe.jarjava -jar '-Dapp-object.name=overridden-name-cevheri' '-Dapp-arrays.roles[0]=overridden-role-0-cevheri' '-Dapp-multiple.paths[0].roles[0]=overridden-path-0-role-0-cevheri' target/soe.jardocker run -p 8080:8080 soe:latestdocker run -p 8080:8080 -e APP_OBJECT_NAME=overridden-name-cevheri-docker -e APP_ARRAYS_ROLES_0=overridden-role-0-cevheri-docker -e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_0=overridden-path-0-role-0-cevheri-docker soe:latest@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app-multiple")
public class AppPaths {
private List<Path> paths;
public List<Path> getPaths() {
return paths;
}
public void setPaths(List<Path> paths) {
this.paths = paths;
}
public static class Path {
private String method;
private List<String> roles;
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
public List<String> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(List<String> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}
}You should override whole array object like below.
docker run -p 8080:8080 \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_METHOD=NEW_POST \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_0=new_create \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_1=new_read \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_2=new_update \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_3=new_delete \
-e APP_MULTIPLE_PATHS_0_ROLES_4=new_admin \
soe:latest
mvn test- This guide showed you how to override environment variables in a Spring Boot application.
- Single and multiple(array) environment variables were overridden.
- When you run a Spring Boot application, the application properties are converted to environment variables.
- You can override environment variables using the
-Dflag when java -jar is used. - You can override environment variables using the
-eflag when running a Spring Boot application in a Docker container.
For further reference, please consider the following sections:
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/spring-boot
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/reference/features/external-config.html
- https://maven.apache.org/guides/index.html
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/3.3.2/maven-plugin
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/3.3.2/maven-plugin/build-image.html
- https://docs.docker.com/compose/environment-variables/set-environment-variables/