A prototype analog of a Kubernetes admission controller for Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) which:
- Terminates any running images without a valid cosign signature.
- Sends alerts to an SNS topic (which can forward to your email).
- Supports configurable keys to use for signature validation.
NOTE: This is Proof of Concept code and not yet production-ready. In the event of a bug or misconfiguration, it can prevent any ECS tasks from running. This system intercepts tasks as they start (not before) and may not fully prevent unsigned containers.
If you'd like to learn more or give feedback, please file an issue or send an email to interest@chainguard.dev.
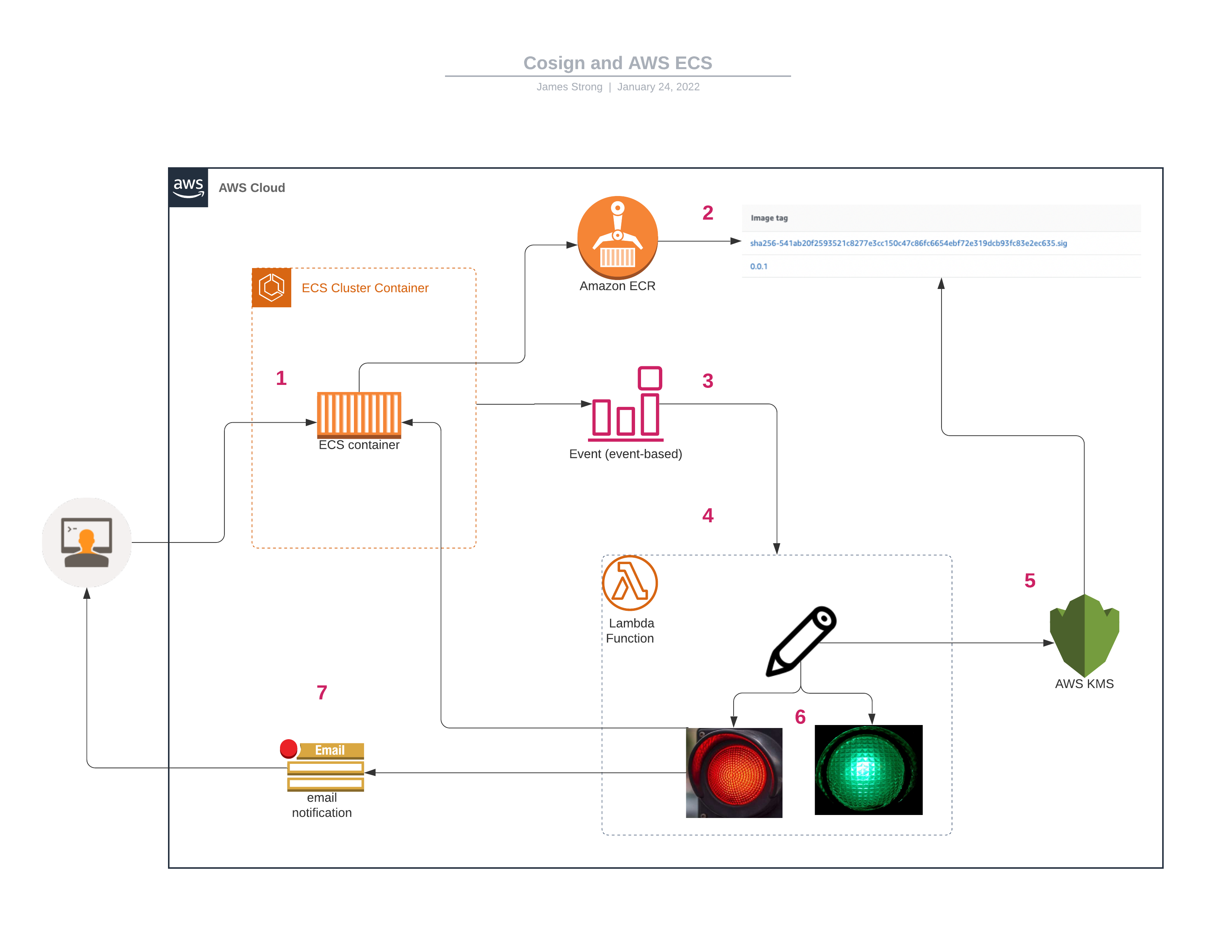
This system comprises a Lambda function (4) which listens to EventBridge events (3) triggered on every ECS task run (1). The function checks that the task's container image has a valid cosign signature in ECR (2) with a specific public key, provided directly or stored in KMS (5). If the check fails, the function terminates the task and sends a notification to an SNS topic (7) which you can subscribe to via email.
In order:
- Start an ECS task in the cluster
- The task definition has the container image stored in ECR
- EventBridge sends a notification to Lambda
- Cluster and Task definition is sent to function
- KMS key that has signed an image
- Lambda function evaluates if container image is signed w/ KMS
- If not signed with specified key it does two things
- Stop task definition
- SNS notification email to alert that the service/task has been stopped
You will need the following tools installed:
make(e.g., GNU make)- Terraform: for local testing
- AWS CLI and AWS SAM CLI: for deploying
cosign: for generating keysdocker: if you need to make images
You should configure the AWS CLI for your project and account.
To deploy, run:
make sam_deployIt will check against the key in cosign.pub (see detailed instructions for how
to change this).
To test, we need an ECS cluster on which to run our signed/unsigned tasks.
The terraform subdirectory contains a Terraform template for such a cluster,
with corresponding task definitions. First, initialize (to download the AWS
provider for Terraform), then deploy:
make tf_init
make tf_apply # run `make tf_plan` to see the plan firstWe can then run our tasks (these will run two public "hello world" Alpine images with and without a signature):
make run_unsigned_task
make run_signed_taskCheck that it worked. You should see the unsigned task in the STOPPED tasks
and the signed task in the RUNNING tasks:
make task_statusTo clean up, run:
make stop_tasks
make tf_destroy
make sam_deletecosign-ecs-verify uses a SAM template (template.yml) to create:
- A Lambda function (source in
cosign-ecs-function/) which:- Runs on every ECS task state change, triggered by EventBridge.
- Gets the key for signature verification.
- For each container in the event:
- Verifies the container image, terminating the task and sending a notification if it is invalid.
- An Amazon SNS topic: if the function stops an unsigned container image, it
will send a message to this topic.
- You can configure email notifications for this topic to be alerted whenever an unverified image is stopped.
- Messages sent to the topic are encrypted using a key in KMS.
To configure, run sam deploy with either the KeyArn set to a KMS key to use, or
KeyPem set to a full public key in PEM format. In the provided Makefile, we
hardcode the key in cosign.pub.
We provide a test ECS cluster configuration (in terraform/), containing;
- An ECS cluster:
- Configured to log to CloudWatch (which will trigger the Lambda via EventBridge).
- Associated task definitions
signedandunsigned, which (by default) run images.
- KMS keys and IAM permissions for the above.
If you would like to use your own images (for example, from a previous post on
the Chainguard blog), export $IMAGE_URL_SIGNED and
$IMAGE_URL_UNSIGNED before running make tf_apply. We give instructions below
for making your own to test.
We need a key against which to verify image signatures. If you have an existing keypair for cosign in AWS KMS, set it:
export KEY_ALIAS=my-keyOtherwise, we can make one:
export KEY_ALIAS=my-key
export AWS_SDK_LOAD_CONFIG=true
make key_genTo see cosign-ecs-verify in action, you need an example of a signed and
unsigned image. Here, we'll build two simple images, push them to Amazon ECR,
and sign only one.
First, login to ECR with Docker. We recommend using a credential helper for
docker, but we also provide a make target make ecr_auth that will authenticate
you to the default registry.
Then, we can create a repository for the signed/unsigned images.
REPO_URL=$(aws ecr create-repository \
--repository-name $REPO_NAME \
--query repository.repositoryUri \
--output text)Finally, we can build and push two simple images (see Dockerfile):
# Export these so we can make ECR task definitions for running them.
export IMAGE_URL_SIGNED=$REPO_URL:signed
export IMAGE_URL_UNSIGNED=$REPO_URL:unsigned
# Make 2 example images and push both.
# The --build-arg is to make sure the images have different digests.
docker build . --build-arg signed=true --tag $IMAGE_URL_SIGNED
docker build . --build-arg signed=false --tag $IMAGE_URL_UNSIGNED
docker push $IMAGE_URL_SIGNED
docker push $IMAGE_URL_UNSIGNEDAnd sign only one of them (make sure you have a key pair):
cosign sign --key awskms:///alias/$KEY_ALIAS $IMAGE_URL_SIGNEDNow, you can proceed with the Terraform instructions.
We require Go 1.17 for development.
You can also use the SAM local feature to run in a simulated Lambda environment:
make sam_local
make sam_local_debug