Nosflare is a serverless Nostr relay purpose-built for Cloudflare Workers and a Cloudflare R2 bucket.
This relay is designed to be easy to deploy, scalable, and cost-effective, leveraging Cloudflare's edge computing infrastructure to provide a resilient relay for the Nostr decentralized social protocol.
Most applicable NIPs are supported along with support for allowlisting or blocklisting pubkeys and event kinds and tags, throttle number of events from a single pubkey through rate limiting, block specific words and/or phrases, and support of NIP-05 for username@your-domain.com verified Nostr addresses.
Nosflare introduces a unique "helper" scheme which allows utilizing helper workers for handling EVENT and REQ messages. This let's the primary websocket worker communicate with helper workers in order to improve the saving and retrieval of events to and from the R2 bucket. At least one helper worker for both EVENT and REQ messages is required, detailed further in the Deployment section.
These helper workers communicate with the primary relay websocket worker through POST requests. This means, you can technically query your R2 bucket using standard HTTP POST requests like this example using cURL:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer AuthToken123" -d '{"type":"REQ","subscriptionId":"sub1","filters":{"kinds":[1]}}' "https://req-helper-1.example.com"
This opens up many possibilities for the relay to share event data outside of a Nostr client. By default, Nosflare is configured to use an Authorization header to secure and authenticate the inter-relay communication between websocket worker and helper workers in order to prevent abuse. However, you could alter the code if you'd like to remove this restriction.
- Supports a range of Nostr Improvement Proposals (NIPs), including NIPs 1, 2, 4, 5, 9, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17, 20, 22, 33, 40.
- A Cloudflare account with Workers and R2 bucket enabled.
- Node.js and npm (for installing dependencies and running the build script).
- (optional) Wrangler CLI
Nosflare requires the @noble/curves package for cryptographic operations and the @evanw/esbuild bundler:
npm install @noble/curves
npm install -g esbuild
Clone this repo to your machine, then cd into its directory, and open relay-worker.js in a file editor. Edit the contents of relayInfo and relayIcon as desired to customize the relay name, icon, etc.
Important! Edit the eventHelpers and reqHelpers section by replacing the placeholder URLs with at least one URL for each. Detailed further in the Deployment steps below.
Optional:
- In the
relay-worker.jsfile: Edit thenip05Userssection to add usernames and their hex pubkey for NIP-05 verified Nostr address, Edit theblockedPubkeysorallowedPubkeysandblockedEventKindsorallowedEventKindsto either blocklist or allowlist pubkeys and event kinds, EditblockedContentto block specific words and/or phrases, EditexcludedRateLimitKindsto exclude event kinds from rate limiting, Edit theblockedTagsorallowedTagsto either blocklist or allowlist tags, and/or Edit theblockedNip05DomainsorallowedNip05Domainsto either blocklist or allowlist domains for the NIP-05 validation (see spam filtering note below).
You can find full list of event kinds here and tags here.
How blocklisting and allowlisting works:
If pubkey(s) and event kind(s) and tag(s) are in blocklist, only that pubkey(s) and event kind(s) and tag(s) will be blocked and all others allowed. Conversely, if pubkey(s) and event kind(s) and tag(s) are in allowlist, only that pubkey(s) and event kind(s) and tag(s) will be allowed and all others blocked.
Spam filtering:
Nosflare has two optional robust spam filtering mechanisms: NIP-05 Nostr address validation and deriving hashes of event content.
The NIP-05 validation is enabled by default and is located within the processEventInBackground function in the relay-worker.js file. There you will see the code block for "NIP-05 validation", which you can either leave intact or remove/comment to disable validating NIP-05 address. Furthermore, within the relay-worker.js file you can explicitly list domains you'd like to allow or block from publishing events.
Additionally, each event submitted to the relay generates a hash based on the author's pubkey and the content of the event, which is stored within the "hashes" directory of the R2 bucket. By default, in the event-worker.js file it is set to bypass all event kinds (effectively disabled). However, it can be configured to remove specific events kinds from being bypassed, which would allow only 1 of the same hash per pubkey. This means, someone could submit an event of a note that says "Hey whatsup" and that'd be the only time that particular pubkey could ever create a single note like that. This prevents someone from repeatedly publishing the exact same note.
As briefly mentioned above, you can change which event kinds are subjected to checking for duplicate hashes in the bypassDuplicateKinds and duplicateCheckedKinds arrays in the event-worker.js file. There you can have more granular control over what event kinds are subjected to the spam filtering. Similar allowlisting/blocklisting logic as explained further above is also relevant here. Effectively, these sections are where you can enable or disable the spam filtering.
Furthermore, you can have even further granular control over the spam filtering by changing the value of enableGlobalDuplicateCheck in the event-worker.js file. By default, this option is set to false value, which means each event submitted to the relay is hashed with the author's pubkey. If set to true value it globally hashes the event content. As with the example given earlier, if one person were to write "Hey whatsup" and the value of enableGlobalDuplicateCheck is set to true then no other person can also write a note with "Hey whatsup" as the hash will already exist and any subsequent events would be dropped. This is particularly useful if your relay is under spam attack and the attackers are using disposable pubkeys, but the content of the spam notes are the same for each (such as the attack by "ReplyGuy").
Once you've made the desired edits, from the project's directory within CLI use the command npm run build to bundle the worker scripts. This will overwrite the relay-worker.js, event-worker.js, and req-worker.js files and save them in the dist/ directory. You will use these three scripts from the dist/ directory to deploy the relay.
You can deploy Nosflare using either the Wrangler CLI or directly through the Cloudflare dashboard. We'll focus on using the Cloudflare dashboard, but many steps for using Wrangler CLI is somewhat similar:
- Log in to your Cloudflare dashboard.
- Go to the Workers section and create a new worker. You can call it whatever you'd like. This will be the primary relay worker (the one Nostr clients connect to).
- Copy the contents of
dist/relay-worker.jsfile and paste into the online editor. - Save and deploy the relay worker.
- Add a custom domain in the relay Worker's settings in "Triggers" tab (this will be the desired relay URL).
- Create another worker. You can call it whatever you'd like. This will be the EVENT messages helper worker.
- Copy the contents of
dist/event-worker.jsfile and paste into the online editor. - Save and deploy the events helper worker.
- Add custom subdomain in Worker's settings in "Triggers" tab (this will be the desired URL used for
eventHelpers). Repeat this step if you want to create multiple event helper workers! - Create another worker. You can call it whatever you'd like. This will be the REQ messages helper worker.
- Copy the contents of
dist/req-worker.jsfile and paste into the online editor. - Save and deploy the req helper worker.
- Add custom subdomain in Worker's settings in "Triggers" tab (this will be the desired URL used for
reqHelpers). Repeat this step if you want to create multiple req helper workers!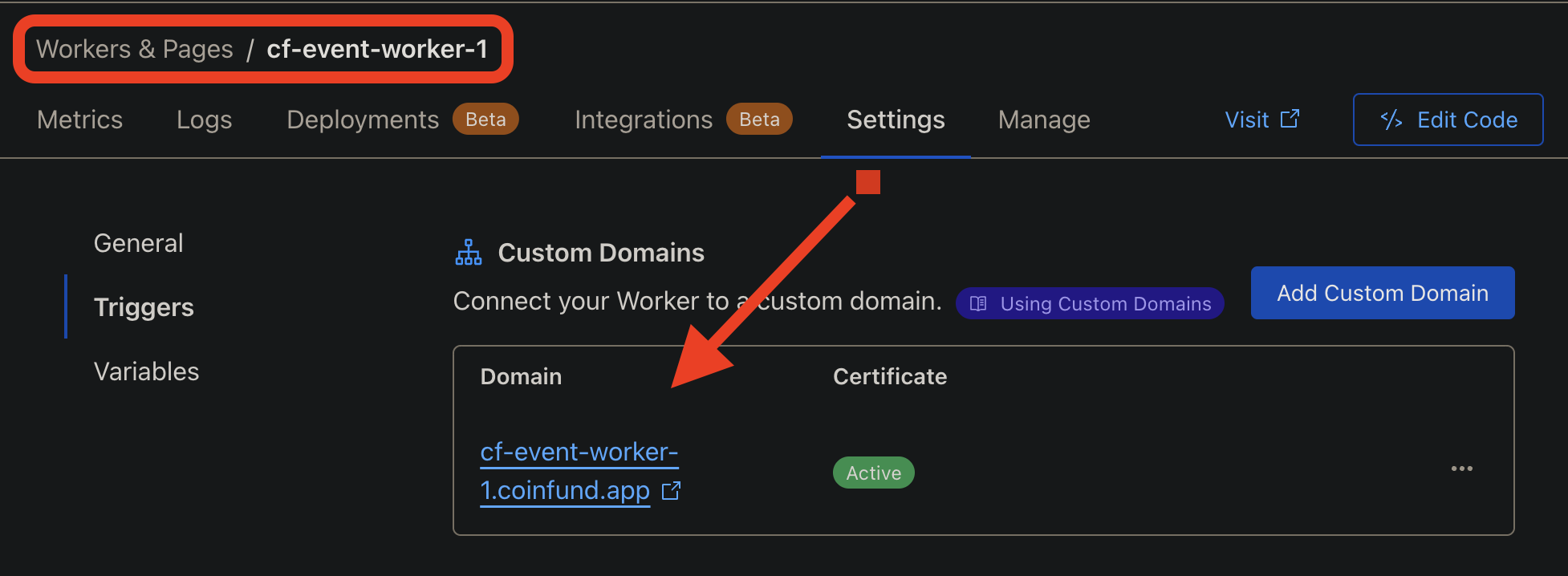
- Create a R2 bucket to store events. You can call it whatever and choose the location you want.
- In R2 bucket settings, add a custom subdomain (ex: nostr-events.site.com).
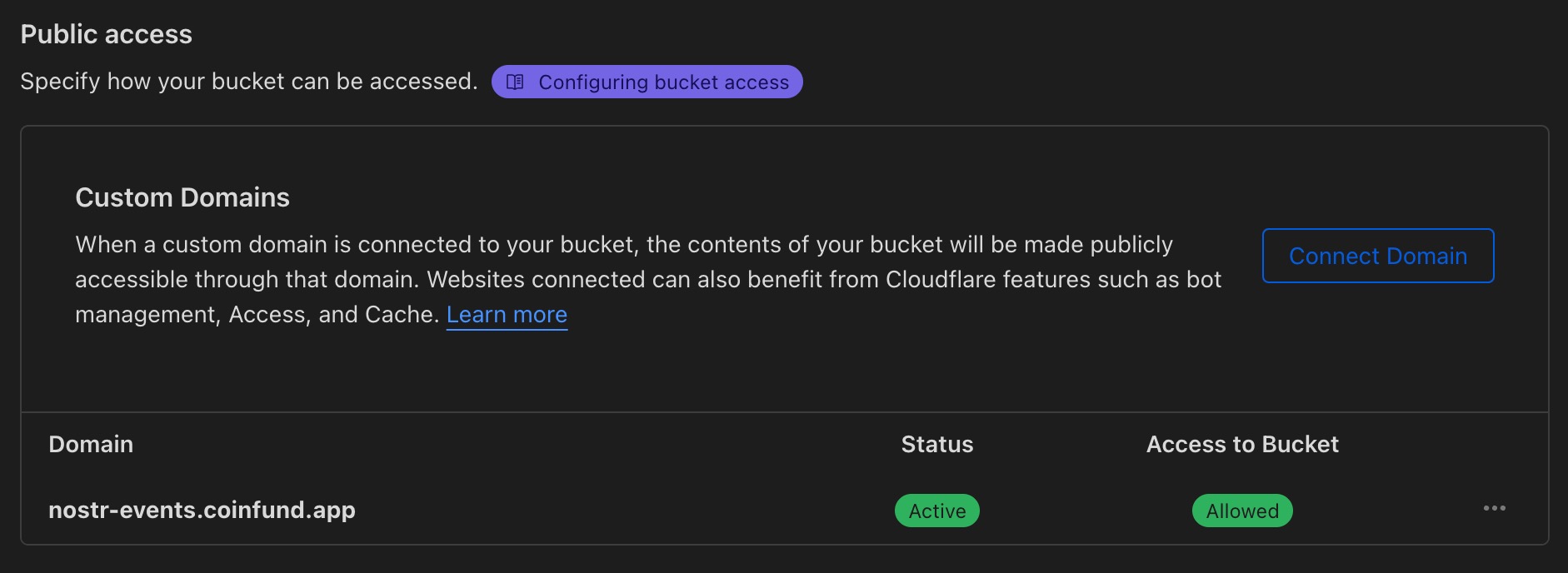
- In each Worker's variables settings add the following environment variables:
r2BucketDomainthat will be the subdomain URL you set as the custom domain in the R2 bucket,authTokenthis will be something unique (think password) that will be used to authenticate the communication from the relay worker to the helper workers,apiTokenthis will be your cloudflare API token (recommended to set a custom API token that only has cache purge privileges),zoneIdwhich is for the domain you're using for the R2 bucket (this ID can be found in the right sidebar of the overview page for the domain).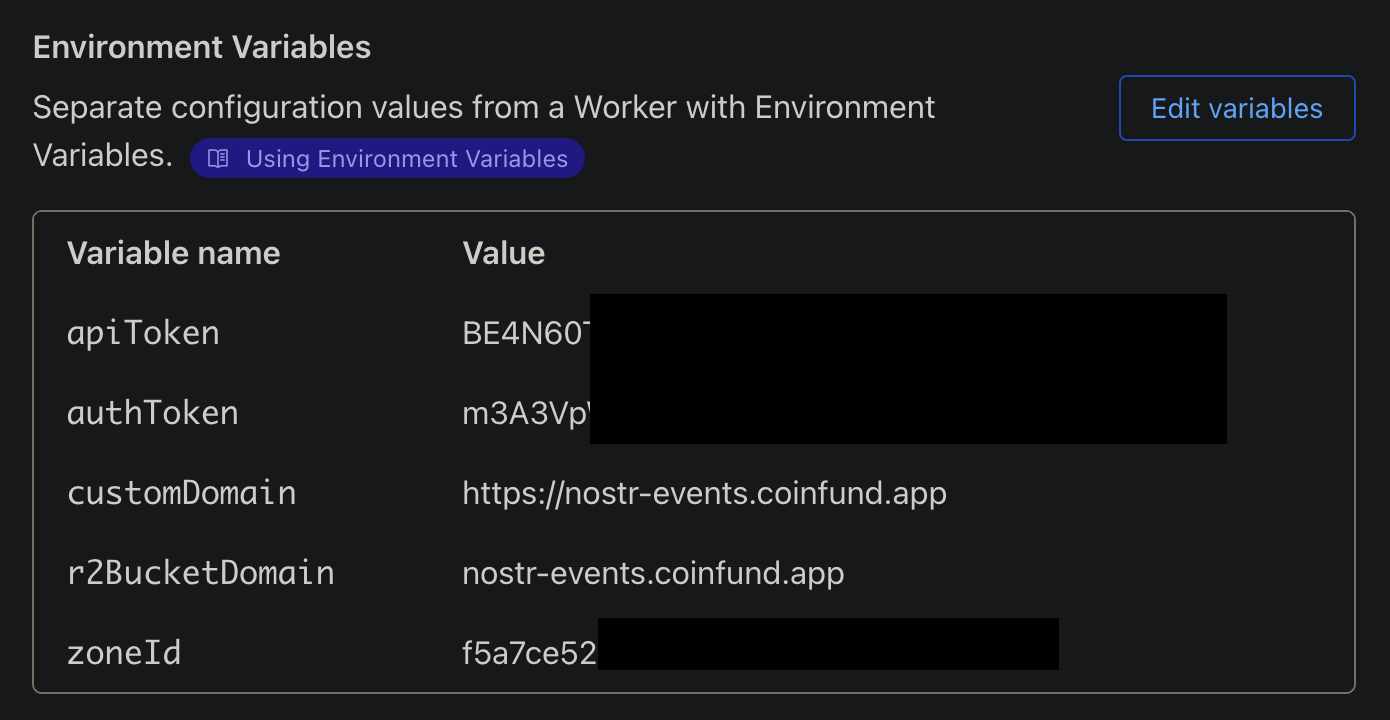
- In a different section on the Settings > Variables page of each worker, bind the
relayDbvariable to the R2 bucket you created in the R2 Bucket Bindings section.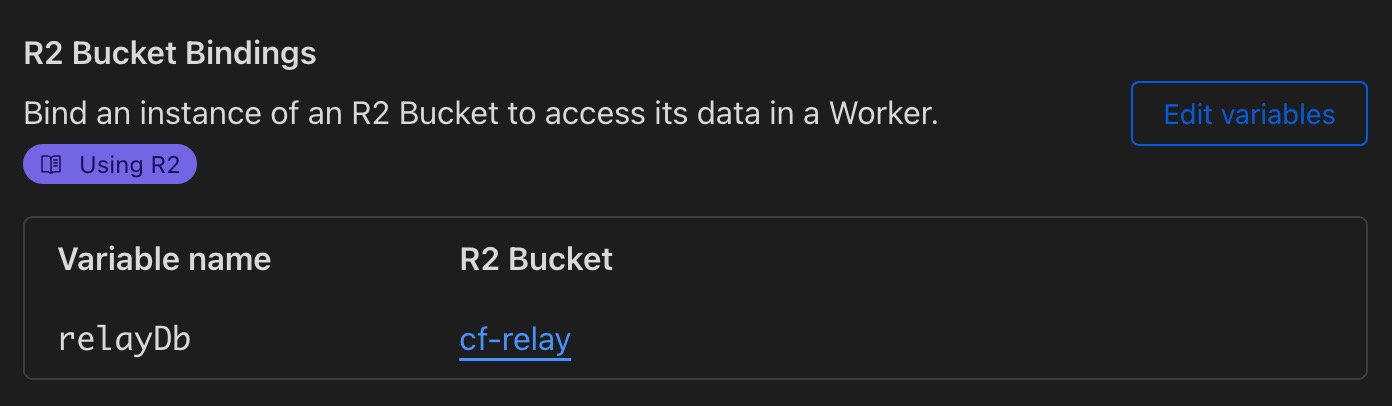
Due to the serverless architecture and object storage through R2 bucket, there is a slight limitation to handling REQ messages that include the since and/or until filters. This relay implementation does not store any timestamp related keys. Therefore, making it impossible to fetch events based on these filters. However, all other filters such as ids, kinds, authors, and tags still work correctly. To reduce unnecessary load from REQ messages that include the since and/or until filters, they have been blocked within the processReq function in the relay-worker.js file.
The current release of Nosflare is primarily focused on basic protocol flow usage. This ensures events are stored and retrieved very quickly. However, the following is a non-exhaustive list of planned features:
- "Pay-to-relay" (charging sats for access)
- Client authorization (NIP-42)
- Encrypted DMs (NIP-44)
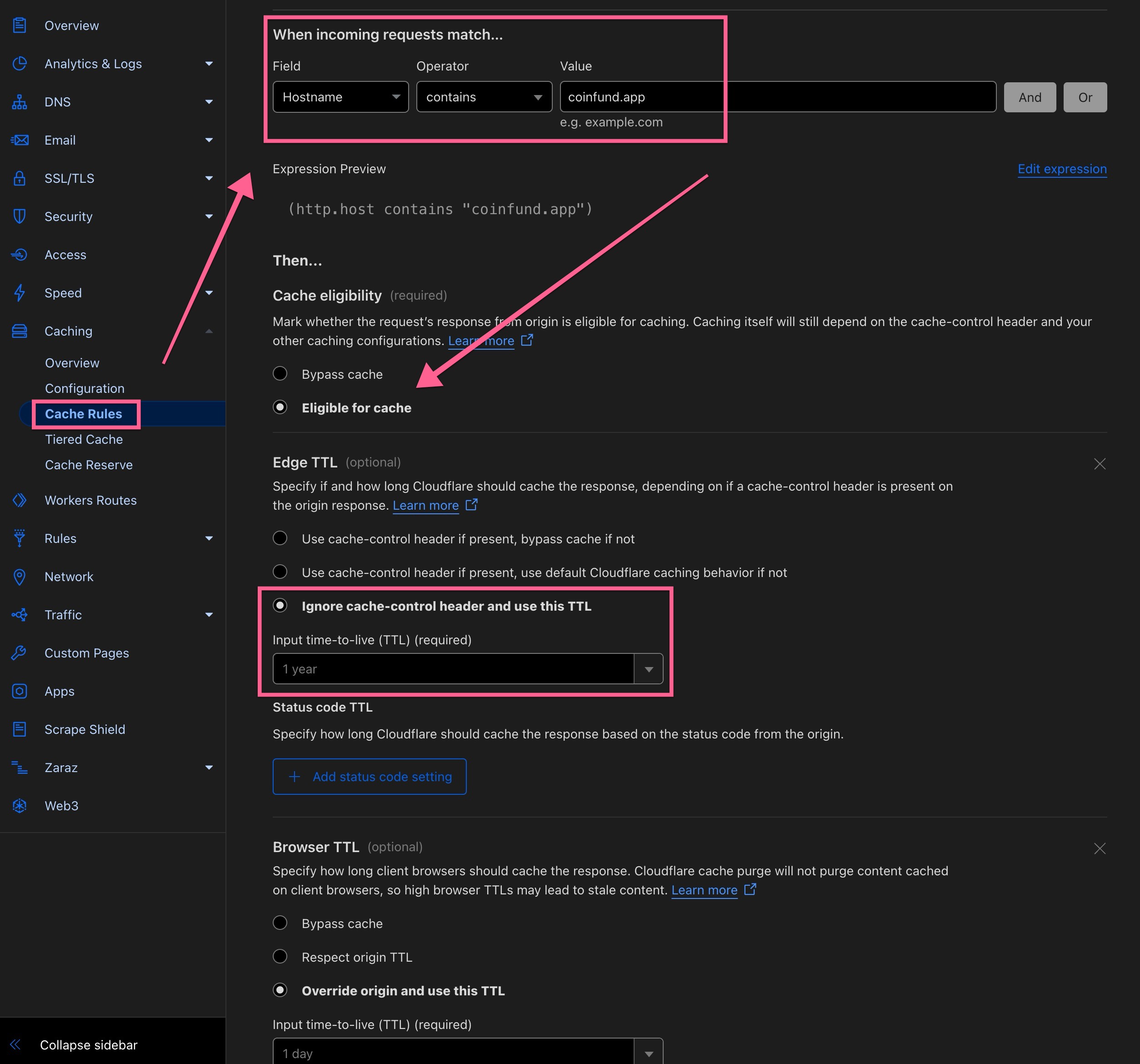
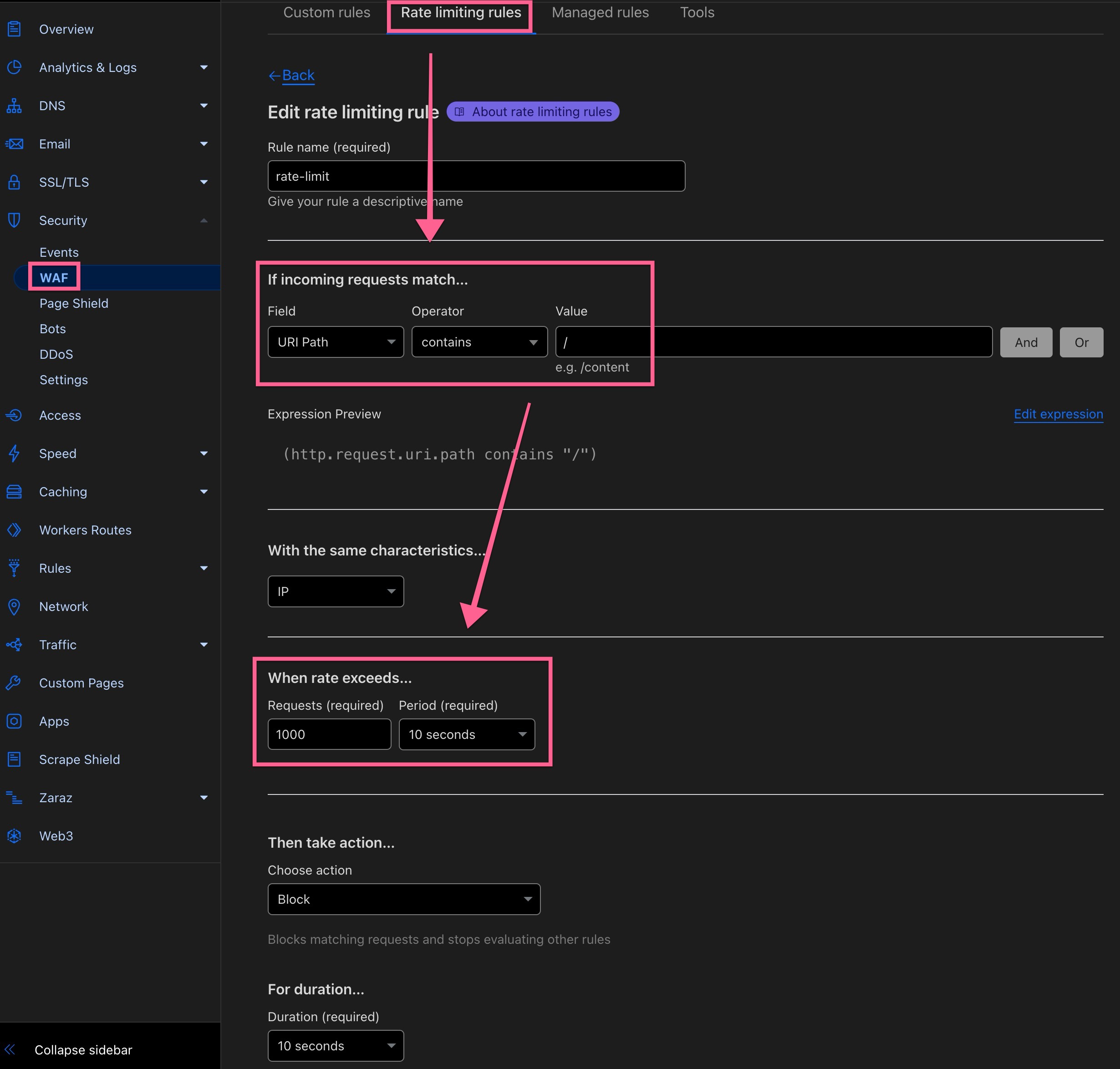
Ensure optimal performance of the relay by creating a Page Rule for enforcing a high cache rate through a "cache everything" rule and lengthy Cloudflare edge TTL as well as enabling rate limiting in order to protect the relay from abuse.
Examples:
Contributions to Nosflare are welcome! Please submit issues, feature requests, or pull requests through the project's GitHub repo.
Nosflare is open-sourced software licensed under the MIT license.
For inquiries related to Nosflare, you can start a discussion on the GitHub repo or reach out on Nostr:
npub16jdfqgazrkapk0yrqm9rdxlnys7ck39c7zmdzxtxqlmmpxg04r0sd733sv