A key/value db implemented by LSM. It is for studying LSM data structure.
I will design the db by the theories, and then compare with other famous
lsm databases. This README is writen before I write any code, because I
can think through every detail before I start.
LSM is Log-Structured MergeTree. It is a data structure, but it's not a common
tree structure like B+ tree. Many popular databases are implemented by LSM.
The core concept of LSM is to use sequential IO to increase writing speed,
so it has horizontal and vertical layers in its design. Because of layers,
it decreases reading speed. It is popular for More-Write-And-Less-Read situation.
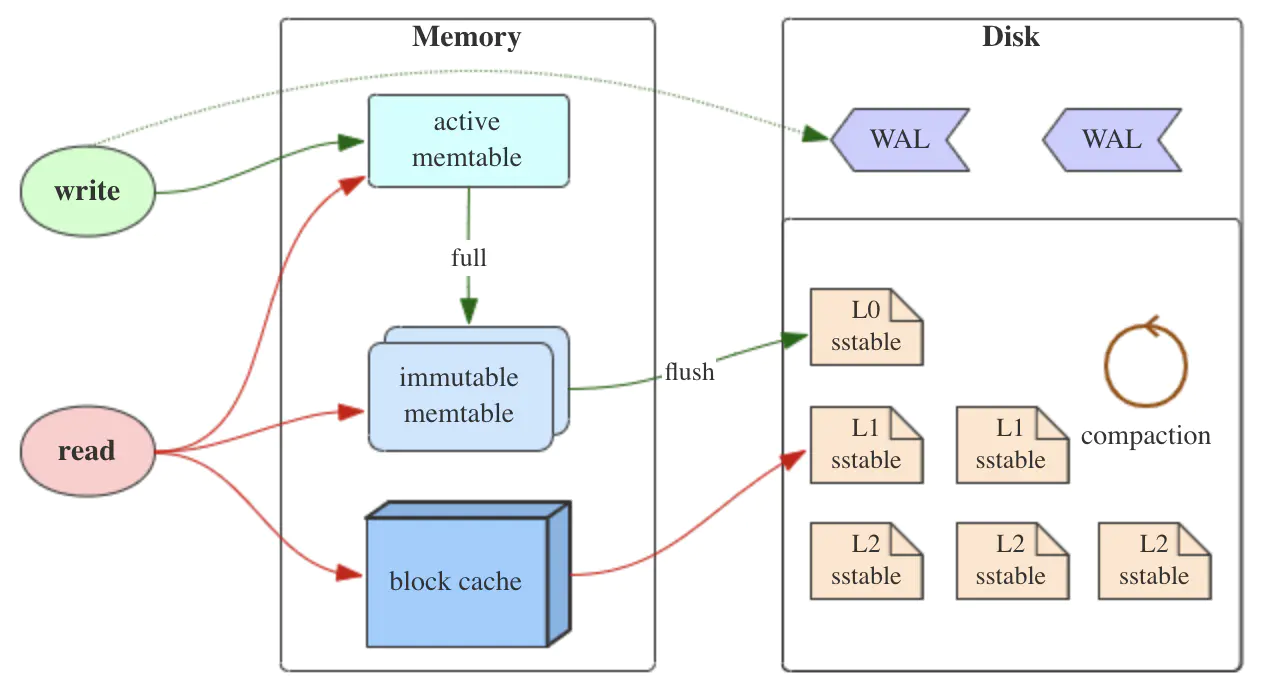
There are different layers in the architecture of RocksDB.
-
MemTable: MemTable is an
in-memorydata structure, and it stores the recent data. All keys are in order by the data structure. It is not restricted to any data structure in this layer. For RocksDB, it is usingskip list. Because it is in the memory, it will lose data for some situation. Therefore, it will use WAL(Write-ahead logging) for data durability. After a failure, it will read the WAL for the backup. -
Immutable MemTable: When size of MemTable is increasing, it will turn into an Immutable MemTable. Immutable is also in the memory, and it is a
middle layerbetween MemTable and SSTable. After the changing from MemTable, Immutable MemTable will beread onlyand wait to be written to SSTable. All writing requests will be processed by the new MemTable. -
SSTable(Sorted String Table): This layer is in the
disk. For the quick searching, it has key indexing and bloom filters(Check whether a key is in the SSTable). In the SSTable layer, it has manylevels(l0, l1, l2...), also each level has many files to store the logs. When there are enough files in same level, it willmergethe files and next level files to decrease the file number in this level. It can cause the cascade situation.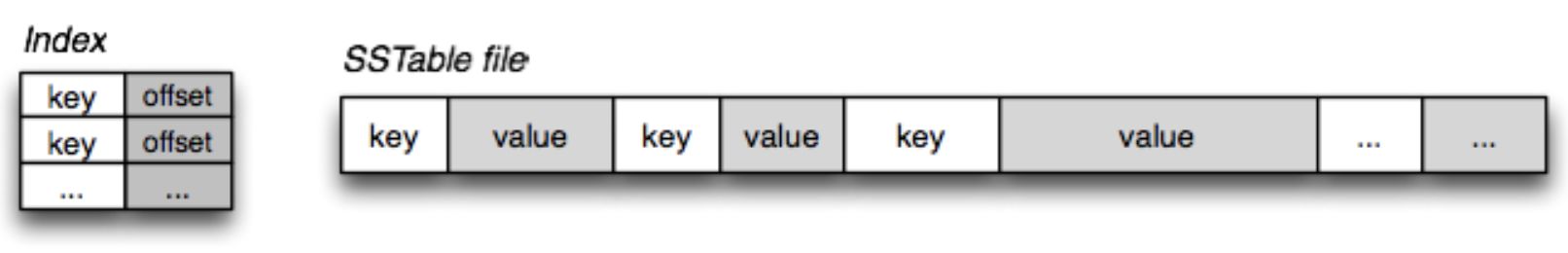
LSM keeps all logs in the memory, when the operations are getting large enough, they will be flushed in the SSTable by sequential IO. LSM is log style data structure, and it saves all operations. It doesn't need to change the previous data for faster sequential IO. In the contrast of B+ tree, it will always update the old data by the new data. Therefore, B+ tree is an in-place update structure, and LSM is an out-place update structure.
-
Read Amplification: Because LSM is log structured, it needs to read through, all layers and all levels to get a key. It can be solved by
mergingmany SSTable files. In the same level of SSTable, it can ensure there is no duplicate log. Also, it can use the bloom filter to speed reading. -
Size Amplification: LSM appends all logs to the disk, and it will not delete any keys. It causes the garbage data in the disk. It also can be solved by the
merging. After the merging, it will only keep the newest log for the same key. -
Write Amplification: For solving read and size Amplification, it will have a background process to merge logs and compaction. For every merge, it repeated writing
useless keyby multiple times. It causes write amplification. This problem can be solved byleveled compaction. It makes sure there is only one log of a key among the files in the SSTable level. There isno duplicatekey log in the same level.
Continue...