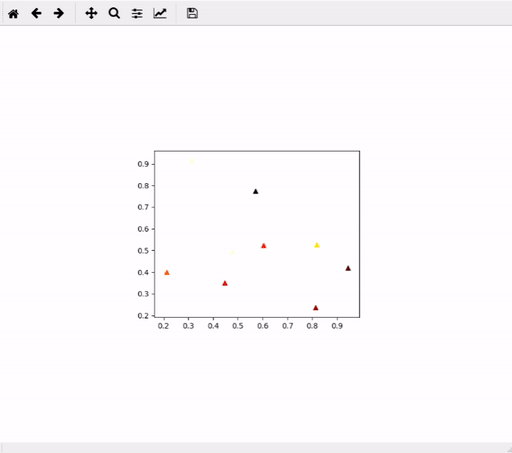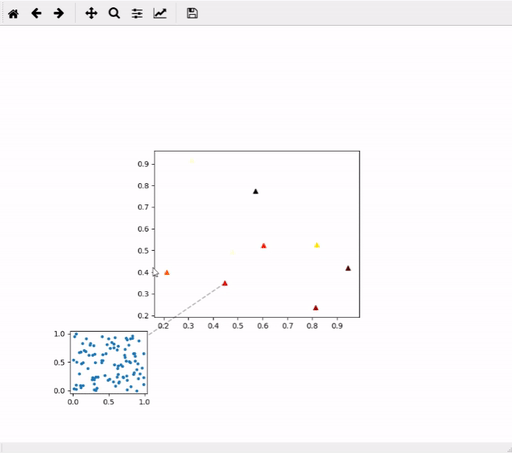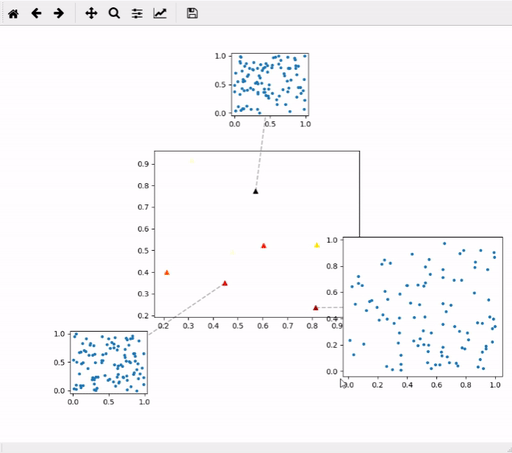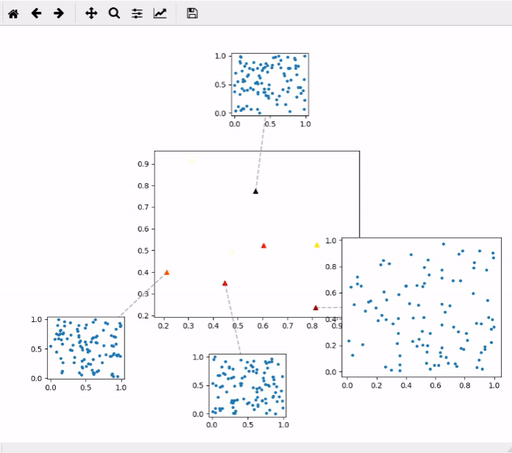
Create plot mosaic. Example:
The class has two interfaces. The zero-state interface is used for creating a new plot mosaic. The load-state interface is used for loading a previously saved mosaic.
Dependencies:
- Numpy
- Matplotlib
Creating the plot mosaic from scratch (zero-state interface)
import mpl_mosaic
import numpy as np
# Function used for creating the smaller plots. It receives a data
# object and an axes. The function plots the data using a matplotlib
# function. The function below receives the variable data containing
# two lists, corresponding to x and y positions.
def plotFunc(data, ax):
x = data[0]
y = data[1]
ax.plot(x, y, 'o', ms=3)
# Generate 10 points for the main axes
points = np.random.rand(10, 2)
x, y = zip(*points)
# Generate some colors for the points
colors = np.random.rand(10)
# Set some properties for points in the main axes
mainPlotKwargs = {'marker':'^', 'c':colors, 'cmap':'hot'}
# Generate 10 arrays of 100 points, each array corresponding to
# a point in the main axes
allData = np.random.rand(10, 2, 100)
mosaic = mpl_mosaic.PlotMosaic(x, y, allData, dragPlotter=plotFunc, mainPlotKwargs=mainPlotKwargs)
# You can save the mosaic for latter use
mosaic.saveState('mosaic.dat')Loading a previously saved mosaic (load-state interface)
import mpl_mosaic
mosaic = mpl_mosaic.PlotMosaic('mosaic.dat')Quick note, if you want the draggable plot to contain images, you can set the plotting function as
def plotFunc(img, ax):
ax.imshow(img)