plotty is a CLI (command-line interface) script that allows plotting data. Its goals are to be flexible enough to replace small matplotlib-like scripts for most use cases.
plotty is a python script. It requires python3.
Basic operation consists of plotting a file containing a timeseries in CSV (comma-separated values) format.
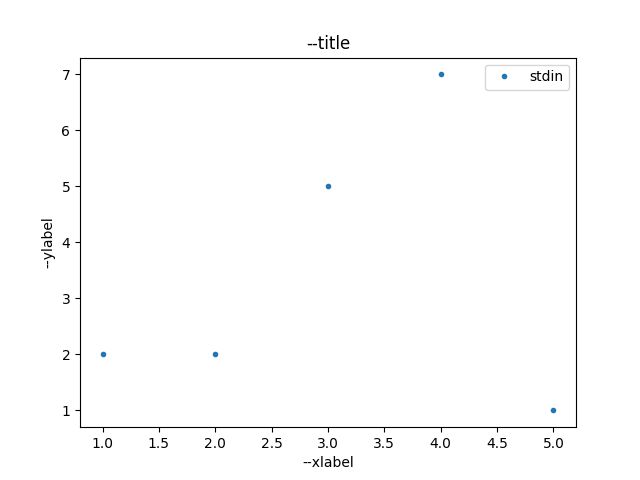
$ echo -e "1,2\n2,2\n3,5\n4,7\n5,1\n" | ./plotty-plot.py -i - /tmp/plot.png
output is /tmp/plot.png
Figure 1 shows the output file of the plot command.
You can modify the values of the xlabel, ylabel, and title by using the corresponding options.
Use --help option to list all possible flasg:
$ ./plotty-plot.py --help
usage: plotty-plot.py [-h] [-d] [--quiet] [--marker MARKER]
[--title PLOTTITLE] [--xcol XCOL] [--xcol2 XCOL2]
[--ycol YCOL] [--ycol2 YCOL2] [--ydelta] [--ycumulative]
[--filter COL OP VAL] [--sep SEP] [--sep2 SEP2]
[--legend-loc LEGEND_LOC] [--histogram]
[--histogram-bins NBINS] [--histogram-sigma SIGMA]
[--histogram-ratio] [--xlabel XLABEL] [--ylabel YLABEL]
[--add-mean] [--add-median] [--add-stddev]
[--xlim left right] [--ylim bottom top]
[--yscale [linear | log | symlog | logit]]
[--xshift XSHIFT] [--yshift YSHIFT] [--fmt FMT]
[--label LABEL] [-i input-file]
[--batch-infile batch_infile] [--batch-sep SEP]
[--batch-col BATCHCOL] [--batch-label-col BATCHLABELCOL]
[--batch-filter COL OP VAL]
output-file
plot.py: simple data plotter. # http://stackoverflow.com/a/11249340 # runme #
$ echo -e "1,2 2,2 3,5 4,7 5,1 " | ./plotty-plot.py -i - /tmp/plot.png
positional arguments:
output-file output file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d, --debug Increase verbosity (multiple times for more)
--quiet Zero verbosity
--marker MARKER use MARKER as plot marker
--title PLOTTITLE use PLOTTITLE plot title
--xcol XCOL use XCOL x col
--xcol2 XCOL2 use XCOL2 for refining x col
--ycol YCOL use YCOL y col
--ycol2 YCOL2 use YCOL2 for refining y col
--ydelta use $y[k] = (y[k] - y[k-1])$
--ycumulative use $y[k] = \sum_i=0^k y[i]$
--filter COL OP VAL select only rows where COL OP VAL is true
--sep SEP use SEP as separator
--sep2 SEP2 use SEP2 as alternate separator
--legend-loc LEGEND_LOC
Legend location
--histogram sort and bin xlist, get ylist as histogram
--histogram-bins NBINS
use NBINS bins
--histogram-sigma SIGMA
use avg += (SIGMA * stddev) to remove outliers
--histogram-ratio use ratio for ylist instead of total number
--xlabel XLABEL use XLABEL x label
--ylabel YLABEL use YLABEL x label
--add-mean Add a line at the mean
--add-median Add a line at the median
--add-stddev Add 2 lines at mean +- stddev
--xlim left right
--ylim bottom top
--yscale [linear | log | symlog | logit]
yscale values
--xshift XSHIFT use XSHIFT x shift(s)
--yshift YSHIFT use YSHIFT y shift(s)
--fmt FMT use FMT format(s)
--label LABEL use LABEL label(s)
-i input-file, --infile input-file
input file(s)
--batch-infile batch_infile
conf input file
--batch-sep SEP use SEP as separator in the batch file
--batch-col BATCHCOL use BATCHCOL batch col
--batch-label-col BATCHLABELCOL
use BATCHLABELCOL batch for label col
--batch-filter COL OP VAL
select only batch rows where COL OP VAL is true
Second operation mode consists of plotting a histogram for a variable in a timeseries in CSV (comma-separated values) format.
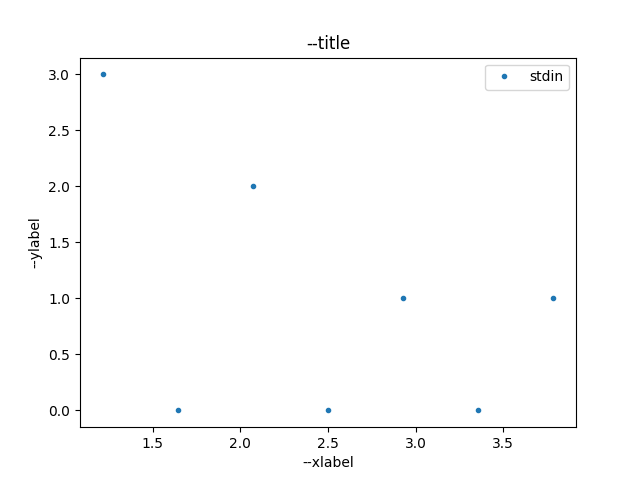
$ echo -e "1\n2\n1\n2\n3\n1\n4\n" | ./plotty-histogram.py -i - /tmp/histo.png
output is /tmp/histo.png
Figure 2 shows the output file of the histogram command.
You can modify the values of the xlabel, ylabel, and title by using the corresponding options.
While plotty allows repeating the -i, --fmt, and --label options to plot data from multiple files at the same time, we end up with shell lines that are too long. Instead, plotty provides a batch mode that allows defining the list of all files that need to be plotted at the same time in yet another CSV file.
$ cat in.csv
# id,ip_src,rtp_ssrc,rtp_p_type_list,ip_len,pkts,duration,filename
0,1.2.3.4,03c6af72,100,123905,398,595.3278110027313,in0.csv
1,1.2.3.4,4bab8bd5,100,121405,402,590.4864630699158,in1.csv
...
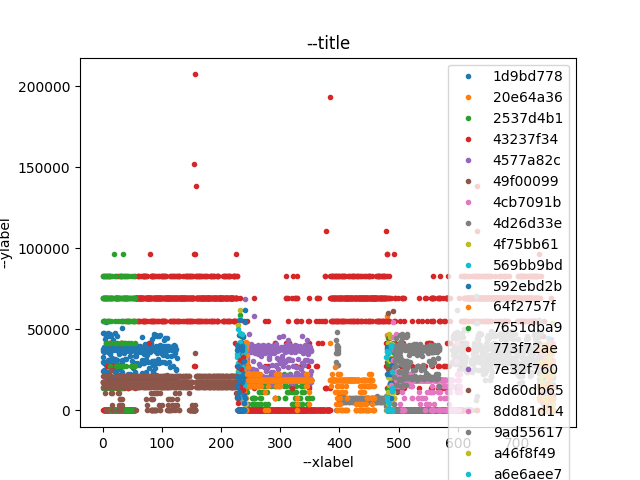
$ ~/proj/plotty/plotty-plot.py -d --xcol frame_time_relative \
--ycol bitrate_last_interval \
--batch-infile in.csv --batch-col filename --batch-label-col rtp_ssrc \
--batch-filter id gt 44 out.png
Figure 3 shows the output file of the batch command.
Requires python3 with some packages.
plotty is BSD licensed, as found in the LICENSE file.