Zelos (Zeropoint Emulated Lightweight Operating System) is a python-based binary emulation platform. One use of zelos is to quickly assess the dynamic behavior of binaries via command-line or python scripts. All syscalls are emulated to isolate the target binary. Linux x86_64 (32- and 64-bit), ARM and MIPS binaries are supported. Unicorn provides CPU emulation.
Full documentation is available here.
Use the package manager pip to install zelos.
pip install zelosTo emulate a binary with default options:
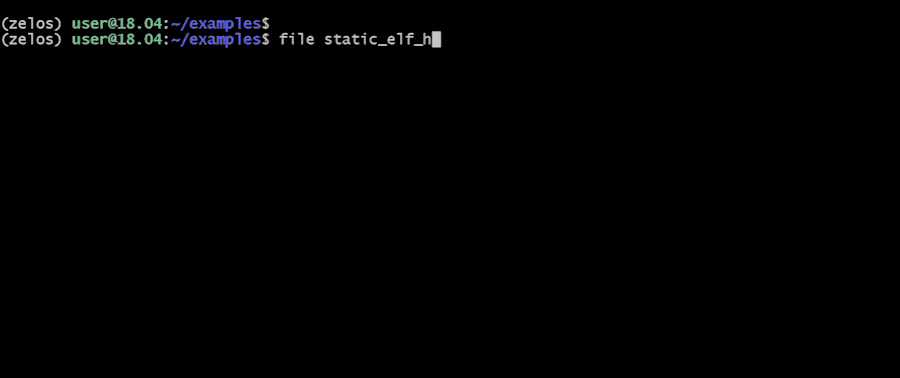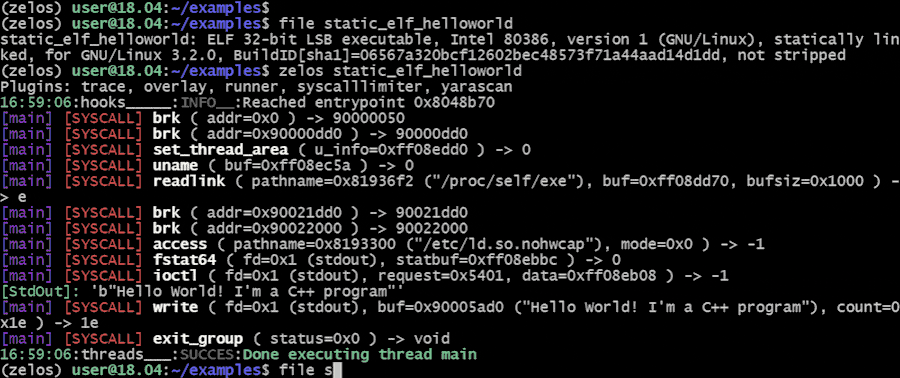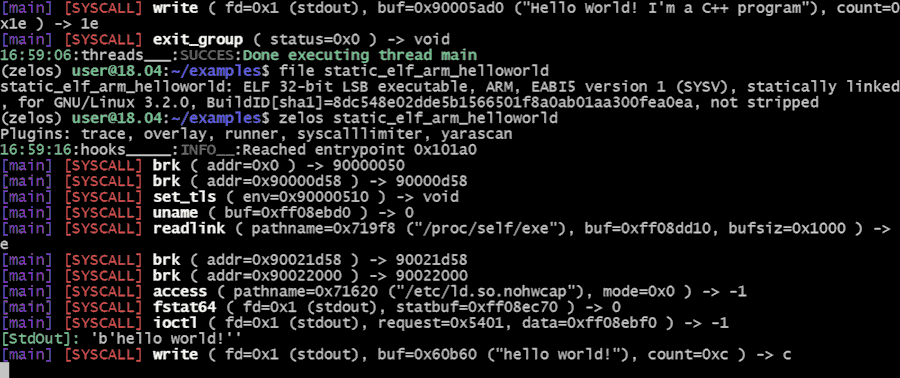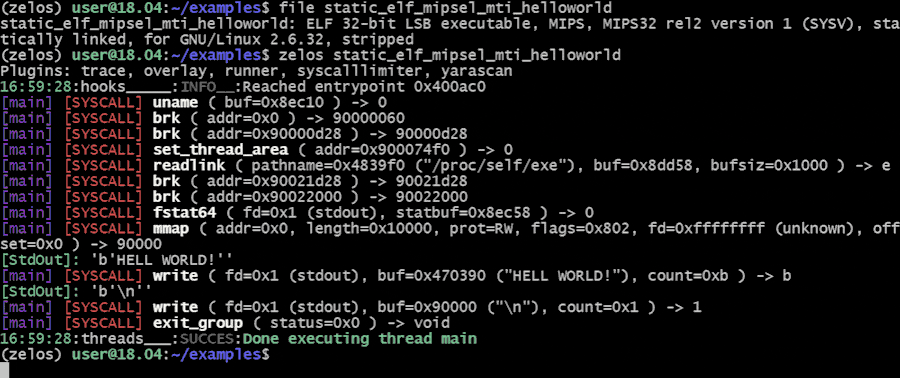
$ zelos my_binaryTo view the instructions that are being executed, add the --inst flag:
$ zelos --inst my_binaryYou can print only the first time each instruction is executed, rather than every execution, using --fasttrace:
$ zelos --inst --fasttrace my_binaryBy default, syscalls are emitted on stdout. To write syscalls to a file instead, use the --trace_file flag:
$ zelos --trace_file path/to/file my_binarySpecify any command line arguments after the binary name:
$ zelos my_binary arg1 arg2import zelos
z = zelos.Zelos("my_binary")
z.start(timeout=3)Zelos supports first- and third-party plugins. Some notable plugins thus far:
- crashd crash analyzer combining execution trace, dataflow and memory sanitization.
- overlay (ida plugin): highlights
zelosexecution trace in IDA with instruction-level comments added. - angr integration: enables symbolic execution in
zelos. - zdbserver: remote control and debugging of emulated binaries.
- syscall limiter: demonstrates event hooking and provides syscall-based execution and termination options.
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
First, create a new python virtual environment. This will ensure no package version conflicts arise:
$ python3 -m venv ~/.venv/zelos
$ source ~/.venv/zelos/bin/activateNow clone the repository and change into the zelos directory:
(zelos) $ git clone git@github.com:zeropointdynamics/zelos.git
(zelos) $ cd zelosInstall an editable version of zelos into the virtual environment. This makes import zelos available, and any local changes to zelos will be effective immediately:
(zelos) $ pip install -e '.[dev]'At this point, tests should pass and documentation should build:
(zelos) $ pytest
(zelos) $ cd docs
(zelos) $ make htmlBuilt documentation is found in docs/_build/html/.
Install zelos pre-commit hooks to ensure code style compliance:
(zelos) $ pre-commit installIn addition to automatically running every commit, you can run them anytime with:
(zelos) $ pre-commit run --all-filesCommands vary slightly on Windows:
C:\> python3 -m venv zelos_venv
C:\> zelos_venv\Scripts\activate.bat
(zelos) C:\> pip install -e .[dev]