LAMS, the Learning Activity Management System, is an open source Learning Design system for designing, managing and delivering online collaborative learning activities. Publicly available learning designs from LAMS Community have been analyzed and stored in a database that can be easily queried to get instructional insights.
LAMS learning designs are represented as Sequences of Learning Activities. Activities mostly pertain to Tools, which are self-contained modules that form most of the "functionality" that the Learner interacts with in LAMS, and the remaining activities have organizational purposes. Activities are divided into simple and complex.
-
Simple activities include Tools, Groupings of learners or Gates that control the pace of the lesson. More information about the LAMS Tool Activities is available in lams activities.
-
Complex activities are used to describe the insertion of sub-sequences within an instructional design. They can refer to branchings of the main learning sequence, tasks that need to be done in parallel or optional activities. A common branching example is the division of the Learners into learning groups. Some special cases are the following:
-
FLOATING_ACTIVITY_TYPE: Refers to the Support Activities which are tasks that do not have to be completed in order to finish a lesson.
-
SEQUENCE_ACTIVITY_TYPE: This is an auxiliary type used for representing the sub-sequences created within a learning design by a complex activity.
-
Activities of type PARALLEL_ACTIVITY_TYPE, OPTIONS_ACTIVITY_TYPE or FLOATING_ACTIVITY_TYPE cause sub-sequences that consists only of a single Tool activity in contrast to the rest of the complex activity types that can produce longer sub-sequences of learning activities.
-
There are detailed descriptions about activities in user documentation and all the attributes of a learning activity as long as the different activity types can be found in the java class Activity.java.
PostgreSQL DBMS has been used to store the learning design sequences. The database can be reproduced using the lamsdb.dump file. To reproduce the database, type in the PostgreSQL interactive terminal:
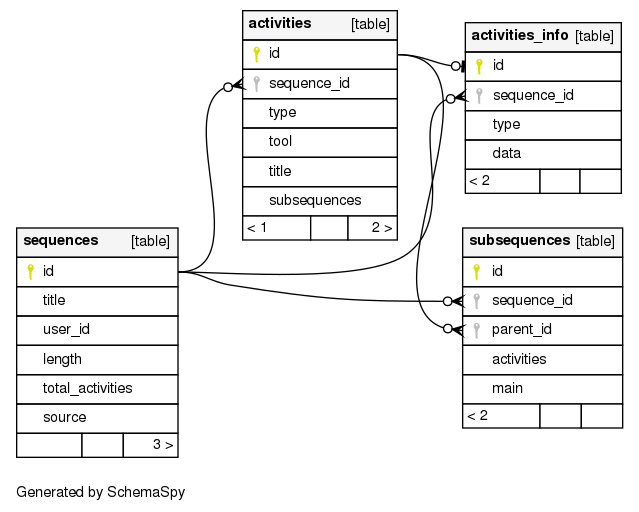
$ psql db_name < lamsdb.dump- sequences(id, title, user_id, length, total_activities)
- activities(id, sequence_id, type, title, subsequences)
- activities_info(id, sequence_id, type, data)
- subsequences(id, sequence_id, parent_id, activities, main)
Learning designs are stored in the table sequences and the lenght attribute refers to the main sequence of the lesson as this is displayed in Preview Mode. In table subsequences, both the main sequence and the sub-sequences of a lesson are stored. The parent_id refers to the complex activity that causes the creation of a sub-sequence ad it is used for retrieving all the possible paths within a lesson without requiring joins with other tables. Information about the Learning activities is stored in the remaining tables. The activities_info table is used for storing the content of Tool Activities in jsonb format.
Most common acitvity types and their frequency
| type | frequency |
|---|---|
| TOOL_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 15964 |
| GROUPING_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 652 |
| PERMISSION_GATE_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 467 |
| PARALLEL_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 368 |
| TOOL_BRANCHING_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 166 |
| GROUP_BRANCHING_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 153 |
| OPTIONS_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 141 |
| CHOSEN_BRANCHING_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 123 |
| SYNCH_GATE_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 94 |
| FLOATING_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 68 |
| SCHEDULE_GATE_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 39 |
| CONDITION_GATE_ACTIVITY_TYPE | 34 |
| OPTIONS_WITH_SEQUENCES_TYPE | 29 |
Query that digs into the jsonb structure to extract every question from all the quizzes in all the graphs (complex because sometimes the field questions has a single question, sometimes an array of questions):
WITH questionrows
AS (SELECT ( data -> 'qaQueContents' ->
'org.lamsfoundation.lams.tool.qa.QaQueContent' ) AS
q
FROM activities_info),
questions
AS (SELECT CASE
WHEN Jsonb_typeof(q) = 'array' THEN Jsonb_array_elements(q)
ELSE q
END AS q
FROM questionrows
WHERE q IS NOT NULL)
SELECT q -> 'question'
FROM questions;