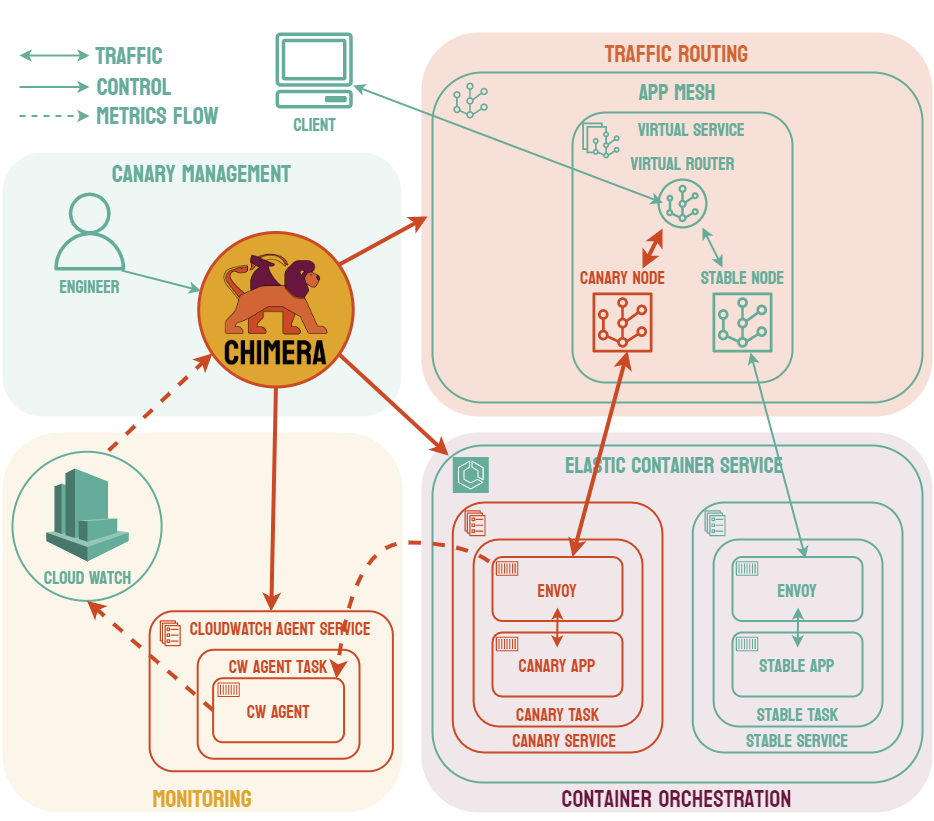
Chimera automates canary deployments for containerized microservices that communicate synchronously on AWS. It reduces the risk of introducing bugs that propagate through your microservice infrastructure by gradually shifting traffic to a canary version of your service while automating simple threshold canary analysis.
Currently, Chimera supports canary deployments for microservices that run on ECS/Fargate and communicate via App Mesh. For monitoring metrics, Chimera uses a Prometheus-configured CloudWatch agent that Chimera must set up before it can perform canary deployments.
For more information, please see Chimera's official webpage.
Chimera is deployed with Docker-Compose. Please ensure that both Docker and Docker-Compose are running on your machine.
To install Chimera, clone this repository. You can use the following terminal command:
git clone https://github.com/chimera-deploy/Chimera.git && cd ChimeraOnce you are inside the Chimera directory, create an .env file and add the following:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your aws access key id>
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your aws secret access key>
Save that file and close it. Once that is complete, you only need to execute the following command:
docker-compose upChimera will now be ready to set up the Prometheus-configured CloudWatch agent in your ECS cluster. You can access Chimera's UI at port 3000. Once there, have Chimera perform the automatic deployment of the CloudWatch agent unless you've already had Chimera do this before. After the CloudWatch agent is set up, your teams can perform canary deployments on your microservices.
To remove Chimera from your machine, simply execute:
docker-compose downOhio, USA
Pennsylvania, USA
Massachusettes, USA
Give a ⭐️ if you liked this project!