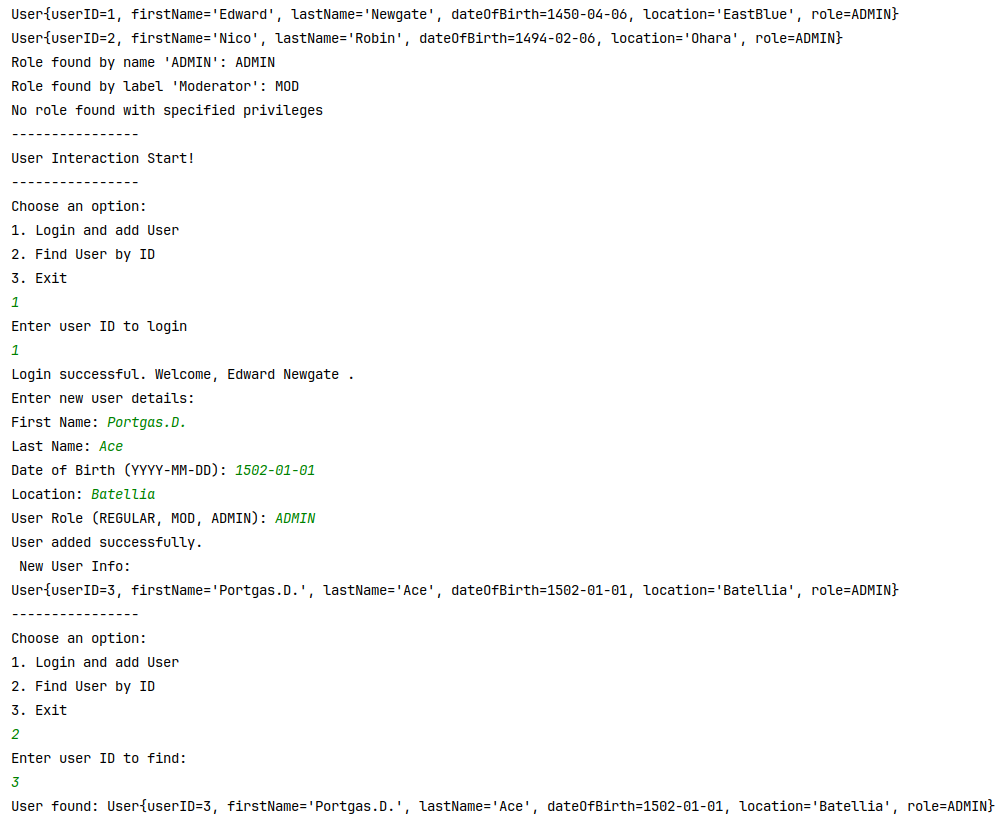
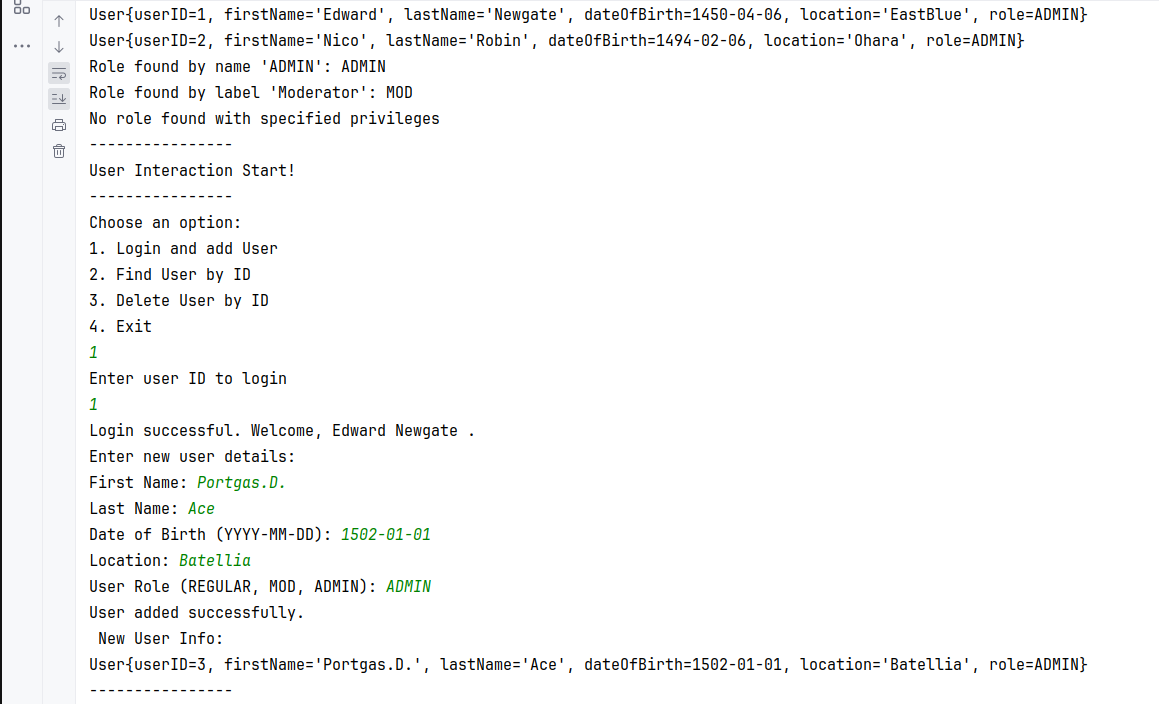
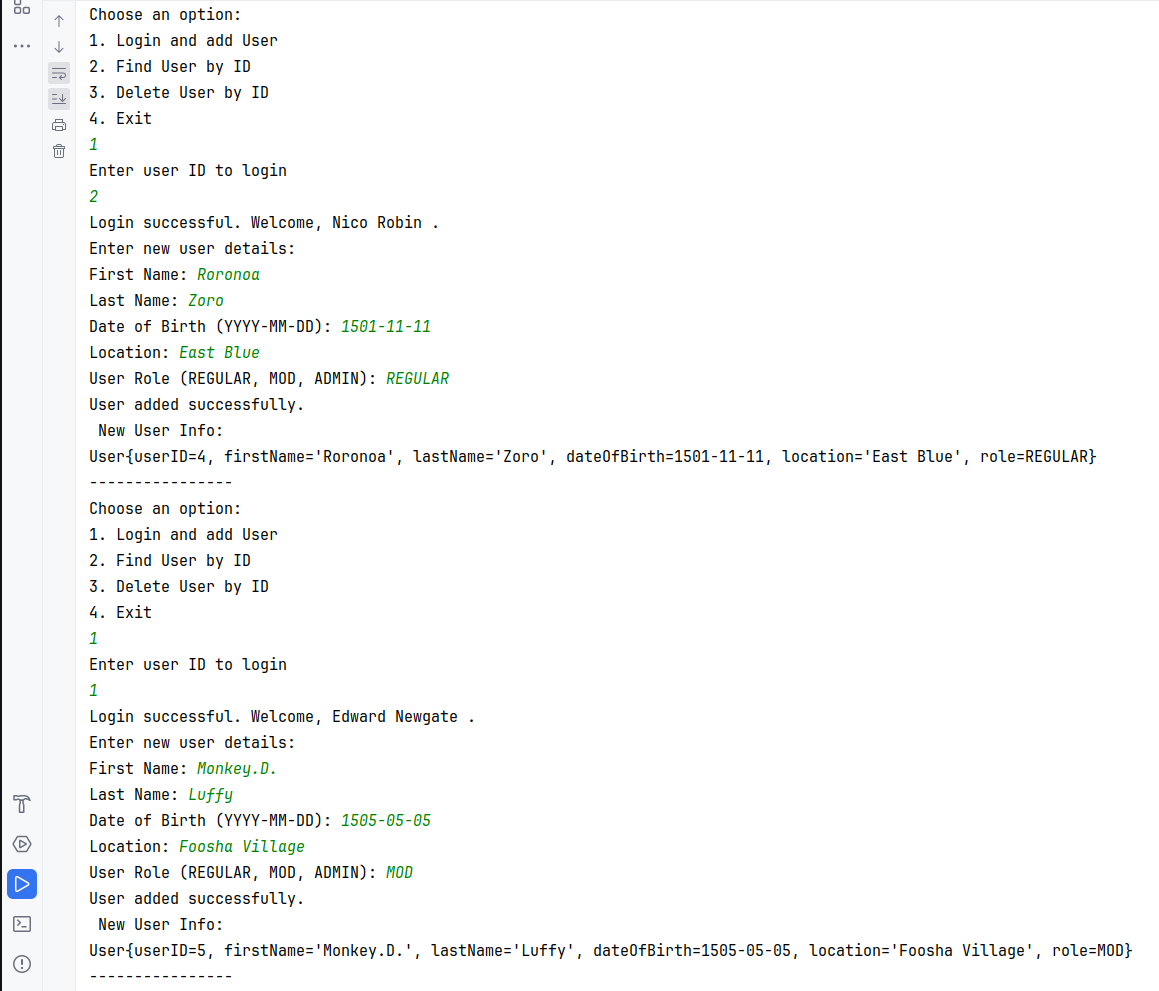
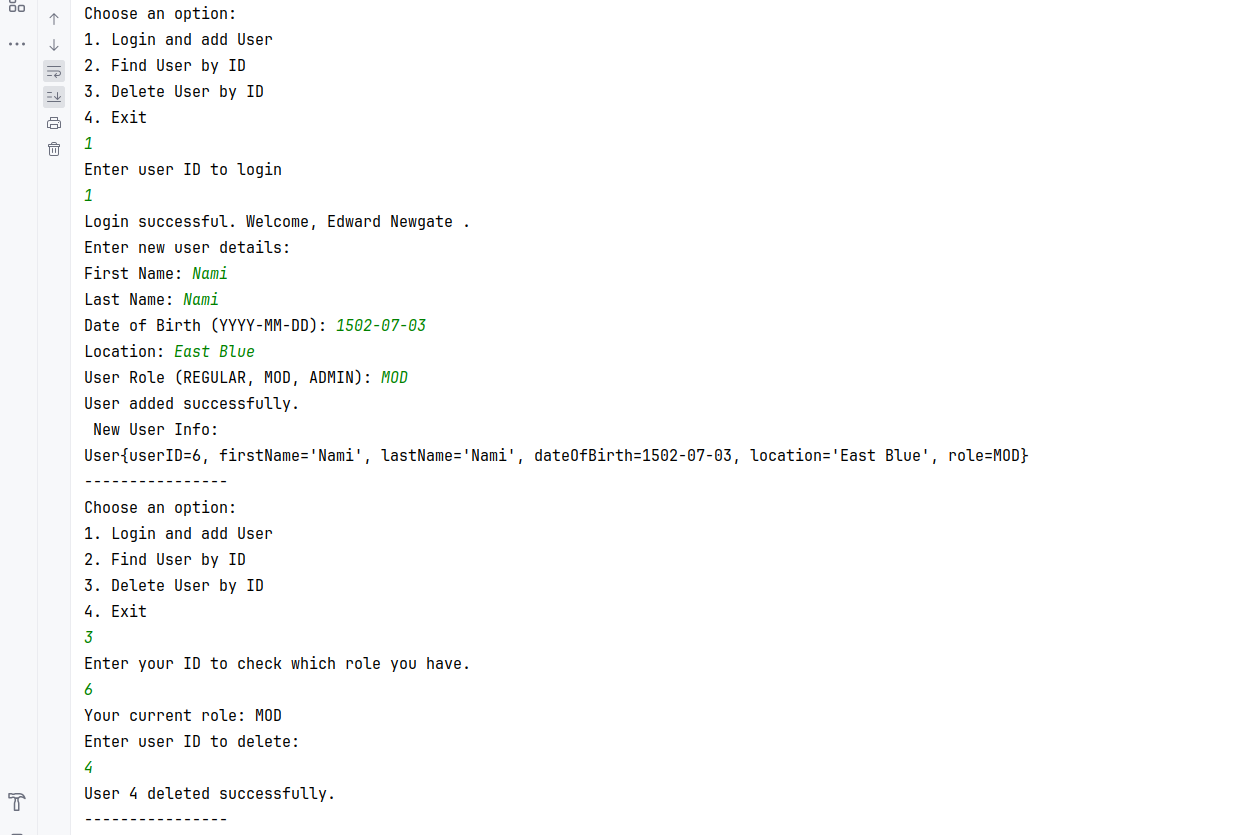
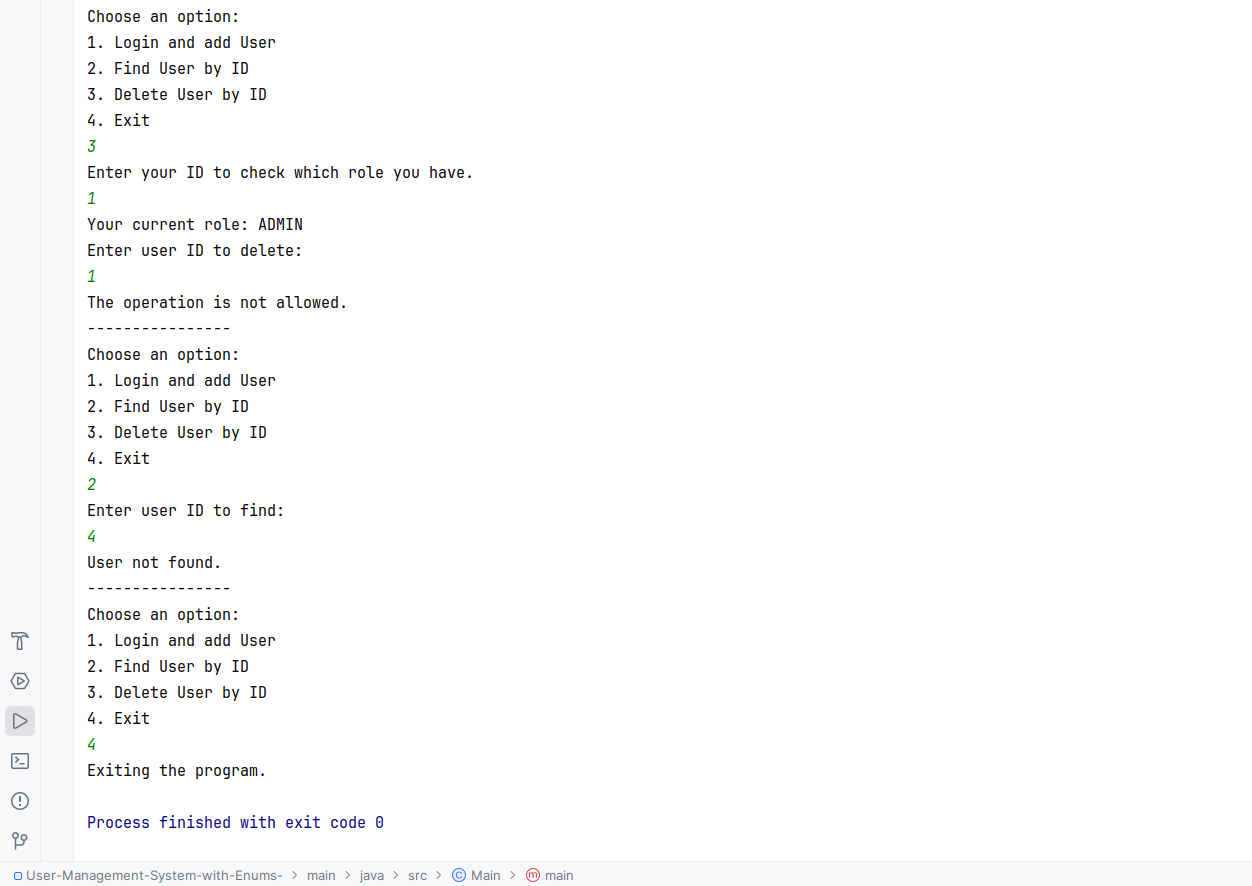
My assignment with Enum in Java online course from (https://github.com/sontyp/j23-e02/tree/main). The result photos at the end.
In this exercise which aims to get more familiar with Enums you will be creating a User Management System that allows
to hold user entries with their corresponding data as well as their system privileges for interacting with the system.
-
Define a class
Userwhich holds the following data:- ID: Integer
- firstname: String
- lastname: String
- dateOfBirth: Date
- location: String
NOTE: All those fields should be private so that they can't be accessed directly from outside the class.
-
Create a proper constructor that initializes the
Userentry. -
Define getter- and setter methods to access the data in the entries.
NOTE: The ID should be immutable!
-
Override the
toString()method, so it prints theUserentry with all its information in a nicely readable way. -
Create a few sample
Userentries in the staticmain(String[] args)method of theorg.example.Mainclass and print them to test your implementation.
If we want to give users the ability to actively interact with the system, we need to think of security, so system privileges and a user role system become a crucial part of our application.
-
Create an
enumUserRolewith the following constants and corresponding values:- REGULAR
- label: String (
"Regular user") - read: boolean (
true) - writeSelf: boolean (
true) - writeOthers: boolean (
false)
- label: String (
- MOD
- label: String (
"Moderator") - read: boolean (
true) - writeSelf: boolean (
true) - writeOthers: boolean (
true)
- label: String (
- ADMIN
- label: String (
"Administrator") - read: boolean (
true) - writeSelf: boolean (
true) - writeOthers: boolean (
true)
- label: String (
NOTE: The MOD and the ADMIN user roles have the same privileges as it seems, but we're going to implement a hierarchy later on so that they will actually differ.
- REGULAR
-
Go back to the
Userclass and add a fieldroleof typeUserRole. -
Extend your seeding part of sample
Userentries in theMainclass so that it takes the new field into account and test it properly. -
Extend the
UserRoleenumwith the following static methods:findRoleByName(String name)it takes a role name (REGULAR, MOD, ADMIN) and returns the correspondingUserRoleentry.findRoleByLabel(String label)it takes a role label (Regular user, Moderator, Administrator) and returns the correspondingUserRoleentry.findRolesByPrivileges(boolean read, boolean writeSelf, boolean writeOthers)it takes booleans for all the different privileges and returns a list of allUserRoleentries that match all of these privileges ->findRolesByPrivileges(true, true, true)returns a list of{MOD, ADMIN}.
NOTE: Create a proper exception handling in case a role couldn't be found!
In order to store users in a structured way you're going to create a UserTable class,
where User entries are stored as a Map in value with their ID as the key in a field users: Map<Integer, User>.
The
usersfield must be private and will only be accessible through certain methods of the new class.
Add the following management methods:
findUserById(Integer currentUserId, Integer targetUserId)addUser(Integer currentUserId, User newUser)- only admins should be able to do sodeleteUserById(Integer currentUserId, Integer targetUserId)- mods can only delete regulars, admins can also delete mods, but not other admins
Find a way to make sure how to edit User entries with respect to the privileges.
UserTable.findUserById(Integer currentUserId, Integer targetUserId) creates a vulnerability since it provides direct access to the setters of an entry.
Find a way to prevent that.
- After adding 'Delete User By Id' option