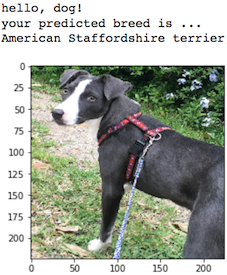
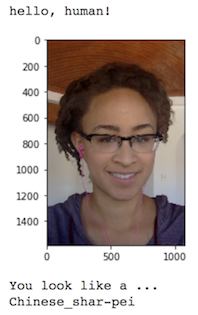
This is the second project of the Udacity Deep Learning Nanodegree. In this project, I built a pipeline that can be used within a web or mobile app to process real-world, user-supplied images. Given an image of a dog, my algorithm will try to identify the closet dog breed. If supplied an image of a human, the code will identify the resembling dog breed.
Model training in this project uses two publicly available datasets of dog and human images. The dog image dataset contains images of 133 breeds of dogs, which have been organized into subfolders. The human image dataset contains more than 13,000 images of faces collected from the web. These datasets are availble for download via AWS and UMass Amherst "Labeled Faces in the Wild," respectively. Links are listed below in the run instructions section (follow steps #2 and #3).
- The first part of the project is to create a detector which tries to identify whether the input image is that of a dog or a human. The human face detector utilizes OpenCV's Haar feature-based cascade classifiers. The dog detector utilizes a pre-trained VGG-16 model. The combined human/dog detector tested for about 97-99% accuracy.
-
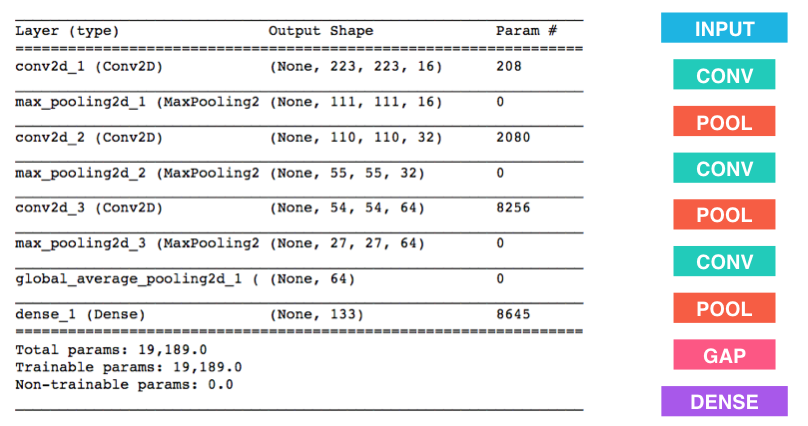
I constructed two models to classify dog images, one from scratch and the other using a pretrained ResNet. The model that I built from scratch uses convolutional neural networks (CNN) and was able to achieve ~21% accuracy on the testing set after about 60 epochs of training. More specifically, the model uses 4 convolutional and maxpooling layers, followed by 2 dropout layers and fully-connected layers (a ReLU activation function is applied after the first fully-connected layer). In addition, it uses cross entropy loss and an SGD optimizer. My transfer learning model uses ResNet, with the last fully connected redesigned to for the appropriate type of classification. The model was then fine-tuned with 100 epochs of training, achieving a testing accuracy of 69% after training.
-
The actual algorithm accepts an image as inputs, tries to detect whether a human/dog face is present in the input image, and either identifies or finds a most similar dog breed accordingly.
-
Clone the repository and navigate to the downloaded folder.
git clone https://github.com/chloeh13q/DLND-Dog-Classification cd DLND-Dog-Classification -
Download the dog dataset. Unzip the folder and place it in the repo, at location
path/to/dog-project/dogImages. ThedogImages/folder should contain 133 folders, each corresponding to a different dog breed. -
Download the human dataset. Unzip the folder and place it in the repo, at location
path/to/dog-project/lfw.
If you are using a Windows machine, you can use 7zip to extract the folder. -
Make sure you have already installed the necessary Python packages.
-
Open a terminal window and navigate to the project folder. Open the notebook and follow the instructions.
jupyter notebook dog_app.ipynb