Replicated Helm Starter
Example project showcasing how power users can leverage the Replicated CLI Tools to manage a helm chart that can be delivered via Replciated.
This helm version of https://github.com/replicatedhq/replciated-starter-kots adds replicated manifests directly in a helm chart's working directory. To release:
helm package . -d manifests/
replicated release create --auto -y
If you already have a helm chart, you should be aware of Importing an Existing Chart before you start setup.
Get started
Copy and Clone
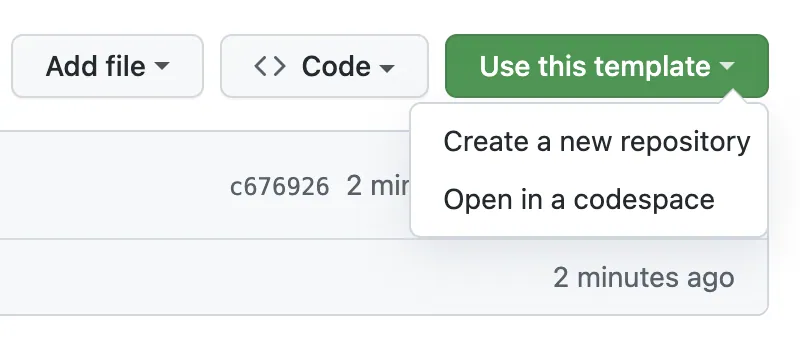
This repo is a GitHub Template Repository. You can create a private copy by using the "Use this Template" link in the repo:
You should use the template to create a new private repo in your org, for example mycompany/replicated-helm or mycompany/replicated-starter-helm.
Once you've created a repository from the template, you'll want to git clone your new repo and cd into it locally.
1. Install CLI
To start, you'll want to install the replicated CLI.
You can install with homebrew or grab the latest Linux or macOS version from the replicatedhq/replicated releases page.
Brew
brew install replicatedhq/replicated/cliManual
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/replicatedhq/replicated/releases/latest \
| grep "browser_download_url.*$(uname | tr '[:upper:]' '[:lower:]')_amd64.tar.gz" \
| cut -d : -f 2,3 \
| tr -d \" \
| cat <( echo -n "url") - \
| curl -fsSL -K- \
| tar xvz replicatedThen move ./replicated to somewhere in your PATH:
mv replicated /usr/local/bin/Verifying
You can verify it's installed with replicated version:
$ replicated version
{
"version": "0.31.0",
"git": "c67210a",
"buildTime": "2020-09-03T18:31:11Z",
"go": {
"version": "go1.14.7",
"compiler": "gc",
"os": "darwin",
"arch": "amd64"
}
}Configure environment
You'll need to set up two environment variables to interact with vendor.replicated.com:
export REPLICATED_APP=...
export REPLICATED_API_TOKEN=...
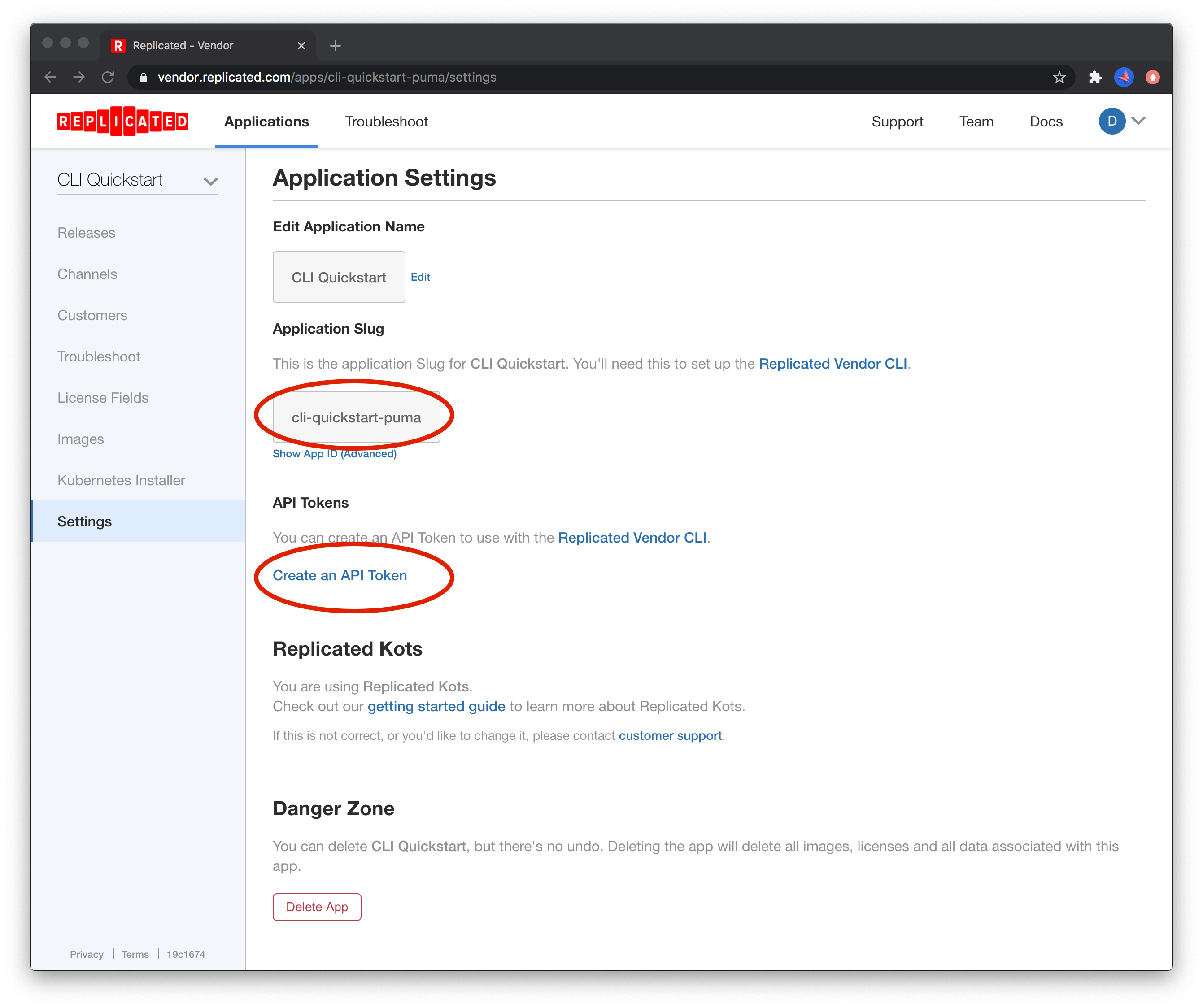
REPLICATED_APP should be set to the app slug from the Settings page:
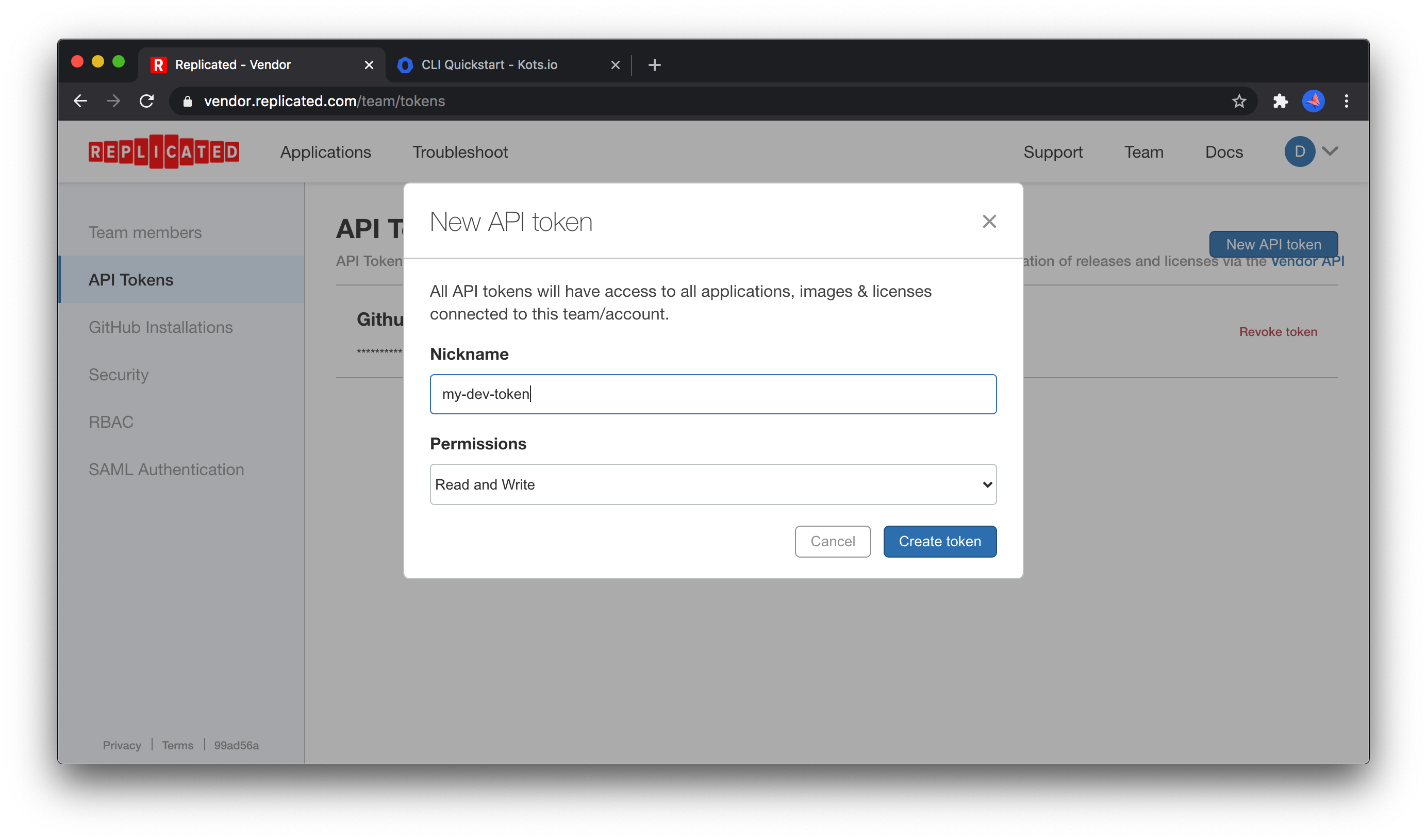
Next, create a Service Account API token from the vendor portal under Service Accounts:
Ensure the token has the appropriate "Write" access in the selected RBAC policy or you'll be unable create new releases. Once you have the values, set them in your environment.
export REPLICATED_APP=...
export REPLICATED_API_TOKEN=...
You can ensure this is working with
replicated release ls
Iterating on your release
Once you've made changes to your manifests, lint them with
replicated release lint --yaml-dir=manifests
You can push a new release to a channel with
replicated release create --auto
By default the Unstable channel will be used. You can override this with the --promote flag:
replicated release create --auto --promote=Beta
Already Have a Helm Chart?
This is meant as a hello-world style starter where you'll just modify the templates/values/etc in this repo directly to develop your app, however you may already have a helm chart you want to use.
In this case you have a few options:
- Grab the replicated-specific files from this repo and add them to your helm chart (
manifests/,.github/workflows/main.yml,kurl-installer.yml, merge in.helmignore) - Remove the templates and values from this chart, and just use this repo as an umbrella chart that includes your main chart as a helm
dependencyinChart.yaml(runhelm dependency updatebeforehelm package . -d manifests/) - Remove all helm manifests from this repo, and configure a pipeline to manually new chart versions as
.tgzarchives intomanifests/and then usereplicated release createfrom there.
Integrating with CI
This repo contains a GitHub Actions workflow for ci at ./.github/workflows/main.yml. You'll need to configure secrets for REPLICATED_APP and REPLICATED_API_TOKEN. On every push this will:
- Ensure a channel exists for the branch that was pushed to
- Create a release based on the contents of
./manifests
Advanced Usage
Integrating kurl installer yaml
There is a file kurl-installer.yaml that can be used to manage kurl.sh installer versions for an embedded Kubernetes cluster. This will be automatically released in CI. You can create a release manually with
replicated installer create --auto
Tools reference
License
MIT