Ingress Operator is an OpenShift component which enables external access to cluster services by configuring Ingress Controllers, which route traffic as specified by OpenShift Route and Kubernetes Ingress resources.
To provide this functionality, Ingress Operator deploys and manages an OpenShift router — a HAProxy-based Kubernetes ingress controller.
Ingress Operator implements the OpenShift ingresscontroller API.
Ingress Operator is a core feature of OpenShift and is enabled out of the box.
Every new OpenShift installation
has an ingresscontroller named default which can be customized,
replaced, or supplemented with additional ingress controllers. To view the
default ingress controller, use the oc command:
$ oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/defaultCreate and edit ingresscontroller.operator.openshift.io resources to manage
ingress controllers.
Interact with ingress controllers using the oc command. Every ingress
controller lives in the openshift-ingress-operator namespace.
To scale an ingress controller:
$ oc scale \
--namespace=openshift-ingress-operator \
--replicas=1 \
ingresscontroller/<name>
$ oc patch \
--namespace=openshift-ingress-operator \
--patch='{"spec": {"replicas": 2}}' \
--type=merge \
ingresscontroller/<name>Note: Using oc scale on an ingresscontroller where .spec.replicas is unset will currently return an error (Kubernetes #75210).
Create new ingresscontroller resources in the openshift-ingress-operator
namespace.
To edit an existing ingress controller:
$ oc edit --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/<name>Important: Updating an ingress controller may lead to disruption for public facing network connections as a new ingress controller revision may be rolled out.
Refer to the ingresscontroller API for full details on defaults and customizing an ingress controller. The most important initial customizations are domain and endpoint publishing strategy, as they cannot currently be changed after the ingress controller is created.
The .spec.endpointPublishingStrategy field is used to publish the ingress
controller endpoints to other networks, enable load balancer integrations, etc.
Every strategy is described in detail in the ingresscontroller API. A brief design diagram for each is shown below.
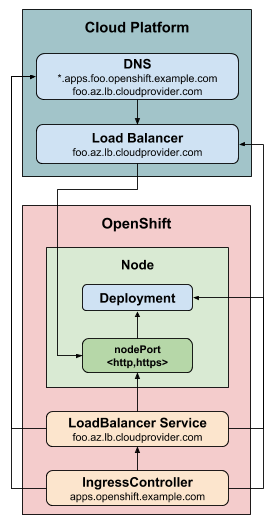
The LoadBalancerService strategy publishes an ingress controller using a
Kubernetes LoadBalancer
Service
and on some platforms offers managed wildcard DNS.
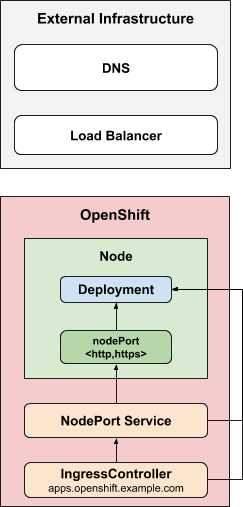
The NodePortService strategy publishes an ingress controller using a
Kubernetes NodePort
Service.
With this strategy, the administrator is responsible for configuring
any external DNS or load balancer.
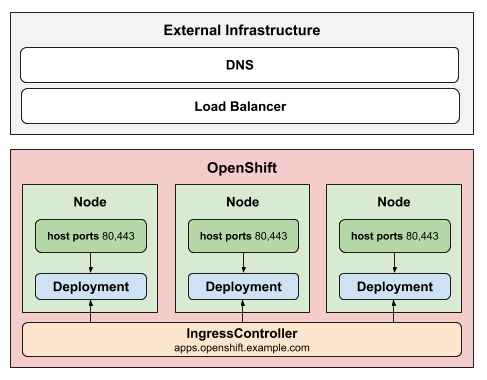
The HostNetwork strategy uses host networking to publish the ingress
controller directly on the node host where the ingress controller is deployed.
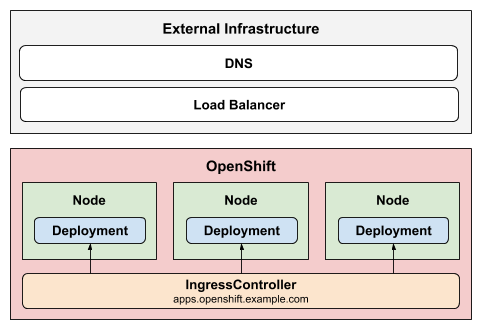
The Private strategy does not publish the ingress controller.
Use the oc command to troubleshoot operator issues.
To inspect the operator's status:
$ oc describe clusteroperators/ingressTo view the operator's logs:
$ oc logs --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator deployments/ingress-operatorTo inspect the status of a particular ingress controller:
$ oc describe --namespace=openshift-ingress-operator ingresscontroller/<name>Report issues in the Red Hat Issue Tracker.
See HACKING.md for development topics.