Screenshot Bot is a Discord bot designed to fetch and display Steam screenshots directly within Discord channels. The bot leverages Selenium to scrape Steam profiles and extract screenshot data, making it easier for users to share their gaming moments with their friends.
Now knows the game title of each screenshot!
- Register and save your Steam ID or custom URL.
- Fetch and display the latest Steam screenshots.
- Fetch multiple screenshots at once, with a limit of 10, ordered from oldest to newest.
- Support for multiple users.
- Persistent storage of user data using pickle.
Use the /register command to register your Steam ID or custom URL:
/register [steamID64 or custom_url]
steamID64: You can look up your Steam ID at steamid.io.custom_url: Set a custom URL in your Steam profile settings.
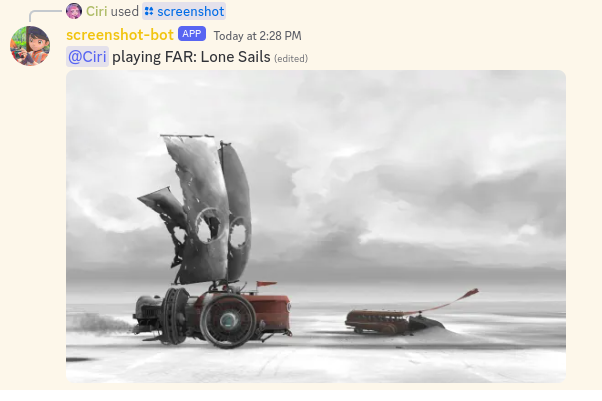
Use the /screenshot command to fetch and display your latest Steam screenshots:
/screenshot
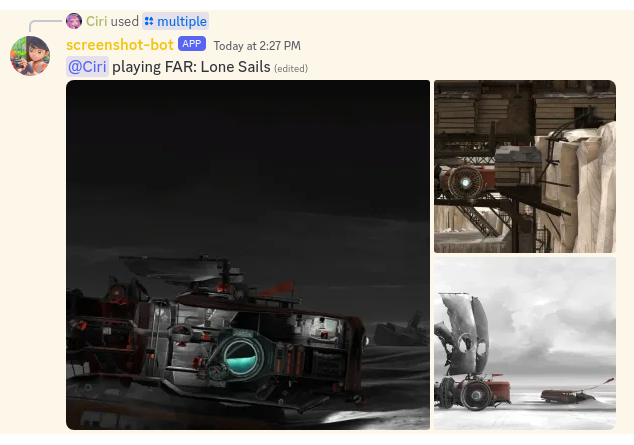
Use the /multiple command to fetch multiple screenshots at once:
/multiple [number]
- Replace
[number]with the number of screenshots you want to fetch (maximum 10). - Screenshots are fetched in order from oldest to newest.
Use the /test command to fetch screenshots for any Steam ID without registration:
/test [steamID64 or custom_url]
Use the /help command to get a list of available commands and usage instructions:
/help
- Python 3.7+
- Discord.py
- Selenium
- BeautifulSoup
- aiohttp
- Requests
- Firefox and Geckodriver
- discord.py
- beautifulsoup4
- selenium
- requests
-
Install Dependencies
Use
pipto install the necessary Python libraries:pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Install Firefox and Geckodriver
Ensure you have Firefox installed on your system along with Geckodriver. You can download Geckodriver from here.
-
Configuration
Create a
config-steam.jsonfile in the root directory of the project with the following structure:{ "guild_id": "YOUR_GUILD_ID", "discord_token": "YOUR_DISCORD_BOT_TOKEN", "users": [] } -
Run the Bot
Execute the bot script:
python screenshot_bot.py
The bot_client class is a custom Discord client that initializes with all necessary intents and synchronizes commands with the Discord server.
The FirefoxWebDriverSingleton class ensures a single instance of Firefox WebDriver is used across the application. It includes methods to manage the browser lifecycle and clean up temporary files.
get_steam_url(username): Generates the Steam URL for the provided username or Steam ID.get_steam_uploads(username, count=1): Scrapes the Steam profile page to get the latest screenshots, with support for fetching multiple screenshots.
The bot uses pickle to save and load the state, which includes registered Steam IDs for users.
- Ensure the
datadirectory exists for storing the state file (state.pickle). - The bot will handle and report exceptions gracefully, providing error messages in Discord where necessary.
Feel free to fork this repository and submit pull requests. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
Happy gaming and sharing your screenshots with Screenshot Bot!