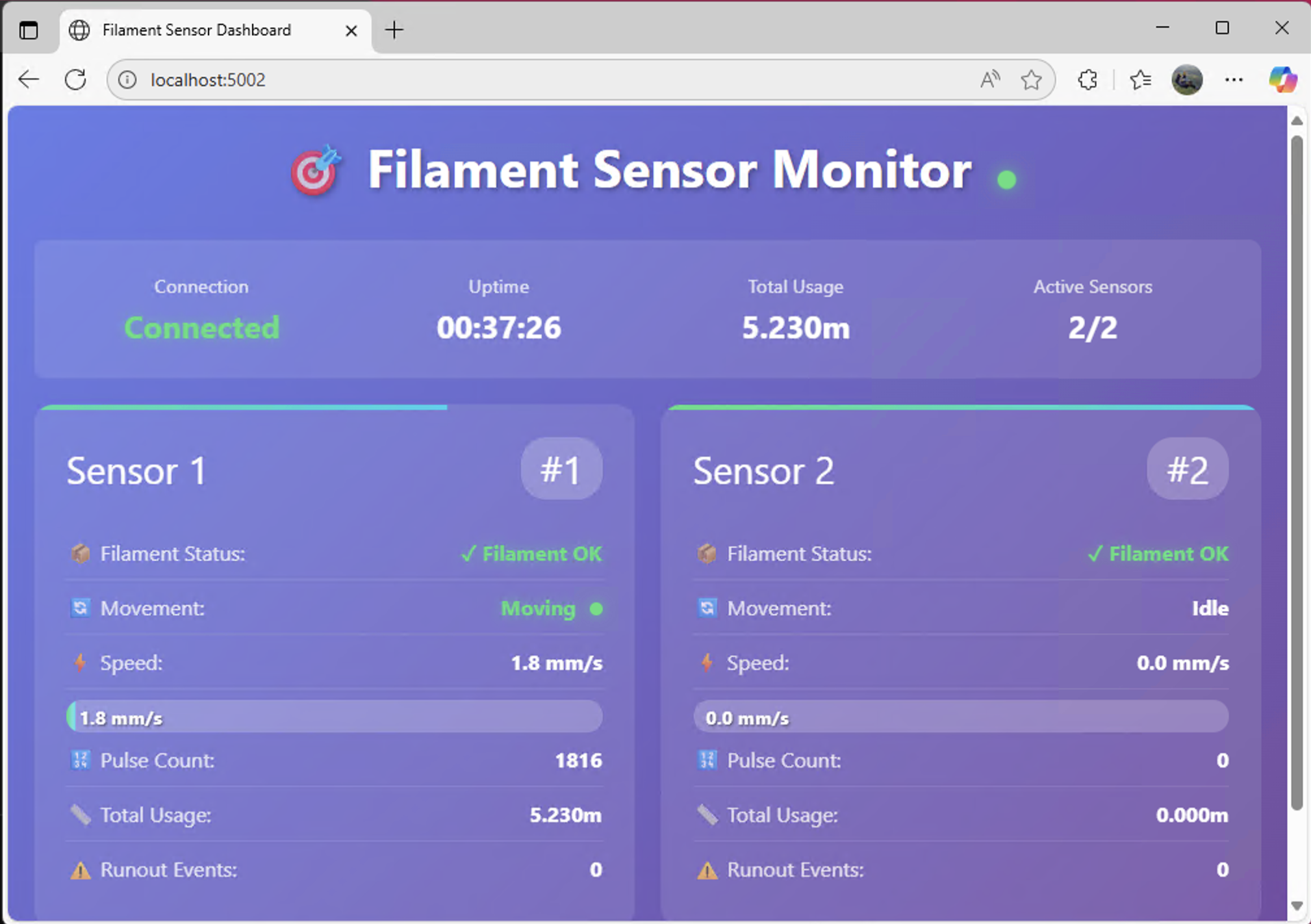
Real-time monitoring system for dual BIGTREETECH Smart Filament Sensors using MCP2221A USB-GPIO adapter.
- 🎯 Dual Sensor Monitoring - Track two filament sensors simultaneously
- 📊 Real-time Display - Terminal UI with split-screen visualization
- 🌐 HTTP API - JSON API on port 5002 for remote monitoring
- 📈 Usage Tracking - Calculate filament consumption (2.88mm per pulse)
- ⚡ WebSocket Support - Real-time updates for web clients
- 🔧 Configurable - YAML configuration with hot-reload
- 💾 Session Storage - SQLite for session-only metrics
Connect your sensors to the MCP2221A:
| MCP2221A Pin | Connection |
|---|---|
| GP0 | Sensor 1 Movement Signal |
| GP1 | Sensor 1 Runout Signal |
| GP2 | Sensor 2 Movement Signal |
| GP3 | Sensor 2 Runout Signal |
| VCC (3.3V) | Both sensors power (+) |
| GND | Both sensors ground (-) |
- Install Python 3.11+ from python.org
- Connect MCP2221A via USB
- Run the quick test:
run_test.bat- Install full application:
pip install -r requirements.txt
python main.py# Clone repository
git clone [repository-url]
cd runout
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
source venv/bin/activate # Linux/Mac
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Test hardware connection
python test_hardware.py
# Run application
python main.py# Simple hardware test (no dependencies)
python test_hardware.py
# Test MCP2221A connection only
python -m src.lib.mcp2221_sensor --test-connection
# Monitor GPIO pins in real-time
python -m src.lib.mcp2221_sensor monitor# Run with simulated data
python main.py --demo
# API server with demo data
python -m src.lib.api_server --demo
# Terminal UI with demo data
python -m src.lib.display --demoEdit config.yaml:
sensors:
sensor_1:
movement_pin: 0 # GPIO pin for movement
runout_pin: 1 # GPIO pin for runout
calibration_mm_per_pulse: 2.88
enabled: true
sensor_2:
movement_pin: 2
runout_pin: 3
calibration_mm_per_pulse: 2.88
enabled: true
polling:
interval_ms: 100 # Sensor polling rate
debounce_ms: 2 # Debounce for noise
timeout_seconds: 5 # Movement timeout
api:
port: 5002
host: "0.0.0.0"GET /status- Current sensor status and filament presenceGET /config- System configurationPOST /config- Update configurationGET /metrics- Session metrics and usageGET /alerts- Active alertsWebSocket /ws- Real-time updates
Access API documentation at: http://localhost:5002/docs
# Main application
python main.py [options]
--config FILE Configuration file (default: config.yaml)
--debug Enable debug logging
--demo Run in demo mode (no hardware)
--no-api Disable API server
--no-display Disable terminal UI
--export-config Export current configuration
# Individual components
python -m src.lib.mcp2221_sensor [test-connection|monitor|info]
python -m src.lib.display [--demo] [--layout split|compact|debug]
python -m src.lib.api_server [--port PORT] [--demo]
python -m src.lib.config [validate|export|create] [FILE]qorCtrl+C- Quit applicationr- Reset session metrics1- Toggle Sensor 12- Toggle Sensor 2a- Acknowledge alertsd- Toggle debug displayTab- Switch layout
- Check Device Manager → Human Interface Devices → MCP2221 USB-I2C/UART Combo
- Try different USB port (avoid hubs initially)
- Install driver from Microchip
- Verify wiring connections
- Check sensor power (3.3V between VCC and GND)
- Run hardware test:
python test_hardware.py - Enable debug:
python main.py --debug
- Calibrate your sensor:
- Mark 100mm of filament
- Pull through sensor
- Count pulses in debug log
- Update
calibration_mm_per_pulse= 100 / pulse_count
- Run as Administrator if needed
- Check Windows Defender/Antivirus exceptions
- Ensure no other application is using the MCP2221A
runout/
├── src/
│ ├── models/ # Data models
│ ├── services/ # Core services
│ ├── cli/ # Main application
│ └── lib/ # Feature libraries
│ ├── mcp2221_sensor/ # Hardware interface
│ ├── display/ # Terminal UI
│ ├── api_server/ # HTTP/WebSocket API
│ └── config/ # Configuration management
├── tests/
│ ├── contract/ # API contract tests
│ ├── integration/ # Integration tests
│ └── unit/ # Unit tests
├── config.yaml # Configuration
├── requirements.txt # Dependencies
└── test_hardware.py # Hardware test script
# All tests
pytest
# Contract tests only
pytest tests/contract/ -m contract
# Integration tests
pytest tests/integration/ -m integration
# With coverage
pytest --cov=src --cov-report=html- Write failing test
- Implement minimal code to pass
- Refactor while keeping tests green
- Commit with descriptive message
- Sensor polling: 10ms hardware, 100ms configurable
- UI update latency: <10ms
- API response time: <5ms
- Memory usage: <50MB for 24-hour session
- CPU usage: <5% idle, <15% active
- Hardware: BIGTREETECH Sensor Docs
Built with:
- EasyMCP2221 - USB-GPIO interface
- FastAPI - API framework
- Textual - Terminal UI
- Pydantic - Data validation