Develop an AI-driven application using machine learning to predict the likelihood of heart disease in individuals based on certain parameters, while also establishing a digital chatbot that can consult on heart disease specific questions.
Heart diseases are the leading cause of death globally. AI can be helpful in predicting heart diseases and help in preventive measures and reduce healthcare costs significantly.
Medical Knowledge: This application is based on established clinical predictions of heart diseases. The factors are identified through a complex dataset, which originally comes from the CDC, who is a major part of the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, which conducts annual telephone surveys to collect data on the health status of individuals.
- Logistic Regression: chosen for its effectiveness in binary classification, perfect for predicting the probability of heart disease based on risk factors.
- Random Forest: utilized for its strength in handling complex datasets and its effectiveness of reducing overfitting through ensemble averaging of decision trees.
- Neural Networks: applied for its feed-forward algorithm, ideal for modeling complex, non-linear relationships in data, crucial for accurate medical diagnostics.
- The models performances is evaluated using k-fold cross validation to ensure robustness and minimize the overfitting.
The models performances is evaluated using k-fold cross validation to ensure robustness and minimize the overfitting.
- Logistic Regression & Random Forests Model: Helped us with clear probability predictions and insights into individual risk factors, aiding in early identification of heart disease.
- Neural Network Model: Assisted us in modeling intricate patterns in data for predictions, thus improving patient interaction and diagnostic accuracy.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enhanced user interaction and provided faster and accurate support for heart disease-related questions, aiding in better user engagement and information.
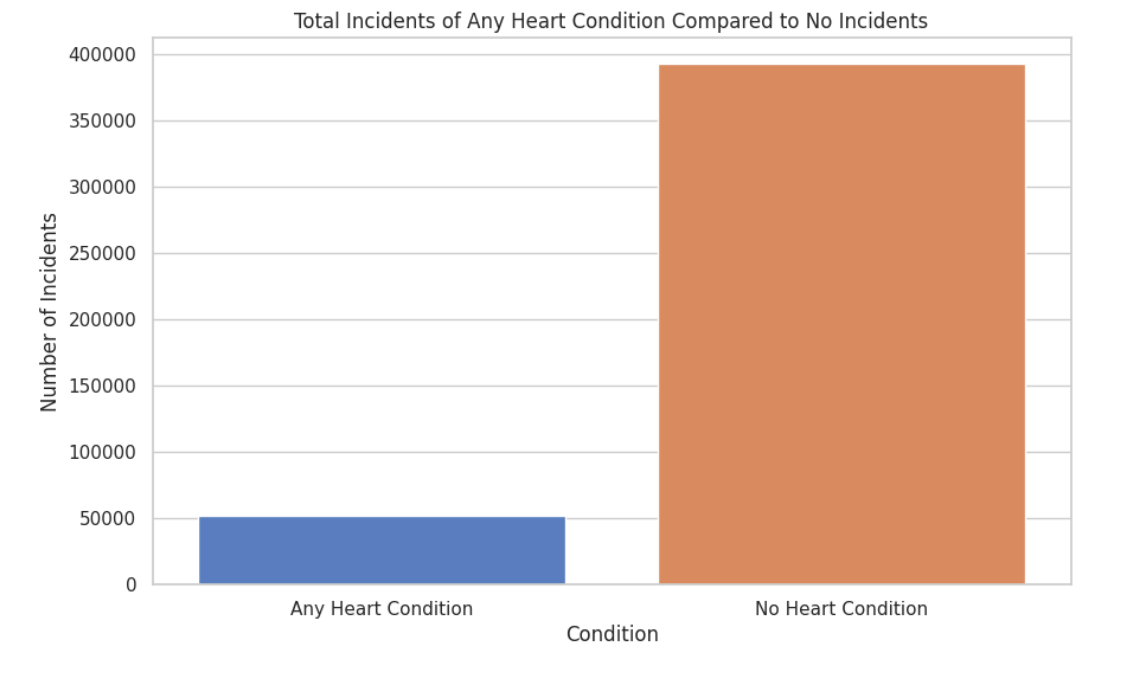
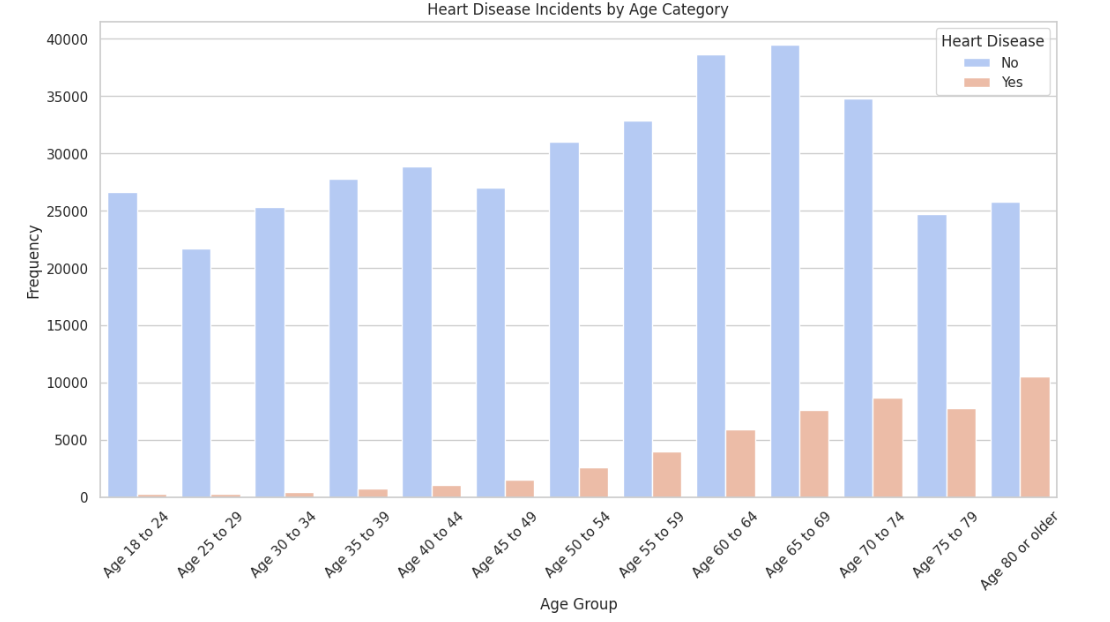
The dataset "Indicators of Heart Disease (2022 UPDATE)" has been selected for training the models because of its data quality and quantity. The dataset is also easily available and the fit to the problem domain further reinforced our choice. Notably, the dataset has a high Kaggle usability score of 9.41, indicating its suitability for machine learning tasks. Furthermore, with over 400,000 rows of data, the dataset offers great opportunities for robust and accurate model development.
- Dataset Link: Kaggle Dataset
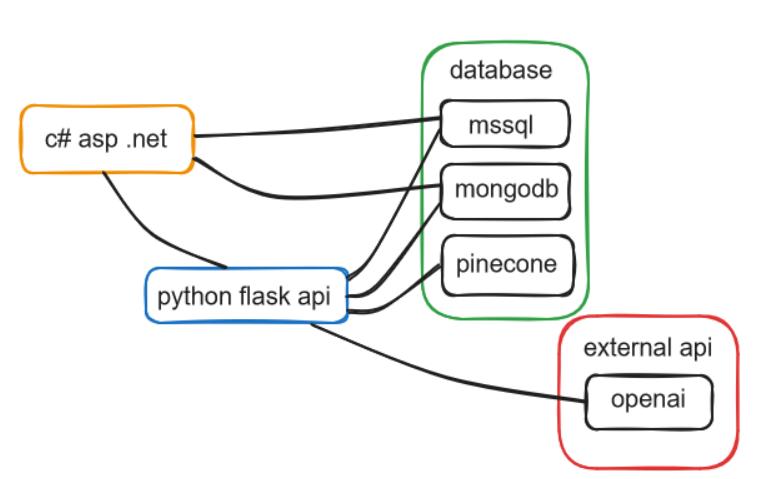
Below is a diagram illustrating the integration and workflow of our AI system as a whole:
Our machine learning and AI code is available in this GitHub repository:
- GitHub Link: GitHub Link The functionality has been integrated into a Flask API for seamless application use.
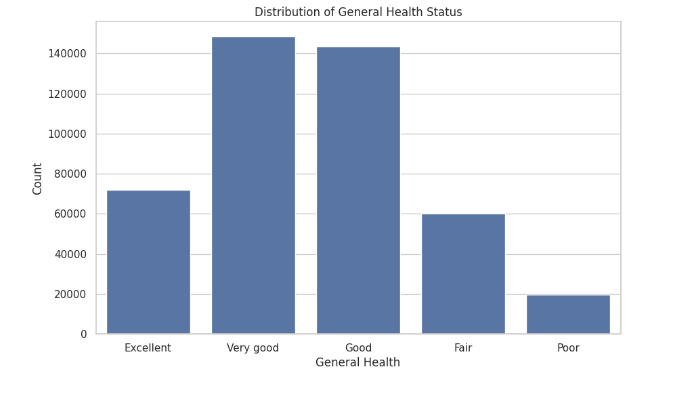
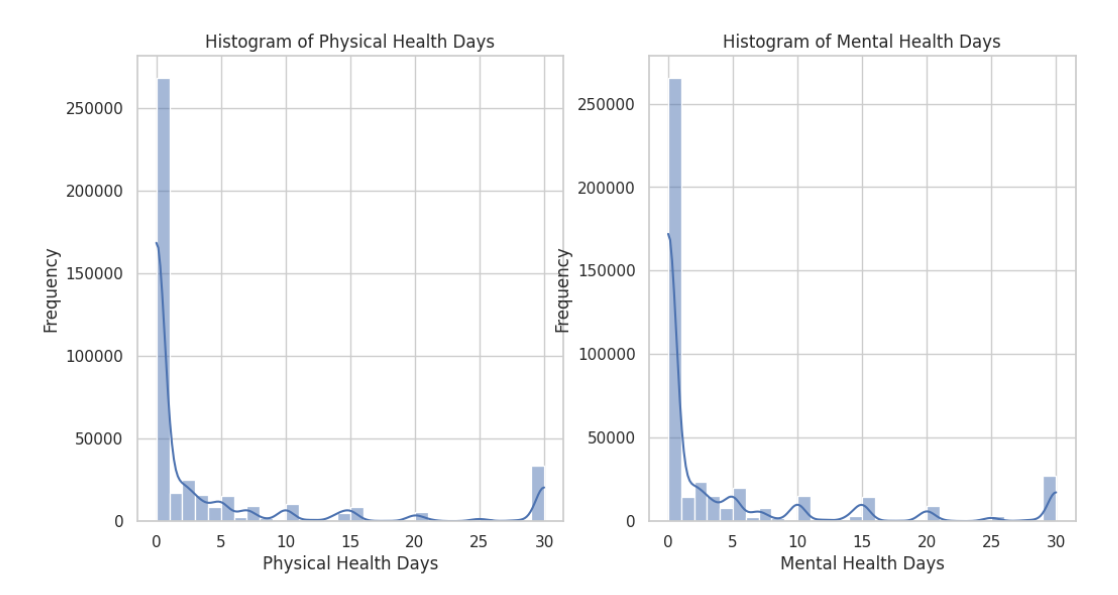
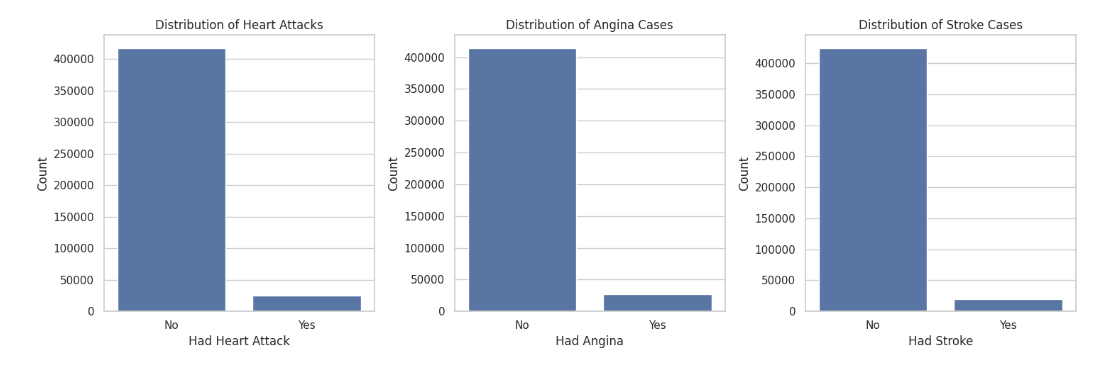
In the 'initial' folder, the data_removal.py script is where we began by loading our dataset and removing irrelevant columns. The 'datawrangling' folder includes data_exploration.py, which generates various charts and plots to explore the dataset, and data_cleaning.py, which cleans the data. For instance, we consolidated three categories—HadHeartAttack, HadAngina, HadStroke—into a single category, HadHeartDisease. Additionally, data_transformation.py converts our data into numerical format and feature scales attributes like "PhysicalHealthDays", "MentalHealthDays", "SleepHours", and "BMI".
The 'api' folder comprises several key scripts: pipeline.py, used for data transformation during model training, and load_data_from_mssql.py, which loads the latest dataset from our database. The app.py script runs our API and houses all our API endpoints. Additionally, the 'api' folder contains two subfolders: 'chatbot' and 'retrain'. The 'chatbot' folder includes code for chatbot functionality and training, while the 'retrain' folder contains scripts to retrain our three machine learning models.
We have also created notebooks for some of the first steps in the machine learning process.
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression (Without Resampling) | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| Logistic Regression (Stratified) | 0.89 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| Logistic Regression (Random Oversampling) | 0.72 | 0.26 | 0.77 | 0.39 |
| Logistic Regression (SMOTE) | 0.77 | 0.27 | 0.61 | 0.38 |
| Random Forest (Without Resampling) | 0.88 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| Random Forest (Stratified) | 0.89 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| Random Forest (Random Oversampling) | 0.88 | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.28 |
| Random Forest (SMOTE) | 0.86 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.26 |
| Neural Network Feed Forward (RO) | 0.75 | 0.28 | 0.75 | 0.41 |
- If you want to run the Machine Learning and AI project then you need to clone the repository: GitHub Link and then type this in the terminal to get the appropriate libraries: ‘pip install -r requirements.txt’.
- To run the API you need to be in the api folder and type ‘flask run’. If you want to run the project as a whole, then you will also need to clone our web application: GitHub Link and setup the Microsoft SQL database by using the bacpac file that can be found here: GitHub Link
- Since MongoDB and Pinecone are running in the cloud you need to add a .env file to both projects. In the Python project you need to add the following: OPENAI_API_KEY, PINECONE_API_KEY and MONGODB_URL. In the web application project you only have to add the MONGODB_URL. After following these steps the project is ready to run.