Conflicted is a Vim plugin that aids in resolving git merge and rebase conflicts. It relies on tpope's fugitive plugin to do the heavy lifting and provides a few wrapper commands and a streamlined workflow to make resolving conflicts much more straightforward.
The easist way to use Conflicted from git is to add an alias for it that opens vim with the conflicted plugin activated. You can add the alias with the following shell command:
git config --global alias.conflicted '!vim +Conflicted'From there, you can run conflicted directly from git with:
git conflictedWhich will open Vim and start up the plugin.
Or if you prefer to start Conflicted via git mergetool:
# Define a custom mergetool called `vim-conflicted` that runs `vim +Conflicted`
git config --global mergetool.vim-conflicted.cmd 'vim +Conflicted'
# Set the `vim-conflicted` mergetool to be used when `git mergetool` is executed
git config --global merge.tool 'vim-conflicted'Conflicted provides three primary commands for working with conflicts:
Conflicted
Conflicted will add all the conflicted files to Vim's arglist and open
the first in Merger mode.
GitNextConflict
After editing the merged file to resolve the conflict and remove all conflict
markers, running GitNextConflict will mark the file as resolved and open
the next file in Merger mode for resolution.
If you are on the last file, GitNextConflict will quit Vim.
Merger
Merger will open the various views of the conflicted file. This command is
exposed for completeness, but likely you will not need to call this command
directly as both Conflicted and GitNextConflict will call it for you.
Conflicted provides mappings to perform a diffget from the working version
of the file, pulling from either the upstream or local version. These mappings
are provided in both normal and visual mode:
dgu- diffget from the upstream versiondgl- diffget from the local version
If you would prefer different mappings, you can overide with the following in your vimrc:
" Use `gl` and `gu` rather than the default conflicted diffget mappings
let g:diffget_local_map = 'gl'
let g:diffget_upstream_map = 'gu'Conflicted will configure the tab label to display the name of the revision in
the tab. This is done via the tabline setting in terminal Vim, and the
guitablabel setting in graphical Vim, ie MacVim.
Add the following to your vimrc to display the version name of each split in the vim statusbar:
set stl+=%{ConflictedVersion()}Normally it will not add anything to the statusline, but if you are in conflicted mode then it will add the conflicted version, ie 'local', 'working', etc.
When Conflicted has finished setting up, it will call the user autocmd VimConflicted.
Usage example:
function! s:setupConflicted()
set stl+=%{ConflictedVersion()}
" Resolve and move to next conflicted file.
nnoremap ]m :GitNextConflict<cr>
endfunction
autocmd myVimrc User VimConflicted call s:setupConflicted()If you don't have a preferred installation method, I recommend using Vundle. Assuming you have Vundle installed and configured, the following steps will install the plugin:
Add the following line to your ~/.vimrc and then run BundleInstall from
within Vim:
" Fugitive is required for Conflicted
Bundle 'tpope/vim-fugitive'
Bundle 'christoomey/vim-conflicted'Conflicted makes reference to four different versions of each conflicted file. These versions are:
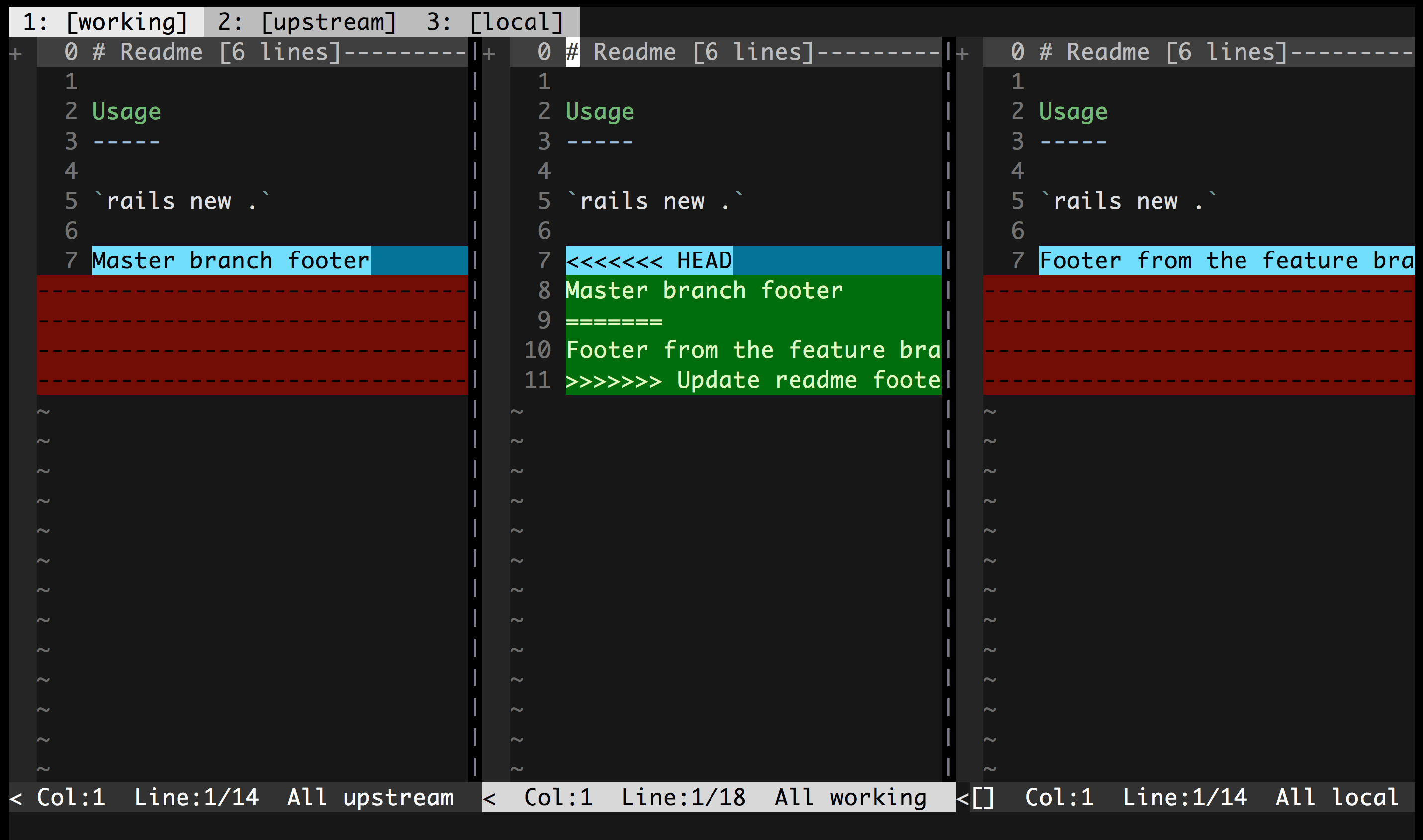
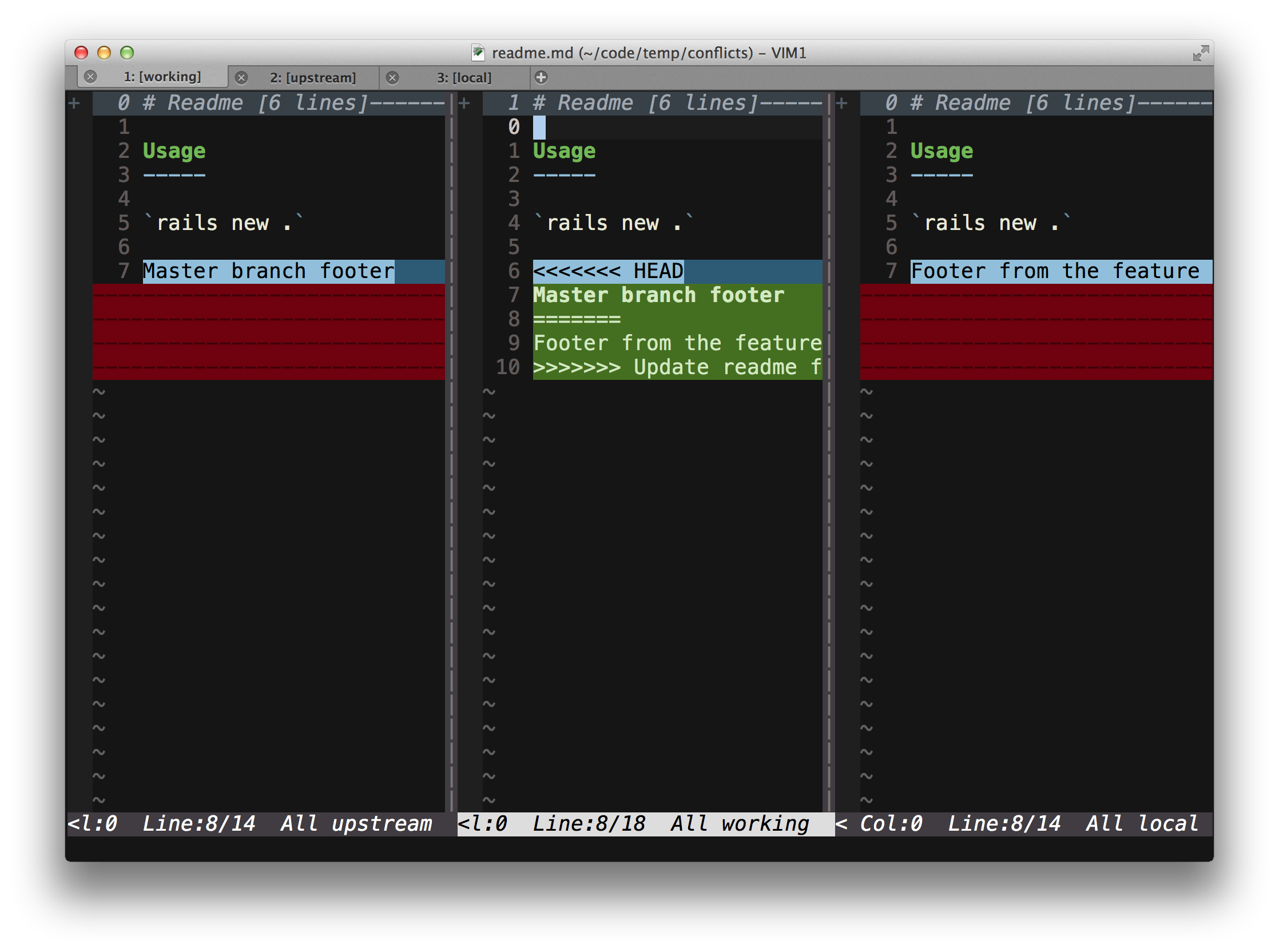
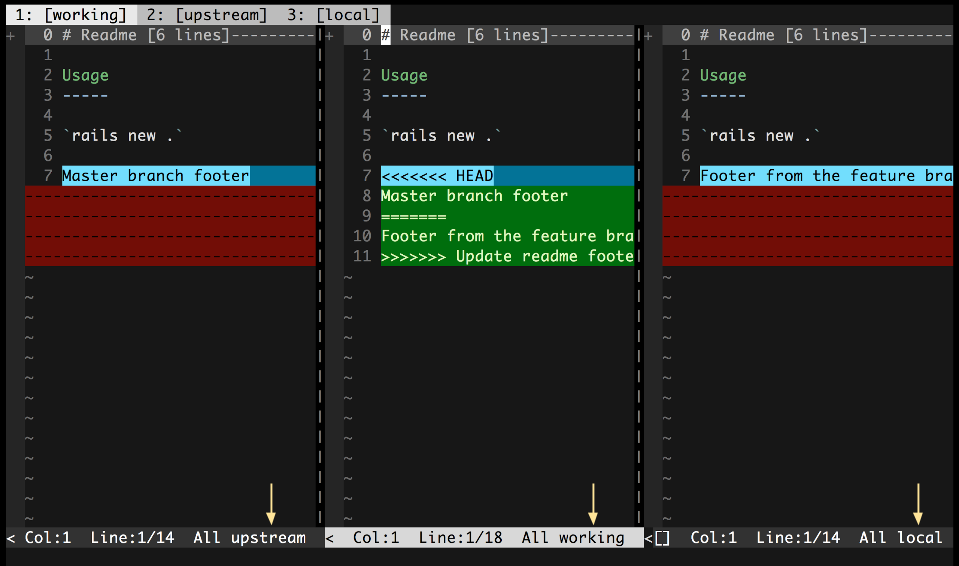
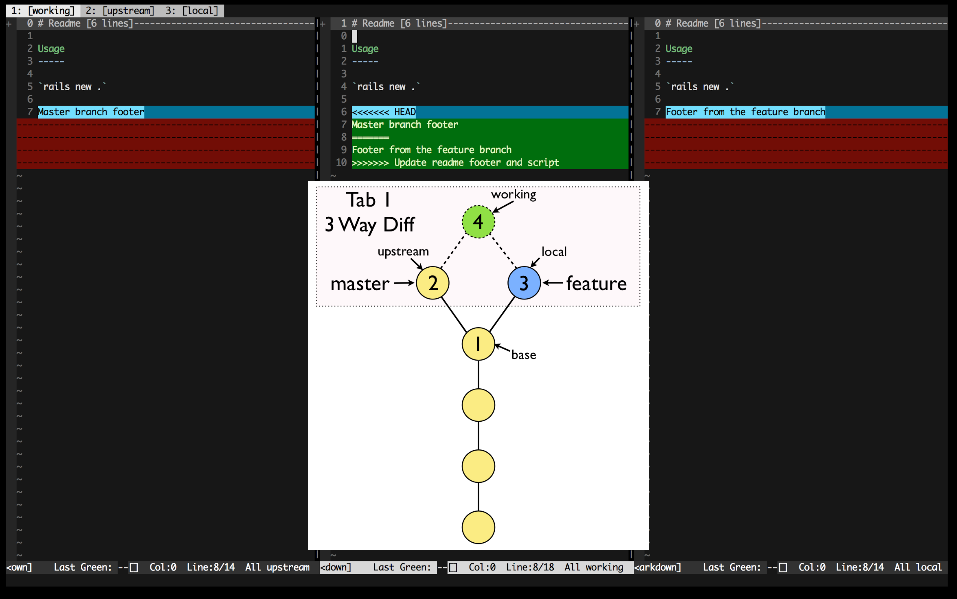
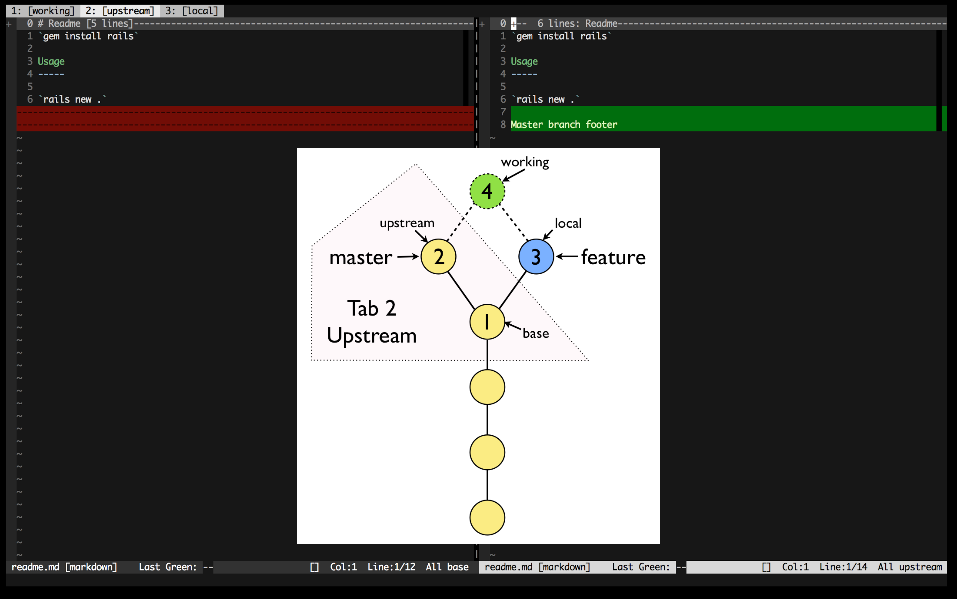
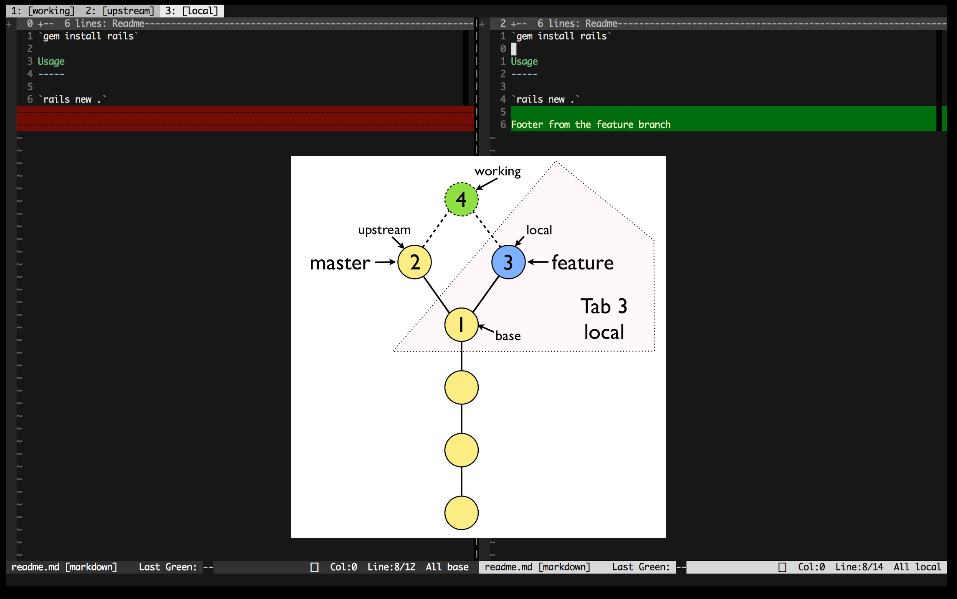
base- The common ancestor of the file in the upstream and local branchesupstream- The core branch (usuallymaster), that you are merging into or rebasing onto.local- The feature branch containing your changesworking- The final combined version of the file
For each conflicted file, Conflicted will open 3 tabs, each with a different diff view presented:
- Gdiffsplit! 3-way - 3 way diff comparing the upstream, working, and local versions of the file.
- Upstream Changes - A 2 way diff between the base and upstream versions of the file.
- Local Changes - A 2 way diff between the base and local versions of the file.