Python and bash scripts to calculate the persistence diagram of an embedded dataset in R^3. Calculate the optimal cycles in the specified dimension and return the indices of points which are vertices of the cycles.
It is necessary to install optiperslp, which can be found
here together with installation instructions.
To guide the installation of CGAL (a requirement) and its dependencies, there is a file
in the folder installation with a .sh file (cgal.sh) specifying packages and installation.
Modify to your use. There is also a .sh file (optiperslp.sh) to install OptiPersLP.
The python packages required are:
- numpy
- umap
The pipeline to use the algorithms is given in the figure below.
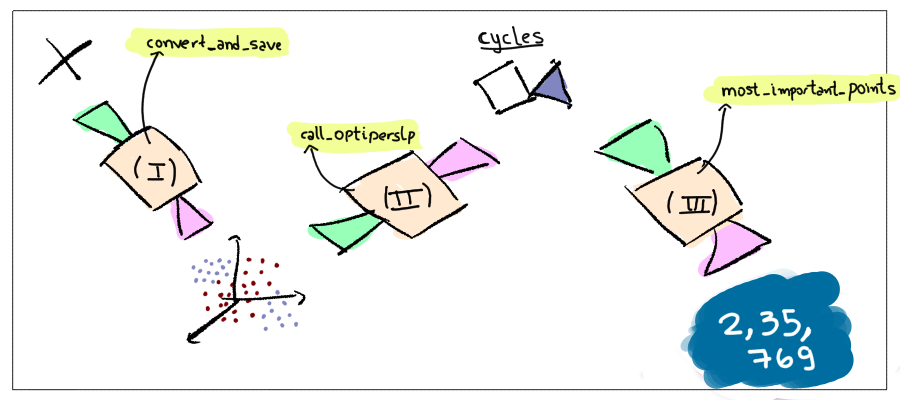
The function convert_and_save() takes 4 arguments:
dataset: Dataset to be embedded using UMAP
save_path: path where the embedded dataset together with radius will be saved
n_components (optional): embedding dimension to be used in UMAP. Default is 3.
dataset_name (optional): name of dataset to be used when saving. Default is None. If None
is used then the dataset is named 'embedded_dataset.txt' when saving
The function call_optiperslp() takes 4 arguments:
dimension_pd (optional): Dimension of persistence diagram to be calculated. Default is '1'
save_path (optional): path where the embedded dataset together with radius was saved
with convert_and_save. Default is '.'
dataset_name (optional): name of dataset used when saving. Default is None. If None is
used then the 'embedded_dataset.txt' is used.
output_path (optional): partial path to the outputs of optiperslp. Default is '.'. The
outputs will be saved in output_path + '/' + dataset_name. If dataset_name is None,
then the output is saved in output output_path + '/embedded_dataset'
The function most_important_points() takes 4 arguments:
embedded_dataset: the embedded dataset with a zero column in the end returned
by convert_and_save.
output_path: total path to the outputs of optiperslp.
dimension_pd (optional): same as in call_optiperslp. Default is '1'
dataset_name (optional): name of dataset used when saving. Default is None. If None is
used then 'embedded_dataset.txt' is used.
n_points (optinal):
import numpy as np
import nlpoptipers
# original dataset
dataset = np.random.rand(50,5)
# parameters to convert_and_save
save_path = '.'
dataset_name = 'example'
# embedding of the original dataset
embedded_dataset = nlpoptipers.convert_and_save(dataset, save_path,
dataset_name = dataset_name)
# call optiperslp to calculate the persistence diagrams and its optimal cycles
output_path = '.'
nlpoptipers.call_optiperslp(save_path = save_path, dataset_name = dataset_name,
output_path = '.')
# call most_important_points to return a list of lists of indices
output_path = os.path.join(output_path, dataset_name)
lists_of_indices = nlpoptipers.most_important_points(embedded_dataset, output_path)If you want, all the steps can be used in only one function, called run_nlpoptipers. Its
arguments and default values are: dataset, save_path='.', output_path='.', dimension_pd = '1', dataset_name = None, n_points = 5, n_components = 3. output_path here is the same as
in call_optiperslp. This function returns the indices and the embedded dataset