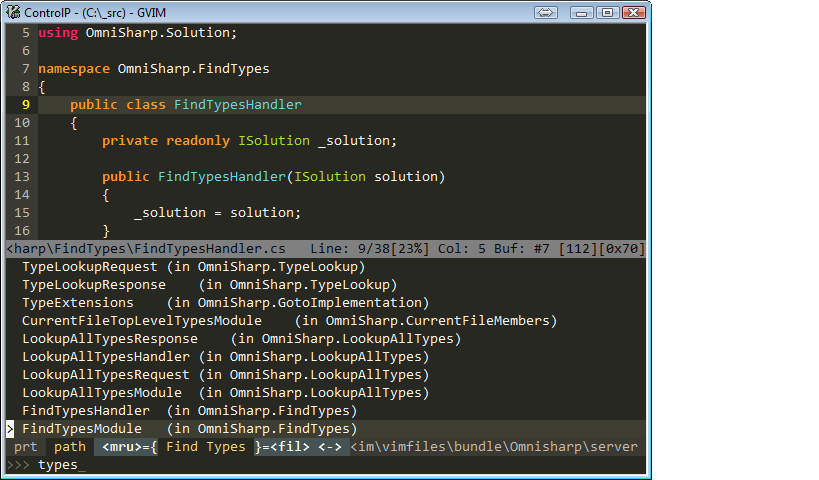
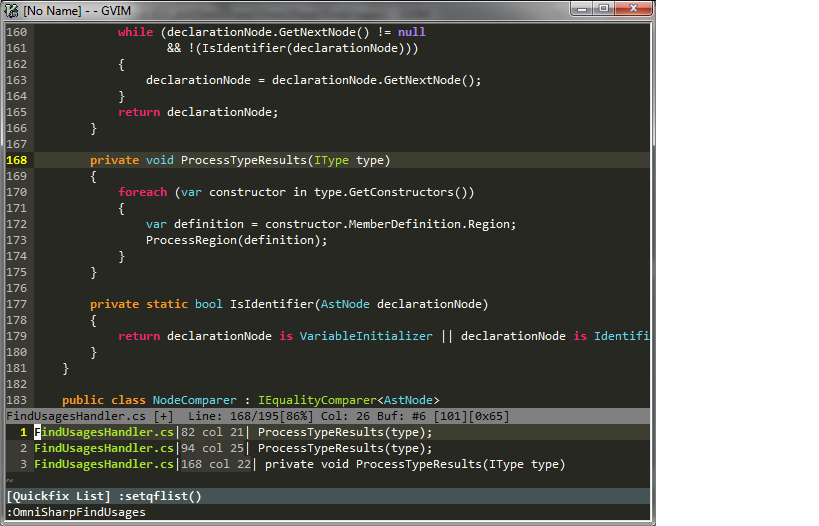
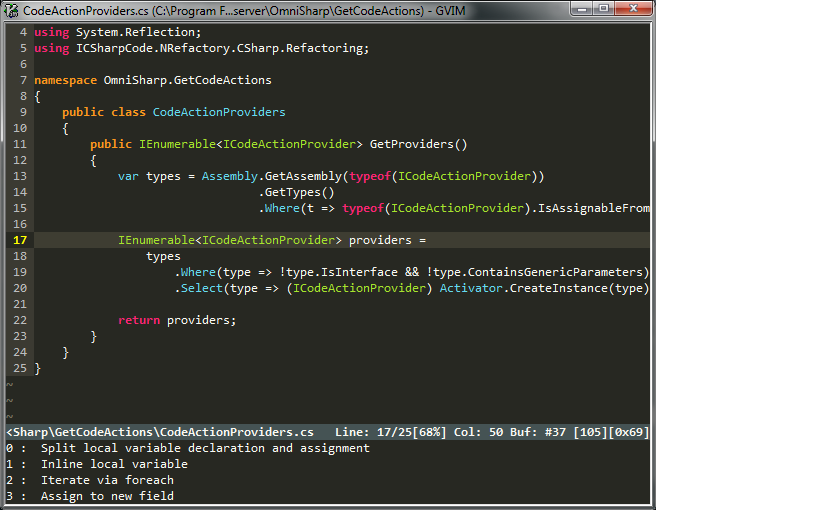
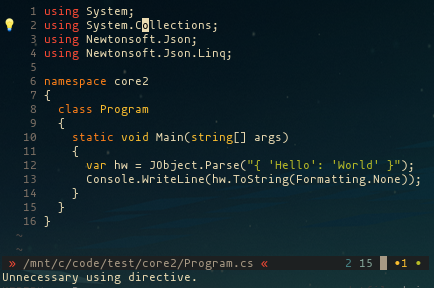
OmniSharp-vim is a plugin for Vim to provide IDE like abilities for C#.
OmniSharp works on Windows, and on Linux and OS X with Mono.
The plugin relies on the OmniSharp-Roslyn server, a .NET development platform used by several editors including Visual Studio Code, Emacs, Atom and others.
For vim8 and neovim, OmniSharp-vim can now use the OmniSharp-roslyn stdio server instead of the HTTP server, using pure vimscript (no python dependency!). All server operations are asynchronous and this results in a much smoother coding experience.
This is initially opt-in only until some user feedback is received. To switch from the HTTP server to stdio, add this to your .vimrc:
let g:OmniSharp_server_stdio = 1Then open vim to a .cs file and install the stdio server with :OmniSharpInstall. Restart vim and feel the difference!
-
Contextual code completion
- Code documentation is displayed in the preview window when available (Xml Documentation for Windows, MonoDoc documentation for Mono)
- Completion snippets are supported. e.g. Console.WriteLine(TAB) (ENTER) will complete to Console.WriteLine(string value) and expand a dynamic snippet, this will place you in SELECT mode and the first method argument will be selected.
- Requires UltiSnips and supports standard C-x C-o completion as well as completion/autocompletion plugins such as asyncomplete-vim, Supertab, Neocomplete etc.
- Requires
set completeopt-=previewwhen using Neocomplete because of a compatibility issue with UltiSnips.
-
Jump to the definition of a type/variable/method
-
Find symbols interactively (can use plugin: fzf.vim, CtrlP or unite.vim)
-
Find implementations/derived types
-
Find usages
-
Contextual code actions (unused usings, use var....etc.) (can use plugin: fzf.vim, CtrlP or unite.vim)
-
Find code issues (unused usings, use base type where possible....etc.) (requires plugin: ALE or Syntastic)
-
Find all code issues in solution and populate the quickfix window
-
Fix using statements for the current buffer (sort, remove and add any missing using statements where possible)
-
Rename refactoring
-
Semantic type highlighting
-
Lookup type information of an type/variable/method
- Can be printed to the status line or in the preview window
- Displays documentation for an entity when using preview window
-
Code error checking
-
Code formatter
Code Actions Available (see wiki for details)
Install the vim plugin using your preferred plugin manager:
| Plugin Manager | Command |
|---|---|
| Vim-plug | Plug 'OmniSharp/omnisharp-vim' |
| Vundle | Bundle 'OmniSharp/omnisharp-vim' |
| NeoBundle | NeoBundle 'OmniSharp/omnisharp-vim' |
| Pathogen | git clone git://github.com/OmniSharp/omnisharp-vim.git ~/.vim/bundle/omnisharp-vim |
OmniSharp-vim depends on the OmniSharp-Roslyn server. The first time OmniSharp-vim tries to open a C# file, it will check for the presence of the server, and if not found it will ask if it should be downloaded. Answer 'y' and the latest version will be downloaded and extracted to ~/.omnisharp/omnisharp-roslyn, ready to use. Note: Requires curl or wget on Linux, macOS, Cygwin and WSL.
Running the command :OmniSharpInstall in vim will also install/upgrade to the latest OmniSharp-roslyn release.
To install a particular release, including pre-releases, specify the version number like this:
:OmniSharpInstall 'v1.32.13'Note: These methods depend on the g:OmniSharp_server_stdio variable to decide which OmniSharp-roslyn server to download. If you are unsure, try using the new stdio option first, and only fall back to HTTP if you have problems.
-
vim8.0+ or neovim: Use the stdio server, it is used asynchronously and there is no python requirement.
-
< vim8.0: Use the HTTP server. Your vim must have python (2 or 3) support, and you'll need either vim-dispatch or vimproc.vim to be installed
" Use the stdio version of OmniSharp-roslyn:
let g:OmniSharp_server_stdio = 1
" Use the HTTP version of OmniSharp-roslyn:
let g:OmniSharp_server_stdio = 0To install the server manually, first decide which version (stdio or HTTP) you wish to use, as described above. Download the latest release for your platform from the OmniSharp-roslyn releases page. For stdio on a 64-bit Windows system, the omnisharp.win-x64.zip package should be downloaded, whereas Mac users wanting to use the HTTP version should select omnisharp.http-osx.tar.gz etc.
Extract the binaries and configure your vimrc with the path to the run script (Linux and Mac) or OmniSharp.exe file (Window), e.g.:
let g:OmniSharp_server_path = 'C:\OmniSharp\omnisharp.win-x64\OmniSharp.exe'let g:OmniSharp_server_path = '/home/me/omnisharp/omnisharp.http-linux-x64/run'No special configuration is required for cygwin. The automatic installation script for cygwin downloads the Windows OmniSharp-roslyn release. OmniSharp-vim detects that it is running in a cygwin environment and automatically enables Windows/cygwin file path translations by setting the default value of g:OmniSharp_translate_cygwin_wsl to 1.
OmniSharp-roslyn can function perfectly well in WSL using linux binaries, if the environment is correctly configured (see OmniSharp-roslyn for requirements).
However, if you have the .NET Framework installed in Windows, you may have better results using the Windows binaries. To do this, follow the Manual installation instructions above, configure your vimrc to point to the OmniSharp.exe file, and let OmniSharp-vim know that you are operating in Cygwin/WSL mode (indicating that file paths need to be translated by OmniSharp-vim from Unix-Windows and back:
let g:OmniSharp_server_path = '/mnt/c/OmniSharp/omnisharp.win-x64/OmniSharp.exe'
let g:OmniSharp_translate_cygwin_wsl = 1OmniSharp-Roslyn requires Mono on Linux and OSX. The roslyn server releases come with an embedded Mono, but this can be overridden to use the installed Mono by setting g:OmniSharp_server_use_mono in your vimrc. See The Mono Project for installation details.
let g:OmniSharp_server_use_mono = 1For the HTTP version, OmniSharp-Roslyn also requires libuv on Linux and Mac. This is typically a simple install step, e.g. brew install libuv on Mac, apt-get install libuv1-dev on debian/Ubuntu, pacman -S libuv on arch linux, dnf install libuv libuv-devel on Fedora/CentOS, etc.
Please note that if your distro has a "dev" package (libuv1-dev, libuv-devel etc.) then you will probably need it.
Note: This is not necessary for the stdio version of OmniSharp-roslyn.
Install the latest version of python 3 (Python 3.7) or 2 (Python 2.7.15). Make sure that you pick correct version of Python to match your vim's architecture (32-bit python for 32-bit vim, 64-bit python for 64-bit vim).
Verify that Python is working inside Vim with
:echo has('python3') || has('python')Note: If you are using the stdio version of OmniSharp-roslyn, you do not need python.
OmniSharp-vim can start the server only if any of the following criteria is met:
- Vim with job control API is used (8.0+)
- neovim with job control API is used
- vim-dispatch is installed
- vimproc.vim is installed
If ALE is installed, it will automatically be used to asynchronously check your code for errors.
No further configuration is necessary. However, be aware that ALE supports multiple C# linters, and will run all linters that are available on your system. To limit ALE to only use OmniSharp (recommended), add this to your .vimrc:
let g:ale_linters = {
\ 'cs': ['OmniSharp']
\}The vim plugin syntastic can be used if you don't have ALE. Configure it to work with OmniSharp with the following line in your vimrc.
let g:syntastic_cs_checkers = ['code_checker']If one of these plugins is detected, it will be used as the selector for Code Actions and Find Symbols features:
If you have installed more than one, or you prefer to use native vim functionality (command line, quickfix window etc.) rather than a selector plugin, you can choose an option with the g:OmniSharp_selector_ui variable.
let g:OmniSharp_selector_ui = 'unite' " Use unite.vim
let g:OmniSharp_selector_ui = 'ctrlp' " Use ctrlp.vim
let g:OmniSharp_selector_ui = 'fzf' " Use fzf.vim
let g:OmniSharp_selector_ui = '' " Use vim - command line, quickfix etc.By default, the server is started automatically when you open a .cs file. It tries to detect your solution file (.sln) and starts the OmniSharp-roslyn server, passing the path to the solution file.
In vim8 and neovim, the server is started invisibly by a vim job. In older versions of vim, the server will be started in different ways depending on whether you are using vim-dispatch in tmux, or are using vim-proc, gvim or running vim in a terminal.
This behaviour can be disabled by setting let g:OmniSharp_start_server = 0 in your vimrc. You can then start the server manually from within vim with :OmniSharpStartServer. Alternatively, the server can be manually started from outside vim:
[mono] OmniSharp.exe -s (path/to/sln)Add -v to get extra debugging output from the server.
To get completions, open a C# file from your solution within Vim and press <C-x><C-o> (that is ctrl x followed by ctrl o) in Insert mode, or use a completion or autocompletion plugin.
To use the other features, you'll want to create key bindings for them. See the example vimrc below for more info.
See the wiki for more custom configuration examples.
OmniSharp-roslyn can provide highlighting information about every symbol of the document.
To highlight a document, use command :OmniSharpHighlightTypes. To have .cs files automatically highlighted when entering a buffer or leaving insert mode, add this to your .vimrc:
let g:OmniSharp_highlight_types = 2In (very) recent versions of Vim, the OmniSharp-roslyn highlighting can be taken full advantage of using Vim text properties, allowing OmniSharp-vim to overwrite the standard Vim regular-expression syntax highlighting with OmniSharp-roslyn's symantic highlighting.
To check whether your Vim supports text properties, look for +textprop in the output of :version, or run :echo has('textprop').
The default highlight groups used for symantic highlighting, along with the standard Vim highlight groups they are linked to are as follows:
| Highlight group | Default link |
|---|---|
| csUserIdentifier | Identifier |
| csUserInterface | Include |
| csUserMethod | Function |
| csUserType | Type |
Highlight groups are mapped to OmniSharp-roslyn keyword "kinds" using variable g:OmniSharp_highlight_groups.
Here is the default mapping dictionary:
let g:OmniSharp_highlight_groups = {
\ 'csUserIdentifier': [
\ 'constant name', 'enum member name', 'field name', 'identifier',
\ 'local name', 'parameter name', 'property name', 'static symbol'],
\ 'csUserInterface': ['interface name'],
\ 'csUserMethod': ['extension method name', 'method name'],
\ 'csUserType': ['class name', 'enum name', 'namespace name', 'struct name']
\}However, any highlight groups can be used, and they can be set to highlight any OmniSharp-roslyn "kinds".
For example, to only highlight namespace name and enum name using highlight group Title, you could add this to your .vimrc:
let g:OmniSharp_highlight_groups = {
\ 'Title': ['enum name', 'namespace name']
\}In order to find out what OmniSharp-roslyn calls a particular element, there is a "debugging" option available, g:OmniSharp_highlight_debug. When this is set to 1, text properties are added to all symbols of the document. The text properties are not highlighted so this has no visible effect, but when this mode is enabled, command :OmniSharpHighlightEchoKind will echo the OmniSharp-rolsyn "kind" of the symbol under the cursor.
Note: Text property highlighting is currently only available when using the stdio server, not for HTTP server usage.
When text properties are not available, or when using the HTTP server, limited symantic highlighting is still possible by highlighting keywords. Note that this is not perfect - a keyword can only match a single highlight group, meaning that interfaces/classes/methods/parameters with the same name will be highlighted the same as each other.
The configuration options are also more limited.
The same 4 highlight groups are used as described above (csUserIdentifier, csUserInterface, csUserMethod and csUserType).
To change a highlight group's colors, change the ctermbg/guibg properties, or link it to another highlight group:
highlight csUserInterface ctermfg=12 guifg=Blue
highlight link csUserType IdentifierTo disable a group, link it to Normal:
highlight link csUserMethod Normal" Use the vim-plug plugin manager: https://github.com/junegunn/vim-plug
" Remember to run :PlugInstall when loading this vimrc for the first time, so
" vim-plug downloads the plugins listed.
silent! if plug#begin('~/.vim/plugged')
Plug 'OmniSharp/omnisharp-vim'
Plug 'w0rp/ale'
call plug#end()
endif
filetype indent plugin on
" Use the stdio OmniSharp-roslyn server
let g:OmniSharp_server_stdio = 1
" Set the type lookup function to use the preview window instead of echoing it
"let g:OmniSharp_typeLookupInPreview = 1
" Timeout in seconds to wait for a response from the server
let g:OmniSharp_timeout = 5
" Don't autoselect first omnicomplete option, show options even if there is only
" one (so the preview documentation is accessible). Remove 'preview' if you
" don't want to see any documentation whatsoever.
set completeopt=longest,menuone,preview
" Fetch full documentation during omnicomplete requests.
" By default, only Type/Method signatures are fetched. Full documentation can
" still be fetched when you need it with the :OmniSharpDocumentation command.
"let g:omnicomplete_fetch_full_documentation = 1
" Set desired preview window height for viewing documentation.
" You might also want to look at the echodoc plugin.
set previewheight=5
" Tell ALE to use OmniSharp for linting C# files, and no other linters.
let g:ale_linters = { 'cs': ['OmniSharp'] }
" Update symantic highlighting on BufEnter and InsertLeave
let g:OmniSharp_highlight_types = 2
augroup omnisharp_commands
autocmd!
" Show type information automatically when the cursor stops moving
autocmd CursorHold *.cs call OmniSharp#TypeLookupWithoutDocumentation()
" The following commands are contextual, based on the cursor position.
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> gd :OmniSharpGotoDefinition<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>fi :OmniSharpFindImplementations<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>fs :OmniSharpFindSymbol<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>fu :OmniSharpFindUsages<CR>
" Finds members in the current buffer
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>fm :OmniSharpFindMembers<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>fx :OmniSharpFixUsings<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>tt :OmniSharpTypeLookup<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>dc :OmniSharpDocumentation<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <C-\> :OmniSharpSignatureHelp<CR>
autocmd FileType cs inoremap <buffer> <C-\> <C-o>:OmniSharpSignatureHelp<CR>
" Navigate up and down by method/property/field
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <C-k> :OmniSharpNavigateUp<CR>
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <C-j> :OmniSharpNavigateDown<CR>
" Find all code errors/warnings for the current solution and populate the quickfix window
autocmd FileType cs nnoremap <buffer> <Leader>cc :OmniSharpGlobalCodeCheck<CR>
augroup END
" Contextual code actions (uses fzf, CtrlP or unite.vim when available)
nnoremap <Leader><Space> :OmniSharpGetCodeActions<CR>
" Run code actions with text selected in visual mode to extract method
xnoremap <Leader><Space> :call OmniSharp#GetCodeActions('visual')<CR>
" Rename with dialog
nnoremap <Leader>nm :OmniSharpRename<CR>
nnoremap <F2> :OmniSharpRename<CR>
" Rename without dialog - with cursor on the symbol to rename: `:Rename newname`
command! -nargs=1 Rename :call OmniSharp#RenameTo("<args>")
nnoremap <Leader>cf :OmniSharpCodeFormat<CR>
" Start the omnisharp server for the current solution
nnoremap <Leader>ss :OmniSharpStartServer<CR>
nnoremap <Leader>sp :OmniSharpStopServer<CR>
" Enable snippet completion
" let g:OmniSharp_want_snippet=1Pull requests welcome!