Rust For Linux 作业报告
Step1: 会生成适用于 x86_64 架构的默认配置文件
make x86_64_defconfig
Step2: 配置linux内核
- 命令
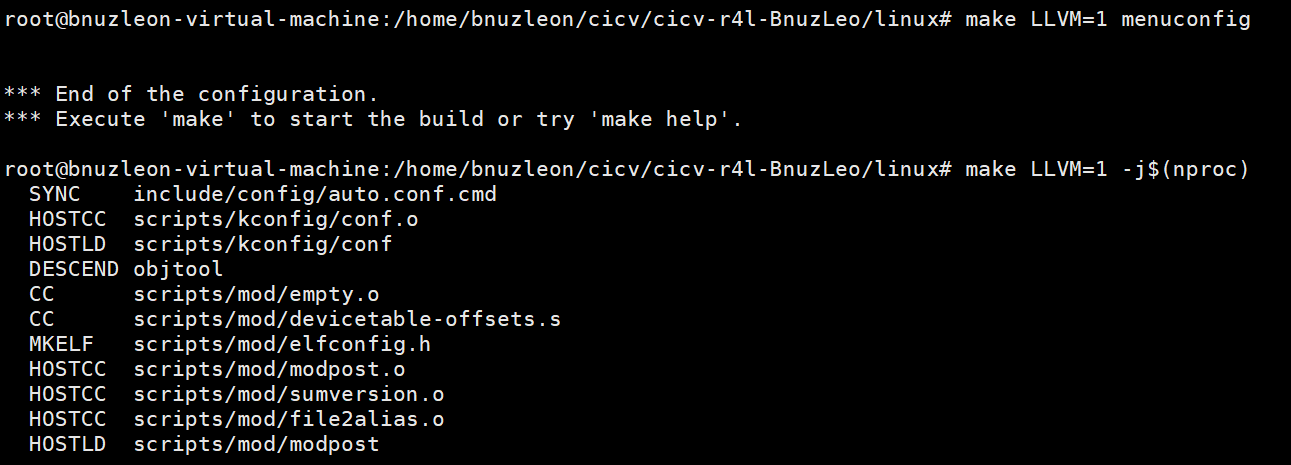
make LLVM=1 menuconfig
- LLVM=1
通常情况下,Linux 内核会使用 GCC(GNU Compiler Collection)作为默认的编译器。这里LLVM=1是告诉内核编译系统使用LLVM(Low Level Virtual Machine)来编译。
- menuconfig
menuconfig 是一个交互式工具,它允许你在命令行界面中配置 Linux 内核。
Step3: 开始编译内核
make LLVM=1 -j$(nproc)
- -j$(nproc)
-j$(nproc): 这个参数用来指定并行编译的任务数量。
-j 参数后面的 $(nproc) 表示使用系统的可用处理器核心数量作为并行编译任务的数目。这样做可以加快编译速度,因为它允许多个任务同时运行,利用多核处理器的能力。
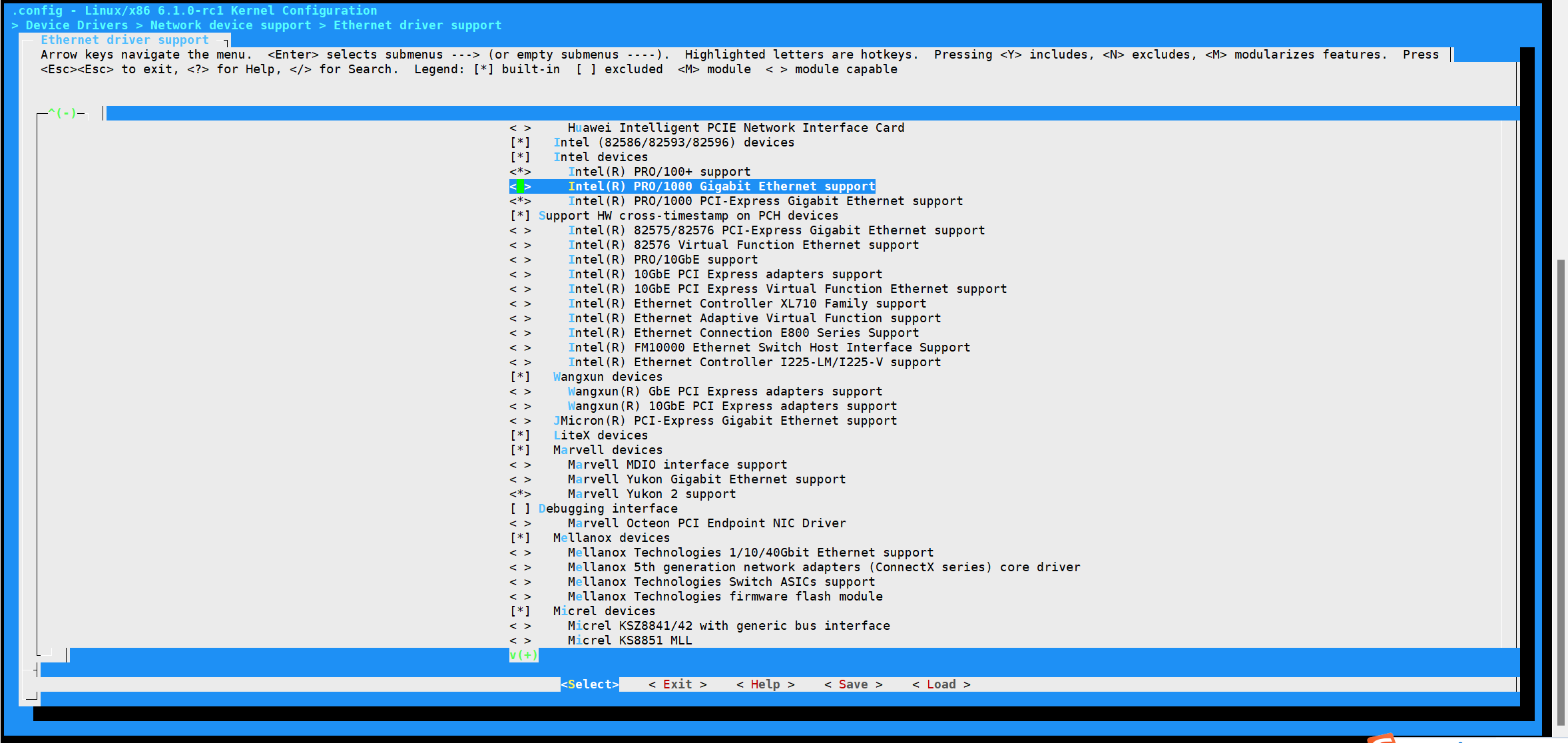
Step 1: 关闭Linux内核默认的e1000网卡驱动
Step2: 重新编译Linux内核
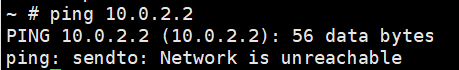
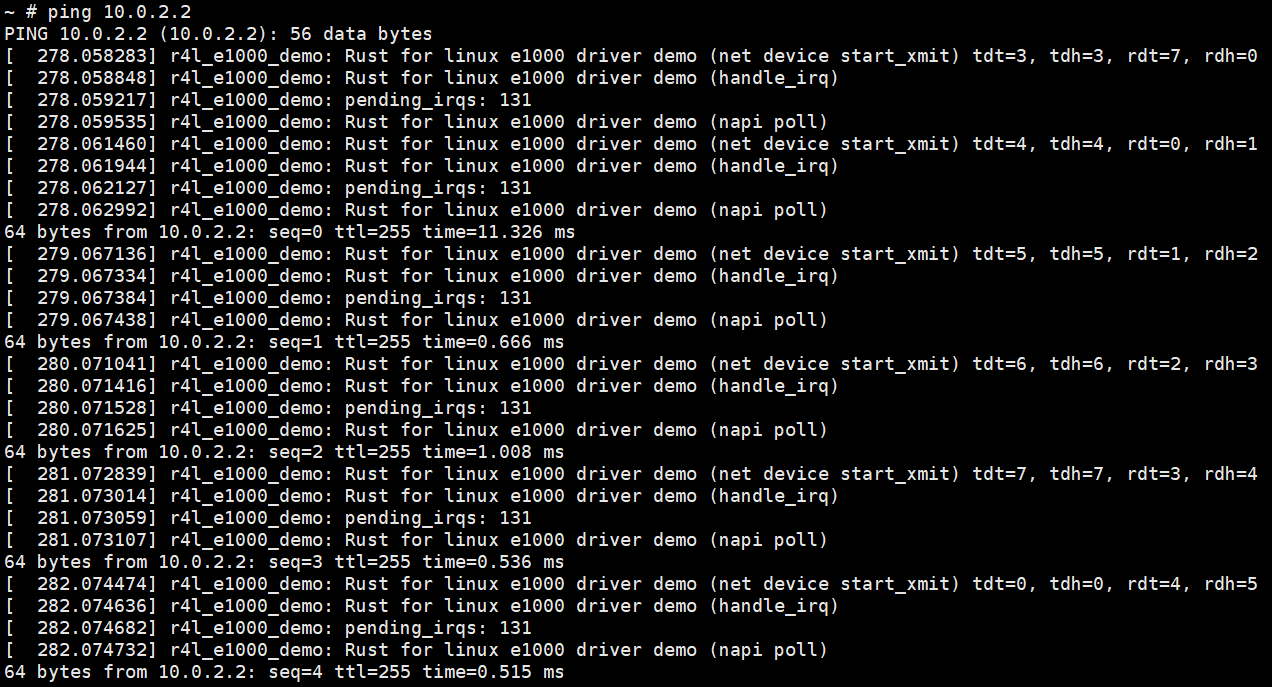
Step3: 进入内核确认不能ping通联通网络
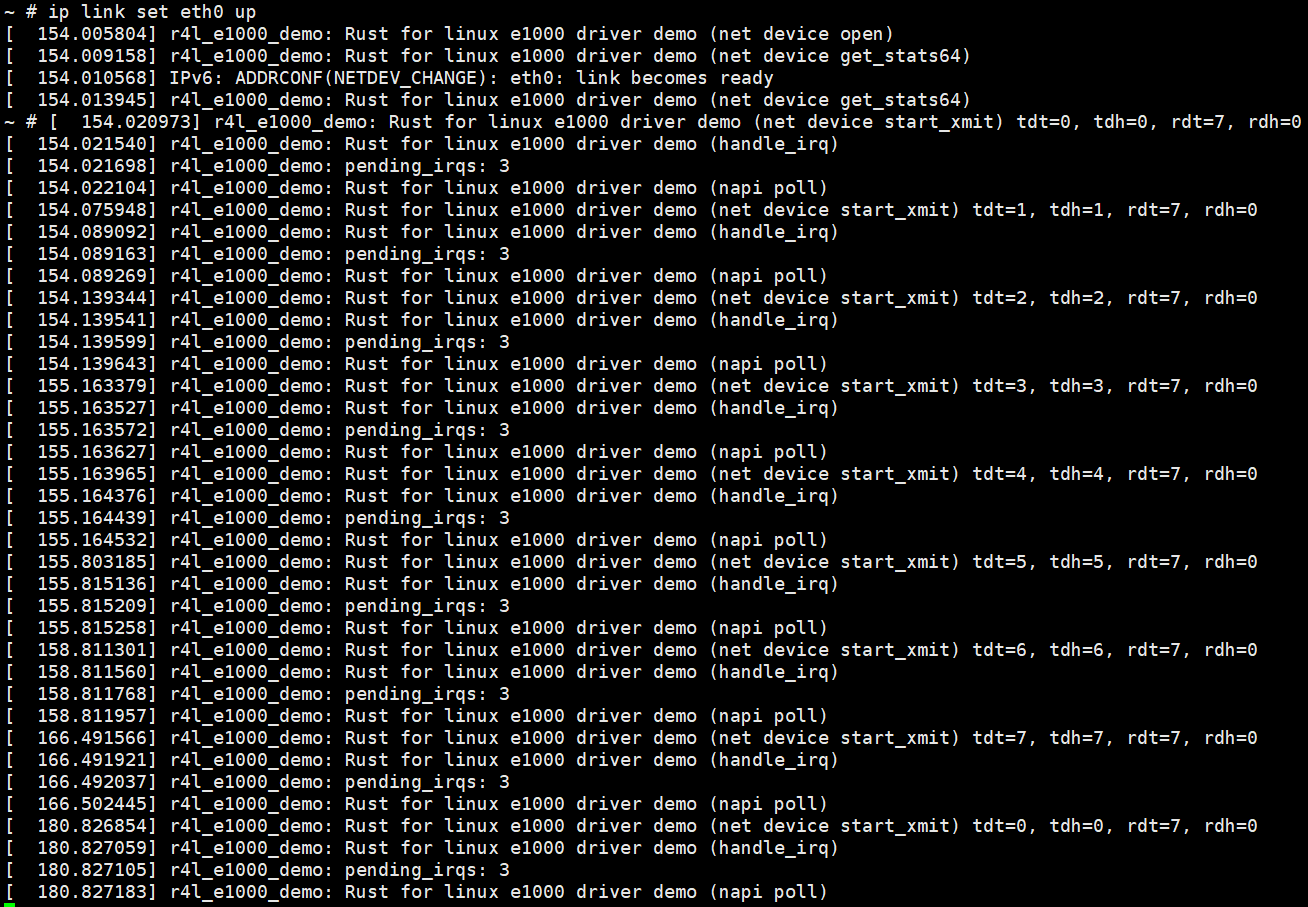
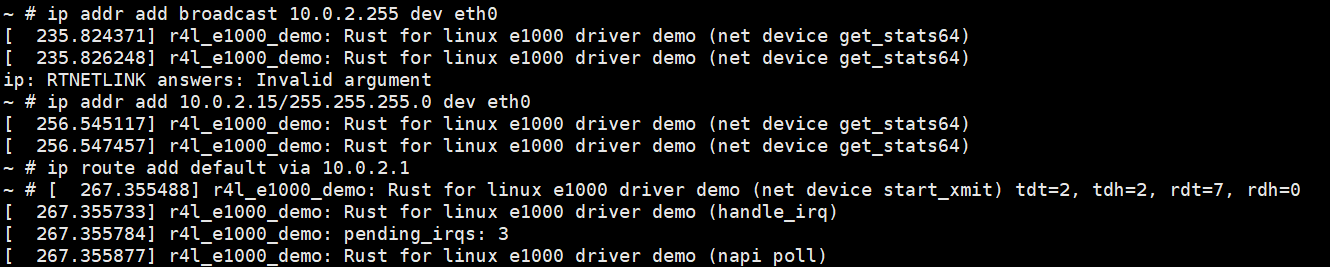
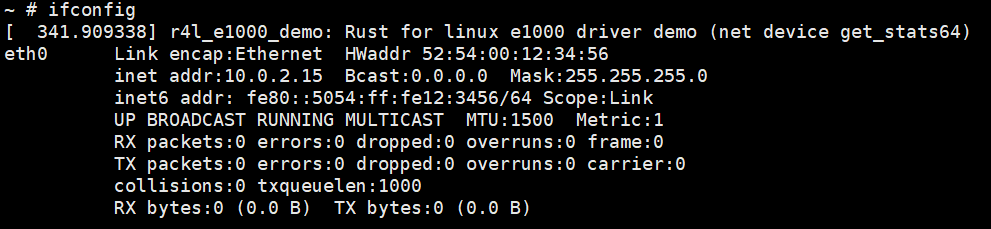
Step4:手动配置,让他联网,且能ping通联通网络
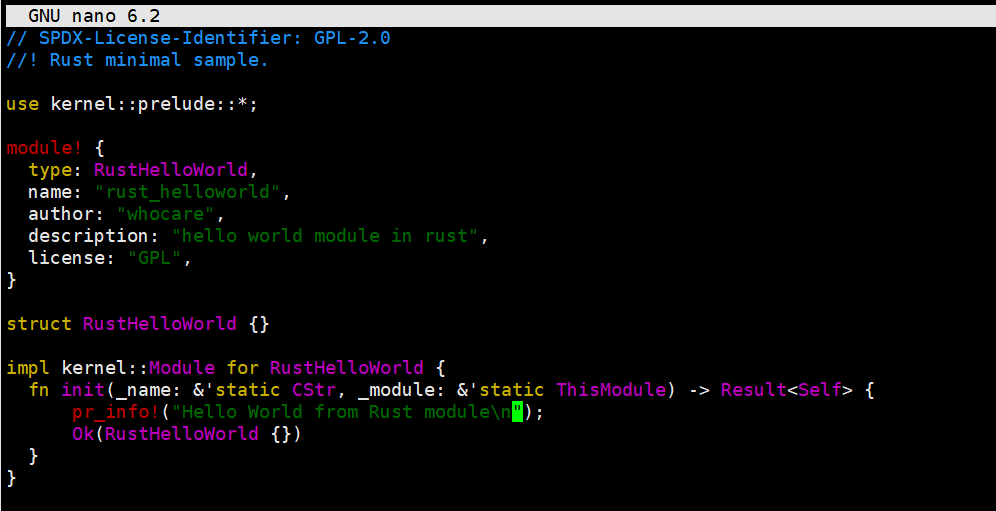
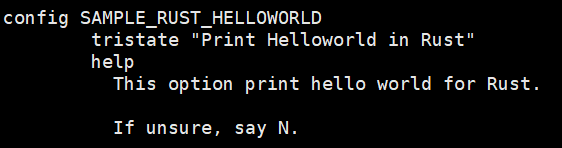
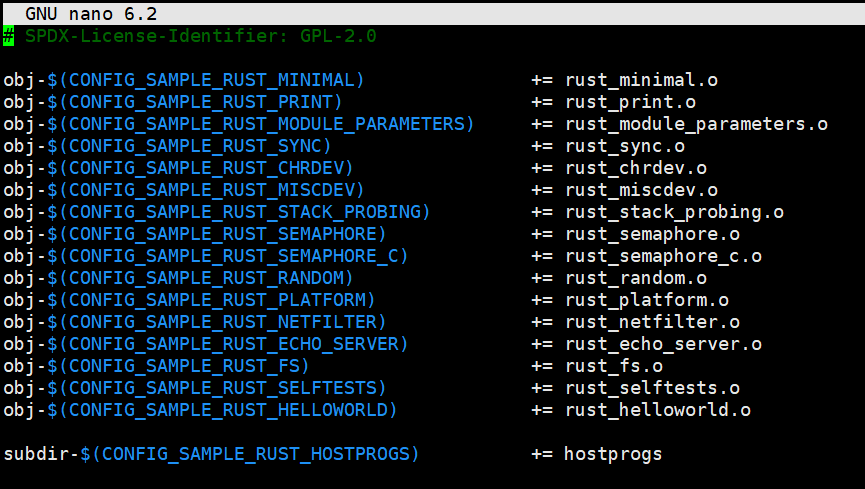
Step1: 添加/samples/rust/rust_helloworld.rs文件
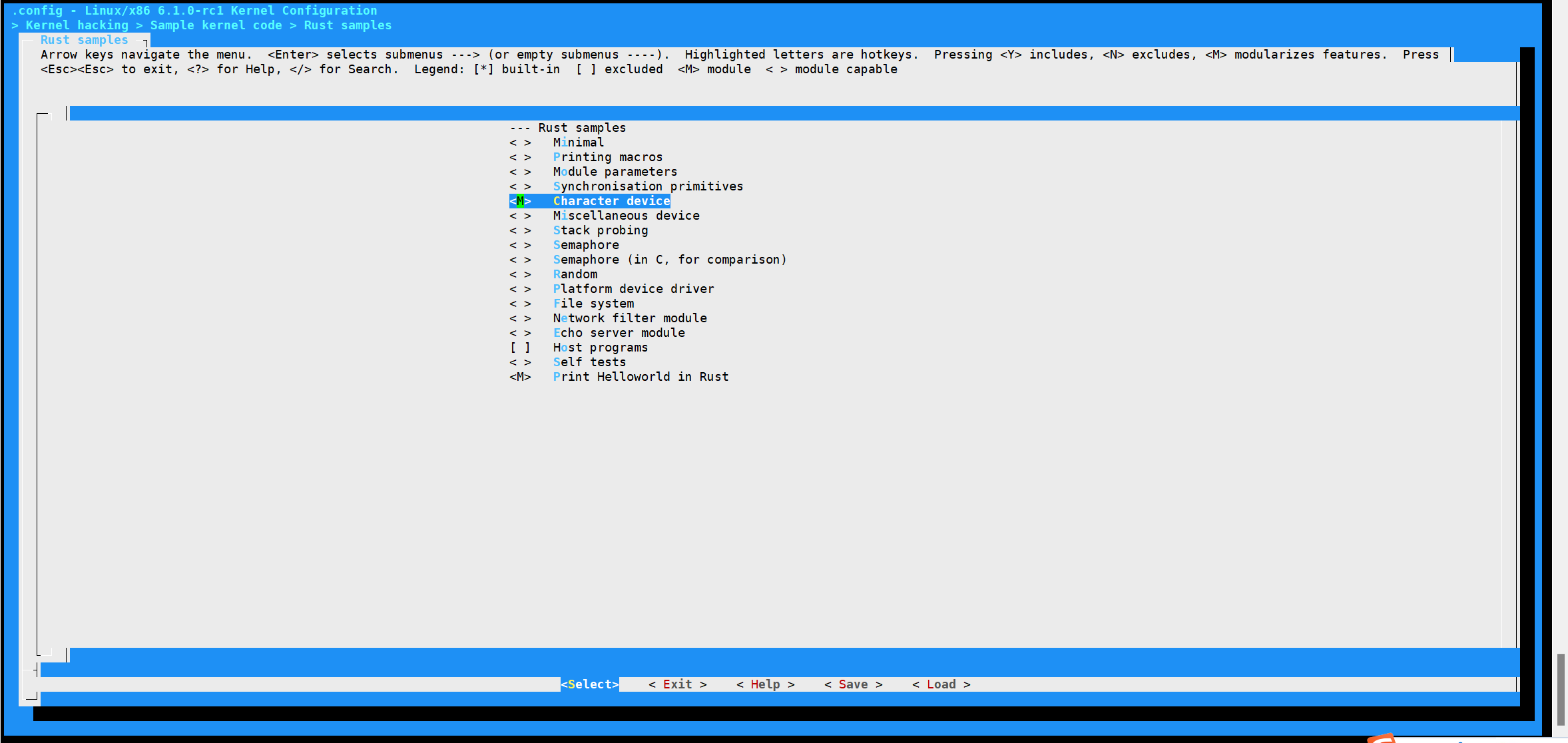
Step2: 修改Kconfig和Makefile
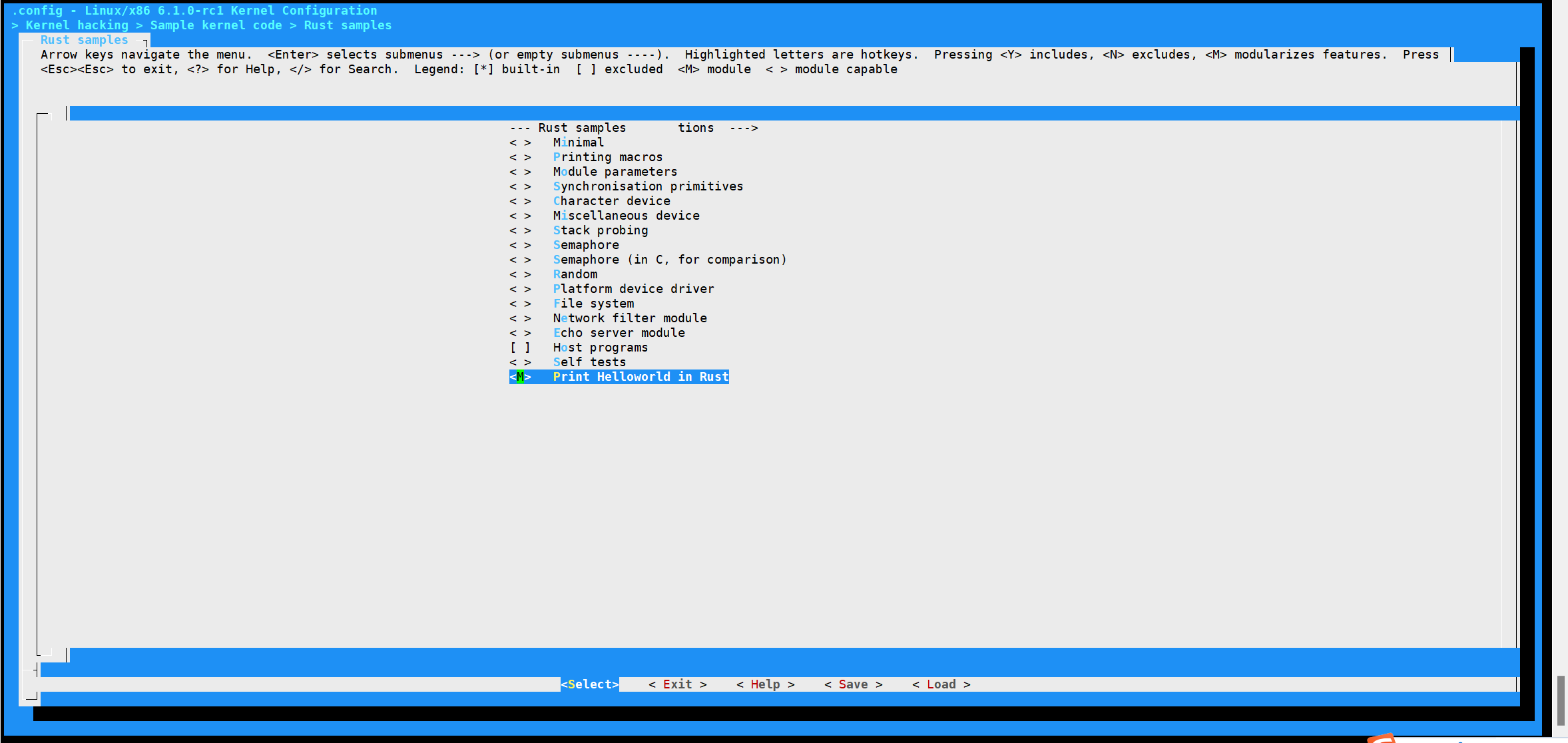
Step3:选择“Print Helloworld in Rust" 然后编译成模块
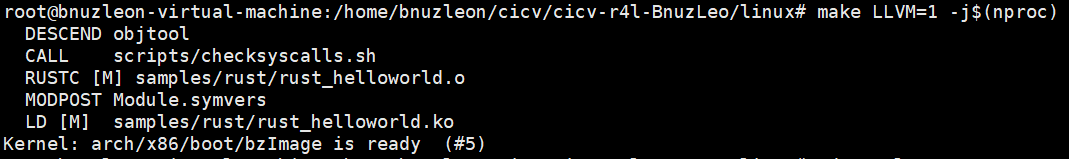
Step4:重新编译内核
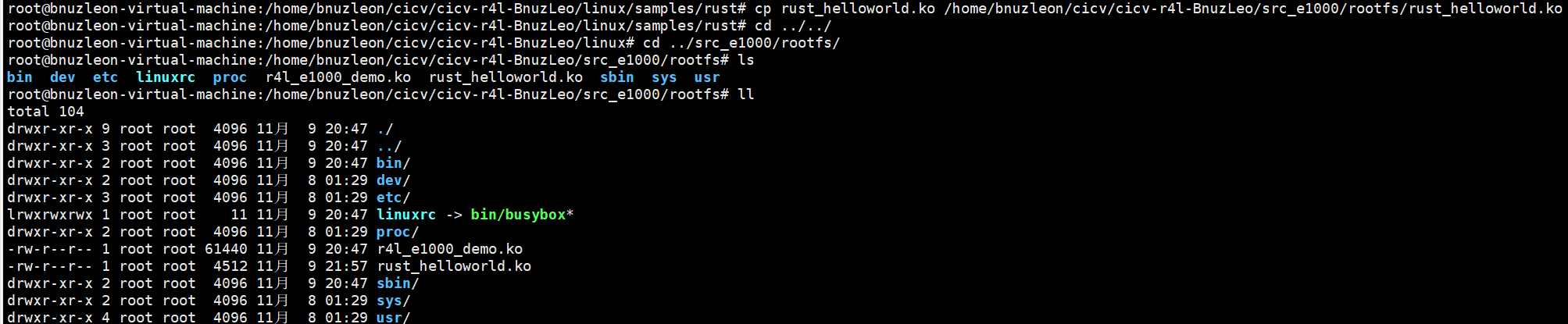
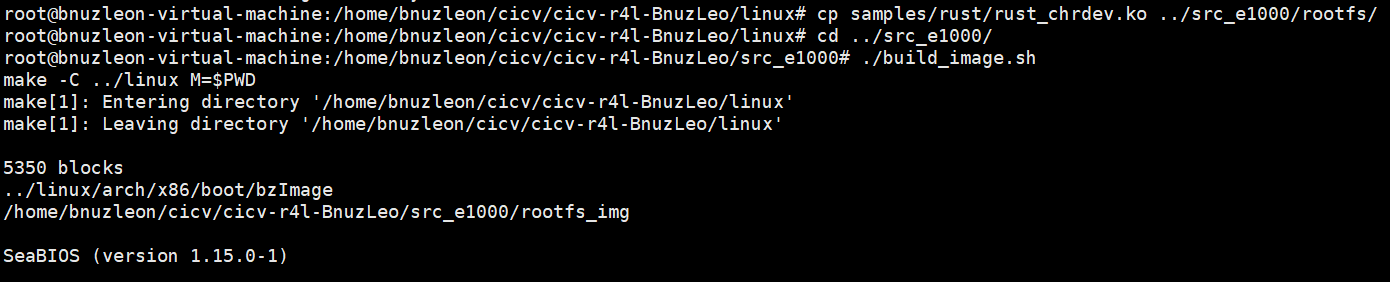
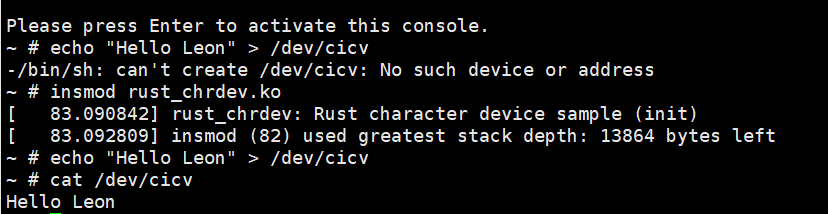
Step5:把/samples/rust/rust_helloworld.rs复制到/src_e000/rootfs中,重新跑build_image.sh
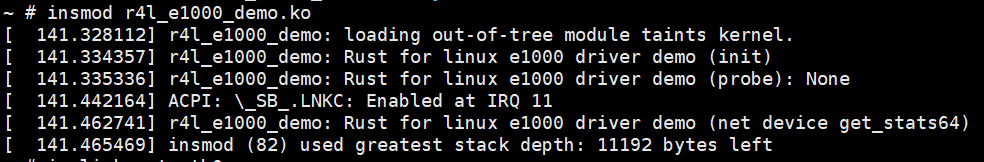
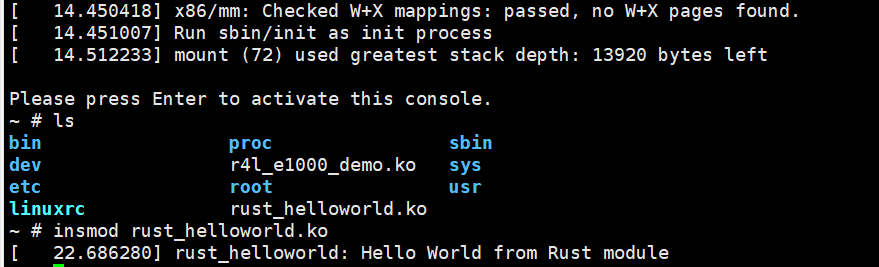
Step6:进入内核安装模块
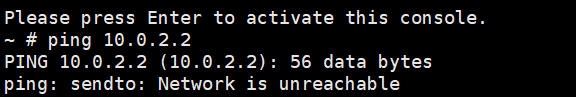
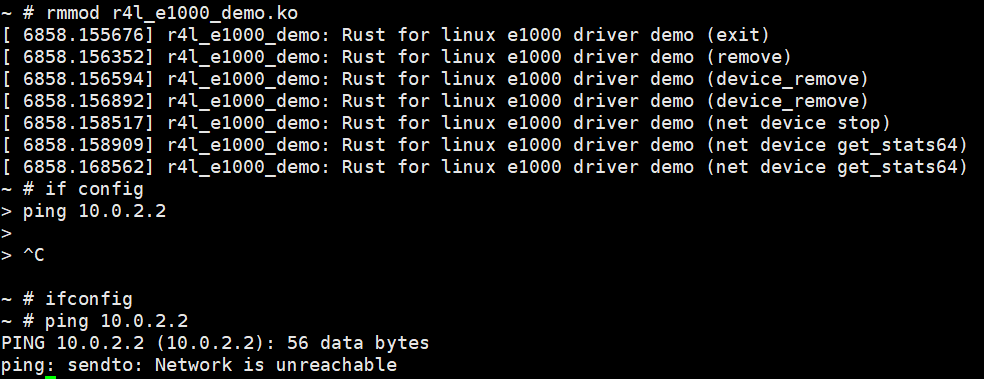
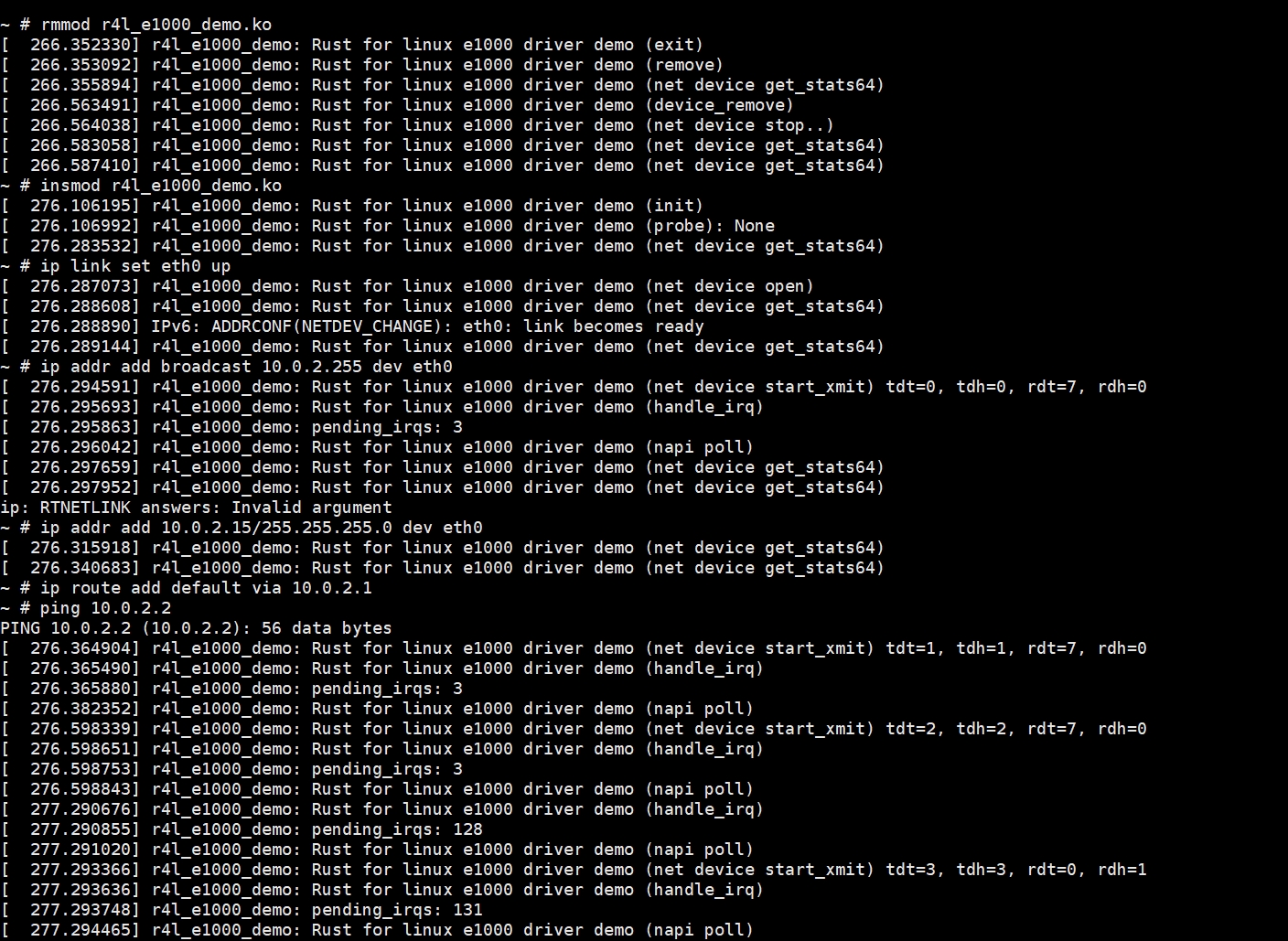
Step1: 确认无法上网
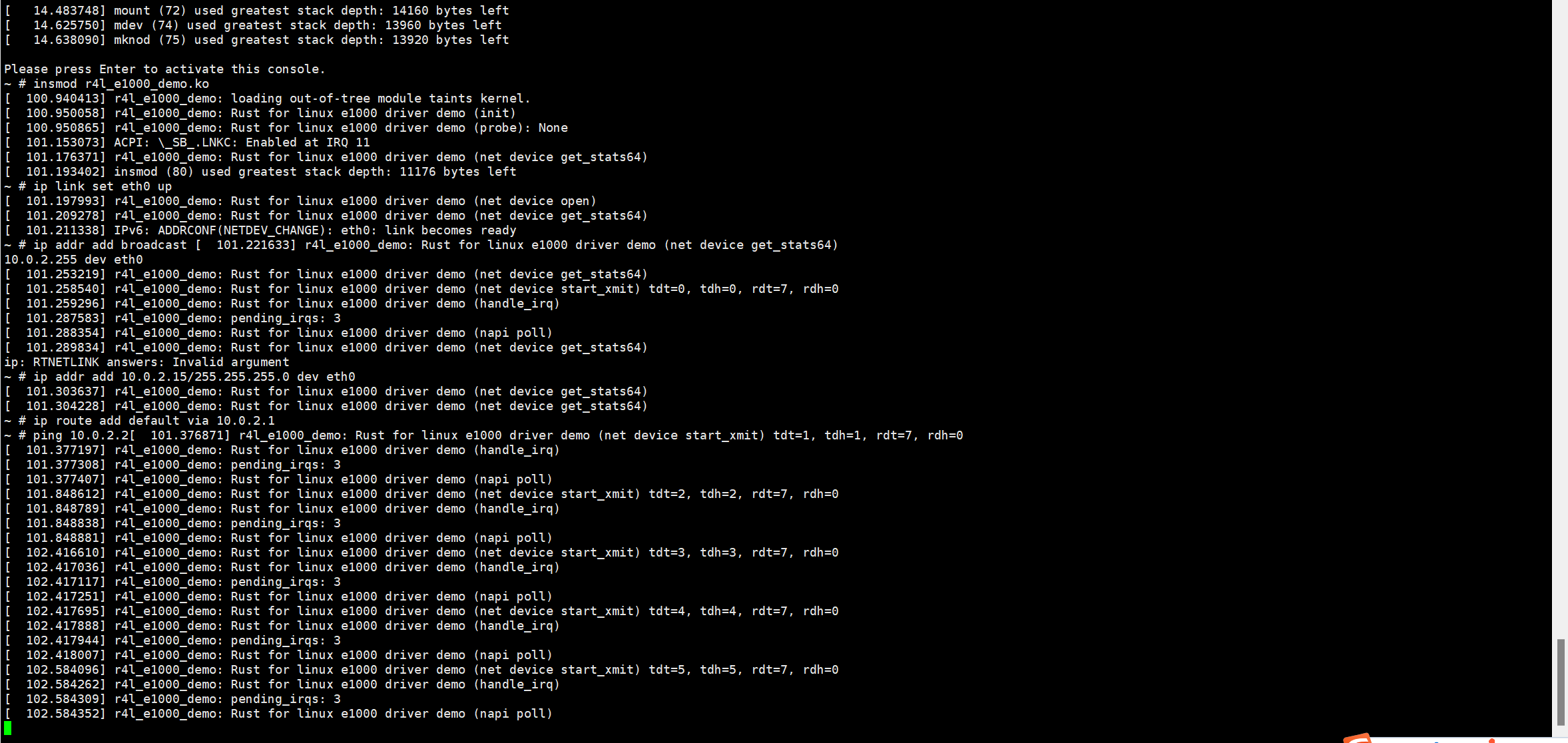
Step2: 通过作业二的方法,让内核再次可以上网
Step3:执行rmmod r4l_e1000_demo.ko,移除模块,无法上网
Step4:再通过作业2的方法,加载模块,顺利ping通
e1000_cleanup_tx_resources
释放之前为发送(TX)资源分配的内存。在网络设备关闭或移除时调用,确保释放相关的资源以避免内存泄漏。
fn e1000_cleanup_tx_resources(data: &NetDevicePrvData) {
let mut tx_ring_guard = data.tx_ring.lock();
if let Some(tx_ring) = tx_ring_guard.take() {
drop(tx_ring);
}
}e1000_cleanup_rx_resources
释放之前为接收(RX)资源分配的内存。在网络设备关闭或移除时调用,确保释放相关的资源,避免内存泄漏。
fn e1000_cleanup_rx_resources(data: &NetDevicePrvData) {
let mut rx_ring_guard = data.rx_ring.lock();
if let Some(mut rx_ring) = rx_ring_guard.take() {
for entry in rx_ring.buf.borrow_mut().iter_mut() {
if let Some((dma_map, skb)) = entry.take() {
drop(dma_map);
drop(skb);
}
}
drop(rx_ring);
}
}stop
停止网络设备的操作,包括停止发送队列、关闭网络设备和重置硬件状态。
// 资源句柄释放
fn stop(_dev: &net::Device, _data: &NetDevicePrvData) -> Result {
pr_info!("Rust for linux e1000 driver demo (net device stop..)\n");
Self::e1000_cleanup_tx_resources(_data);
Self::e1000_cleanup_rx_resources(_data);
// 获取irq_handler的指针
let irq_handler_ptr = _data._irq_handler.load(core::sync::atomic::Ordering::Relaxed);
// 确保指针不为空,然后释放资源
if !irq_handler_ptr.is_null() {
unsafe {
let _irq_handler_box = Box::from_raw(irq_handler_ptr);
}
_data._irq_handler.store(core::ptr::null_mut(), core::sync::atomic::Ordering::Relaxed);
}
_dev.netif_stop_queue();
_dev.netif_carrier_off();
_data.e1000_hw_ops.e1000_reset_hw();
_data.napi.disable();
Ok(())
}remove
在设备移除时执行清理操作,确保释放所有相关资源。具体步骤包括:
// 完善 remove 方法,进行资源释放
fn remove(data: &Self::Data) {
pr_info!("Rust for linux e1000 driver demo (remove)\n");
let netdev = data._netdev_reg.dev_get();
let bars = data.bars;
let pci_dev_ptr = data.dev_ptr;
let netdev_reg = &data._netdev_reg;
netdev.netif_carrier_off();
netdev.netif_stop_queue();
unsafe {
bindings::pci_release_selected_regions(pci_dev_ptr, bars);
bindings::pci_clear_master(pci_dev_ptr);
bindings::pci_disable_device(pci_dev_ptr);
}
drop(netdev_reg);
drop(data)
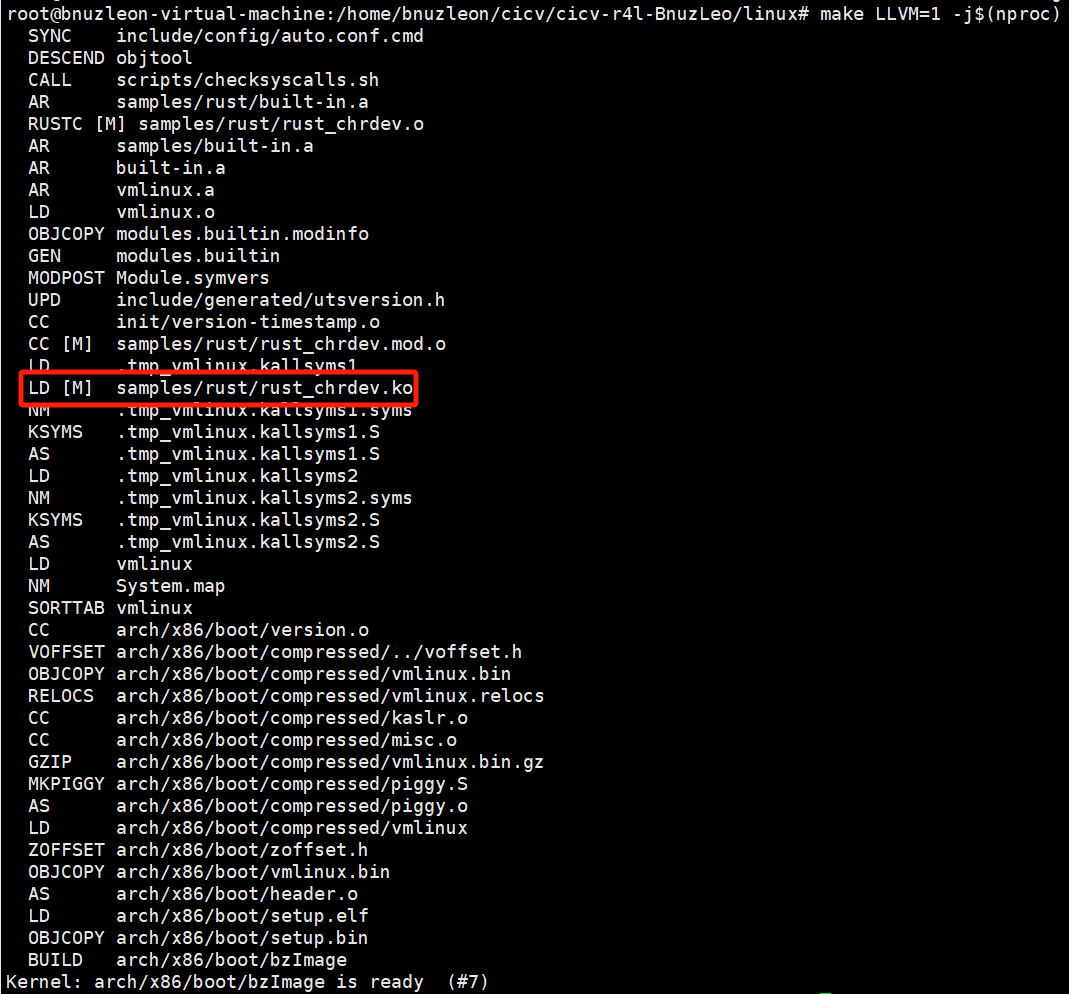
}Step 1: 打开Character device模块的编译配置
Step2:重新编译linux内核,然后进入内核