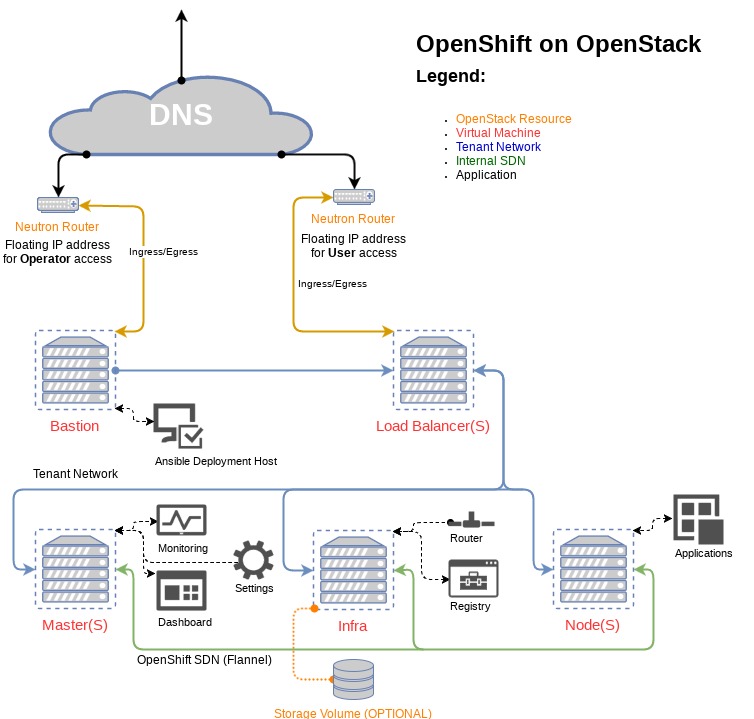
This repository will deploy several VMs in an OpenStack cloud assign a floating
IP address to a bastion host, run some basic commands across the cluster to
ensure a successful deployment, and then leverage
OpenShift-Ansible to deploy
OpenShift. The deployment on the bastion host will be conducted from a tmux
shell named build-openshift on the bastion host.
- Ansible 2.2 is required
- the python library "shade" is required to provision the virtual machines.
- The host which you run the playbooks needs access to both the OpenStack API and the deployed VMs.
- We're using OpenStack as an IaaS solution and provisioning VMs but we are not using additional "as a service" offerings; everything is contained within nova.
- DNS services are external to the cluster.
- Access to the Load balancer is ONLY accessible via a floating IP address.
This deployment setup will create all resources within openstack.
- DNS is assumed to be managed outside of the OpenShift Cluster
- Servers are used for all aspects of this deployment
- Tenant networks are used to connect all servers
- A floating IP address is assigned to the bastion server
- Load balancers, Masters, and Nodes can all have multiple servers
- The infra node is a single server
- The Bastion host is an Ansible deployment host for the entire OpenShift cluster
- Internal cluster connectivity is handled by flannel
Once the VMs are online and the hosts have been bootstrapped these playbooks
will create a tmux session named build-openshift and will run the byo
configuration playbook.
If you run ansible from a venv you will need to set the python path within the inventory for the localhost inventory entry.
Within the credentials file add the OpenStack credential information
- os_net_name - name of the network used for intra cluster connectivity
- os_vip_pool_name - name of the network used for floating IP addresses
- os_flavor_name - name of the flavor for a given VM
- os_auth - hash containing the credentials to log into OpenStack, See the
creds.ymlfile.
Neutron needs to have the DNS plugin enabled for OpenShift to work properly.
is enabled by adding dns to the extension_drivers within the
ml2_conf.ini file. The dns_domain option, set within the neutron.conf
file will also need to be set to an FQDN. If you've deployed the cloud with
OpenStack-Ansible add the following item to your user_variables.yml.
neutron_plugin_base:
- router
- metering
- neutron_lbaas.services.loadbalancer.plugin.LoadBalancei
- dns
neutron_dns_domain: "openstacklocal."Within the included inventory file example OpenShift OpenStack options have been included. In order for these options to work the deployed instances will need to have access to the control plane on a public network. If your deployment of OpenStack is using SSL the certificate MUST be a signed certificate and part of the instances certificate chain.
Deploying within OpenStack gives OpenShift the ability to connect to persistent storage using cinder and access to Load Balancer as a Service as well as the ability to connect OpenShift to Keystone for authentication. If these options are used CARE should be taken as this could open the Infrastructure as a Service platform up to significant risk.
With ansible and shade installed locally, run the playbooks sourcing the credentials file.
ansible-playbook -i inventory site.yml -e @creds.ymlAccess to the control panel is gated by security groups and access to the floating IP. DNS names are assumed to be setup for the floating cluster. The inventory default within these playbooks sets the cluster public DNS name name to loadbalancer-1. In production this should be changed to something more suitable for the use. If remote DNS is not available simply add an entry into the host file for the load balancer and the floating IP address.
Adding more nodes to the deployment is as simple as adding the needed entries into inventory and then rerunning these playbooks. Note not all node types can scale horizontally, see the architecture diagram for more details.