Group Project of CLPS1291 Fall 23 @ Brown
Group members: Xueru MA, Yingwei Song, Yunxi Liang, Yuxiang Wang
In the pursuit of artificial intelligence that mirrors the deftness of human cognition, the concept of biological plausibility stands as a beacon, guiding the design of neural networks toward the intricate workings of the human brain. A neural network that is considered biologically plausible emulates the structure and functions of the biological nervous system, often with the purpose of improving the performance of neural networks or gaining insights into processes of the biological brain.
While backpropagation (BP) is a cornerstone in training modern neural networks, it deviates from how biological neural systems function. Key differences include BP's reliance on inter-layer weight dynamics, unlike the local information transmission in biological neurons, its use of symmetric weights for both forward and backward passes which contrasts with the one-directional, asymmetric nature of biological synapses, and its continuous output neuron firing, as opposed to the all-or-none firing based on a threshold in biological neurons. Recognizing these discrepancies, this project focuses on exploring neural network techniques that better mimic human brain functions. The aim is to investigate how these biologically inspired alternatives to backpropagation could enhance the performance and interpretability of neural networks.
A full version final report can be found here: Link to PDF
- Python
- numpy
- torch
- torchvision
- matplotlib
- CUDA (for hybridBio_learning)
Feedback_Alignment:
- A Pytorch implementation of Random synaptic feedback weights support error backpropagation for deep learning based on L0SG/feedback-alignment-pytorch
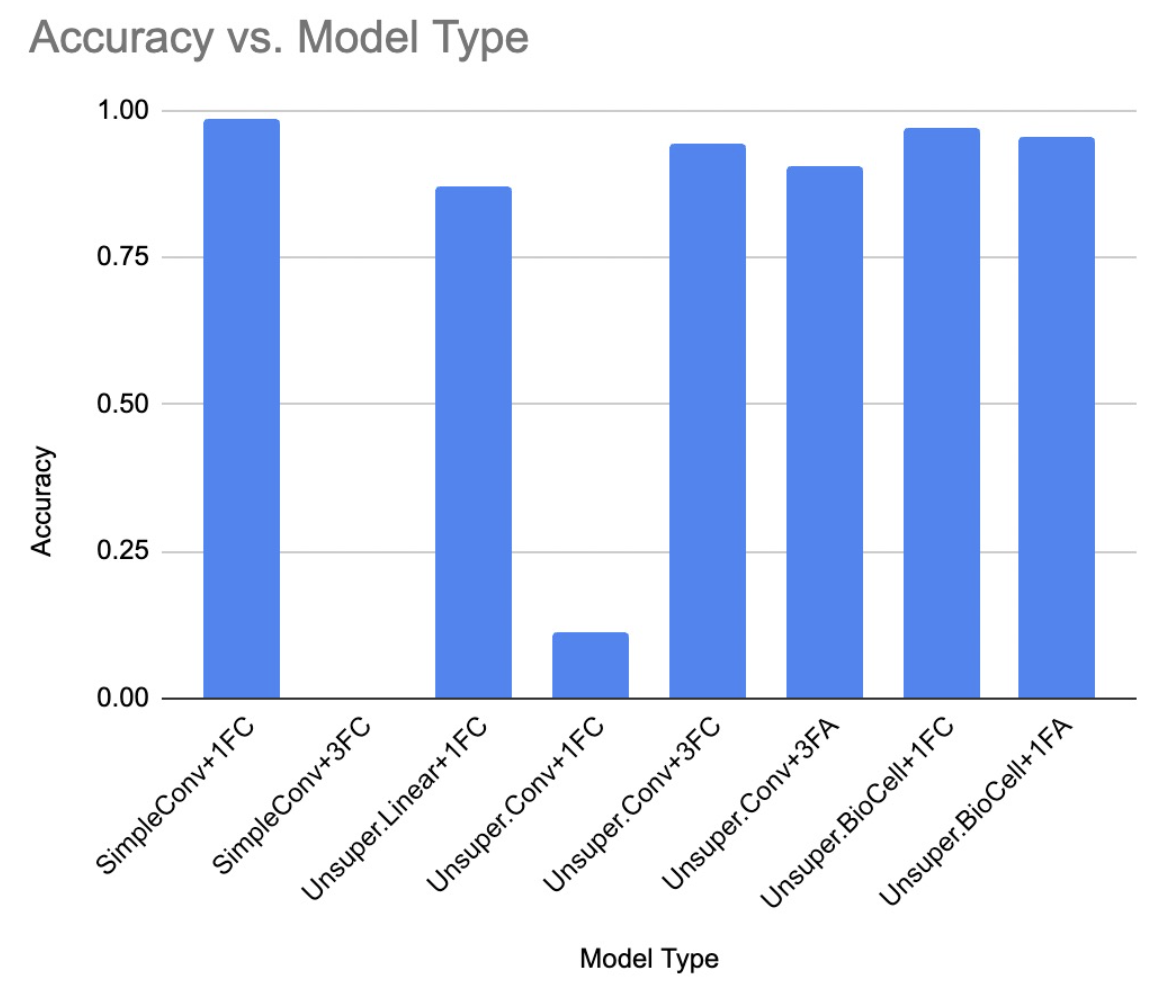
- Experiments on the blend of Pretrained Convolutional Layers and Feedback Alignment Layers (CNN + FA)
semiHebb_learning:
- A Pytorch implementation of HEBBNET: A SIMPLIFIED HEBBIAN LEARNING FRAMEWORK TO DO BIOLOGICALLY PLAUSIBLE LEARNING from sratch. Original descriptive documentation can be found at Andy-wyx/biologically_plausible_learning.
- Experiments on the blend of Hebbian Layers and Linear Layers (Gupta's HebbNet + fc)
hybridBio_learning:
- A PyTorch implementation of Unsupervised learning by competing hidden units MNIST classifier based on gatapia/unsupervised_bio_classifier, combining with Feedback alignment. Original descriptive documentation can be found at here.
- Experiments on
- the blend of Krotov's unsupervised layers w/o biocells and Linear Layers (Krotov's HebbNet w/o Biocells + fc)
- the blend of Krotov's unsupervised layers w biocells and Linear Layers (Krotov's HebbNet w Biocells + fc)
- the blend of Krotov's unsupervised layers w or w/o biocells and Feedback Alignment Layers (Krotov's HebbNet + FA)
See the final report: Link to PDF
Training & Experiments
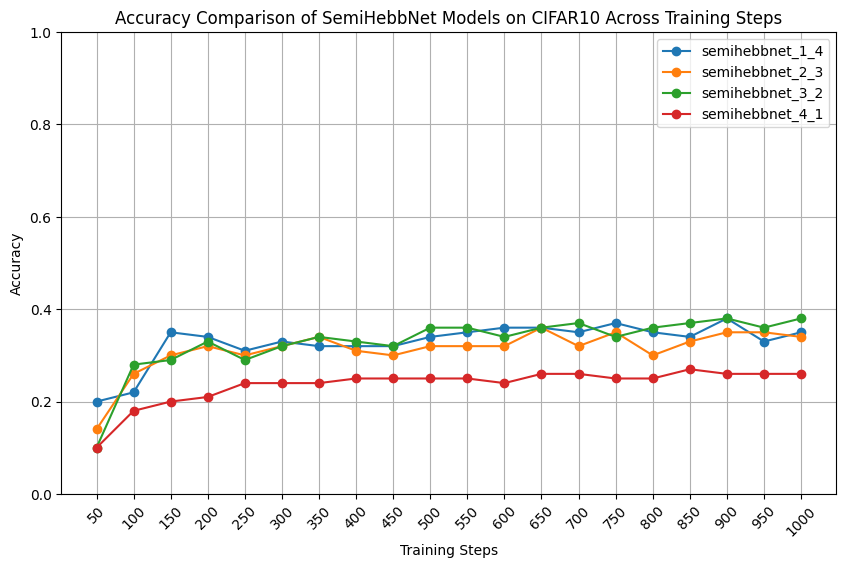
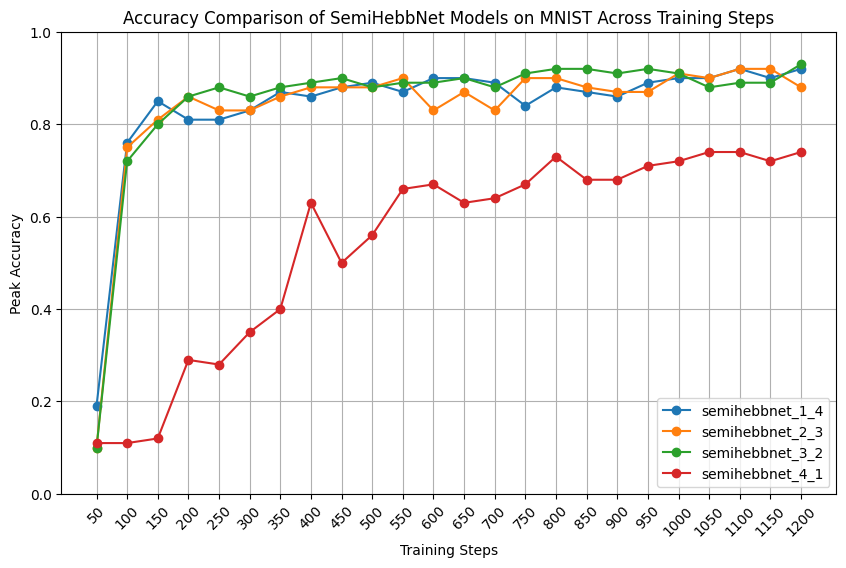
- Try to train semiHebbNet in one phase, find the best learning rate for Hebbian layers and linear layers respectively.
- More Hyperparameter tuning on these models to compare their Peak Accuracy.
- Compare Efficiency in the same experimental settings.(same epoch, dataset, lr, hardward etc)
Algorithms & Learning rules
- Implement modified Gupta's update rule
- Explore more Biologically Plausible Neural Networks e.g. SCALING FORWARD GRADIENT WITH LOCAL LOSSES
Others
- Enable GPU mode for semiHebbNet and Feedback Alignment
- Interpretability: Figure out a way to make XPlique applicable to our models. (our models have no filters as attributes, and are not differentiable sometimes)
Except for torchvision models, GluonCV includes many pretrained sota models in CV.