This SDK (Software Development Kit) makes it easy to call Stargate services using idiomatic Java APIs.
- 2.1 - Prerequisites
- 2.2 - Start Stargate
- 2.3 - QuickStart
- 2.4 - Working with Rest API
- 2.5 - Working with Document API
- 2.6 - Working with GRPC API
- 2.7 - Working with Graph API
- 2.8 - Working with Json API
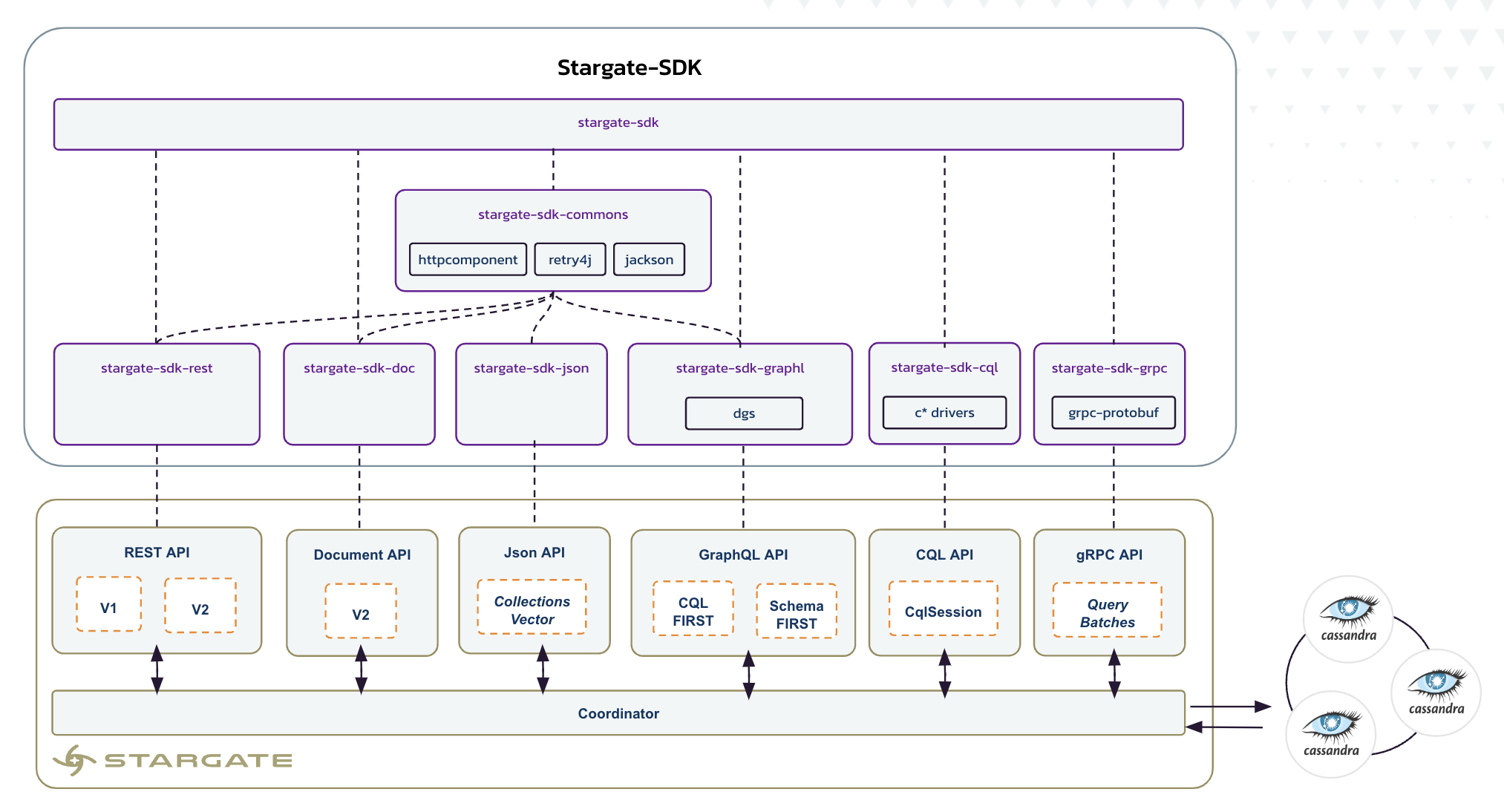
Stargate is a data API gateway that deploys between your apps and your Apache Cassandra database(s). Stargate is a framework used to customize all aspects of data access. It is deployed between client applications and a database to provide an abstraction layer that can be used to shape your data access to fit your application’s needs.
Stargate exposes multiple APis to access data stored in Cassandra, including REST, GraphQL, and schemaless Document APIs. This SDK provides a Java API to access to all of them.
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| CQL | Stargate functions as a Cassandra node, allowing existing Cassandra drivers to be utilized for connections. The primary goal is to minimize the number of open connections by enabling clients to connect only to Stargate, rather than directly to the Cassandra data nodes. This approach also serves as an effective method to separate computing and storage components. |
| JSON API | Mongoose compatible Http API exposing operation to use Cassandra as a document database. It should be consider and an upgrade to the previously discussed document API. It also introduces support for vectors and semantic searches. |
| REST | Stargate is a data gateway deployed between client applications and a database. The REST API exposes CRUD access to data stored in Cassandra tables. |
| Document | Stargate serves as a data gateway positioned between client applications and a database. It features the Stargate Document API, which enables the modification and querying of data stored in the form of unstructured JSON documents within collections. A key advantage of the Document API is its schema-less nature, eliminating the need for data modeling. When integrated with Apache Cassandra, the Document API leverages Cassandra's secondary indexes for document indexing. Conversely, when used in conjunction with DataStax Enterprise, it utilizes SAI indexing for this purpose. Further insights into the architecture and storage methodologies of collections can be found in the blog post 'The Stargate Cassandra Documents API. |
| GraphQL | API implementation for exposing Cassandra data over GraphQL. The Stargate GraphQL API is implemented to easily modify and query your table data using GraphQL types, mutations, and queries with any Cassandra deployment. The Stargate GraphQL API has two modes, one developed from native GraphQL schema principles, and one developed with the Cassandra Query Language (CQL) in mind. To distinguish these two modes, the rest of the documentation will refer to the modes as schema-first and cql-first. |
| GRPC | Stargate is a data gateway deployed between client applications and a database. gRPC is a modern, open source remote procedure call (RPC) framework. It enables client and server applications to communicate transparently, and makes it easier to build connected systems. The Stargate gRPC API is implemented to create language-specific queries using CQL with any Cassandra deployment. |
- Use the reference documentation to install Docker Desktop
- Validate your installation with
docker -v
docker run hello-world- Use the reference documentation to install a Java Development Kit
- Validate your installation with
java --version- Use the reference documentation to install Apache Maven
- Validate your installation with
mvn -version- ✅ Use the script
start.shat root of the repository or start stargate with the following docker-compose command:
docker-compose -f ./stargate-sdk-test/src/test/resources/docker-compose.yml up -dExpected output
[+] Building 0.0s (0/0) docker:desktop-linux [+] Running 6/6 ✔ Network resources_stargate Created 0.0s ✔ Container resources-coordinator-1 Healthy 0.0s ✔ Container resources-jsonapi-1 Started 0.0s ✔ Container resources-restapi-1 Started 0.0s ✔ Container resources-graphqlapi-1 Started 0.0s ✔ Container resources-docsapi-1 Started 0.0s
With development mode enabled, Stargate also plays the role of a data node, as such you do not need any extra Cassandra container.
Multiple ports have been declared are here what they are used for. The tools listed here (playground, swagger-ui( will be available about 40s after the docker run commmand.
8080is the Graphql port you can access the playground on http://localhost:8080/playground8081is the Authentication port to retrieve a your token based on user/password8082is the Rest API port. You can access Swagger documentation on http://localhost:8082/swagger-ui/#/ also the health check is done through http://localhost:8082/health8181is the Json Api port. You can access Swagger documentation on http://localhost:8181/swagger-ui/#/ also the health check is done through http://localhost:8181/health8090is the Grpc port. A socket is open listening from Grpc calls.9042is the default CQL port. A socker is open listening CQL calls coming from the native drivers.
- ✅ Create the project
sdk-quickstart-stargatewith a maven archetype:
mvn archetype:generate \
-DarchetypeGroupId=org.apache.maven.archetypes \
-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart \
-DarchetypeVersion=1.4 \
-DgroupId=com.datastax.tutorial \
-DartifactId=sdk-quickstart-stargate \
-Dversion=1.0.0-SNAPSHOT \
-DinteractiveMode=false- ✅ Import the project favorite IDE, and replace the
pom.xmlwith the following XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.datastax.tutorial</groupId>
<artifactId>sdk-quickstart-stargate</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>sdk-quickstart-stargate</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.datastax.stargate</groupId>
<artifactId>stargate-sdk</artifactId>
<version>0.2.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>- ✅ Delete folder
src/test/java, we will experiment with a main class.
ℹ️ Informations:
- We removed the Junit classes generated as we will work a main class.
- We added the latest version
of
stargate-sdkdependency. The xml below may no be up-to-date.
StargateClient is the class you will have to work with, from there you leverage on a fluent api.
Rename App.java to QuickstartStargate.java and update the class accordingly.
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (StargateClient stargateClient = configureStargateClient()) {
// work with Stargate
}
}
public static StargateClient configureStargateClient() {
return StargateClient.builder()
.withCqlContactPoints("localhost:9042")
.withLocalDatacenter("datacenter1")
.withAuthCredentials("cassandra", "cassandra")
.withApiNode(new StargateNodeConfig("127.0.0.1"))
.build();
}ℹ️ Informations
-
Based on parameters provided in the builder, the 5 apis (cql,rest,doc,graphQL,grpc) will be enabled of not.
-
As
CqlSessionis stateful you need to close it at the application shutdown.StargateClientis no different, if you enable Cql api, you need to close it at the application shutdown. To cope with this constraint the class isAutocloseable. -
Cql: needs
contact-points,localdatacenterandcredentials. If not provided the default values for contact points islocalhost:9042 -
Https Api need the
hostname,port numbersandcredentials. But if you are using the default ports no need to specified them.
To run the application you can either use your IDE or maven
mvn exec:java -Dexec.main=com.datastax.tutorial.QuickstartStargate
👁️ Expected output
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: Initializing [StargateClient]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: + Stargate nodes #[1] in [datacenter1]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: + CqlSession :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.rest.ApiDataClient �: + API Data :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.doc.ApiDocumentClient�: + API Document :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.gql.ApiGraphQLClient �: + API GraphQL :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.grpc.ApiGrpcClient �. : + API Grpc :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: Closing CqlSession.public static void testCqlApi(StargateClient stargateClient) {
CqlSession cqlSession = stargateClient.cqlSession().get();
System.out.println("Cql Version (cql) : " + cqlSession
.execute("SELECT cql_version from system.local")
.one().getString("cql_version"));
}
public static void testRestApi(StargateClient stargateClient) {
System.out.println("Keyspaces (rest) : " +
stargateClient.apiRest()
.keyspaceNames()
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
public static void testDocumentaApi(StargateClient stargateClient) {
System.out.println("Namespaces (doc) : " +
stargateClient.apiDocument()
.namespaceNames()
.collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
public static void testGraphQLApi(StargateClient stargateClient) {
System.out.println("Keyspaces (graphQL) : " +
stargateClient.apiGraphQL().cqlSchema().keyspaces());
}
public static void testGrpcApi(StargateClient stargateClient) {
System.out.println("Cql Version (grpc) : " +
stargateClient.apiGrpc()
.execute("SELECT cql_version from system.local")
.one().getString("cql_version"));
}public static void main(String[] args) {
try (StargateClient stargateClient = configureStargateClientDefault()) {
testCqlApi(stargateClient);
testRestApi(stargateClient);
testDocumentaApi(stargateClient);
testGraphQLApi(stargateClient);
testGrpcApi(stargateClient);
}
}👁️ Expected output
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: Initializing [StargateClient]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: + Stargate nodes #[1] in [datacenter1]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: + CqlSession :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.rest.ApiDataClient �: + API Data :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.doc.ApiDocumentClient�: + API Document :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.gql.ApiGraphQLClient �: + API GraphQL :[ENABLED]
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.grpc.ApiGrpcClient �. : + API Grpc :[ENABLED]
Cql Version (cql) : 3.4.4
Keyspaces (rest) : [system_distributed, system, data_endpoint_auth, system_schema, java, stargate_system, system_auth, system_traces]
Namespaces (doc) : [system_distributed, system, data_endpoint_auth, system_schema, java, stargate_system, system_auth, system_traces]
Keyspaces (graphQL) : {"data":{"keyspaces":[{"name":"system_distributed"},{"name":"system"},{"name":"data_endpoint_auth"},{"name":"system_schema"},{"name":"java"},{"name":"stargate_system"},{"name":"system_auth"},{"name":"system_traces"}]}}
Cql Version (grpc) : 3.4.4
INFO �com.datastax.stargate.sdk.StargateClient �: Closing CqlSession.ℹ️ Reminder: You can download the code here 📥 Download
Congratulations: you are ready to explore each Api leveraging the fluent api. |
Related Api Reference documentation and endpoints can be found there
Class ApiDataClient is the core class to work with Rest DATA. There are multiple ways to retrieve or initialize it.
// Option1. Given an astraClient
ApiDataClient client1 = astraClient.apiStargateData();
ApiDataClient client2 = astraClient.getStargateClient().apiRest();
// Option 2. Given a StargateClient
ApiDataClient client3 = stargateClient.apiRest();
// Option 3. Constructors
ApiDataClient client4_Astra = new ApiDataClient("http://api_endpoint", "apiToken");
ApiDataClient client5_Stargate = new ApiDataClient("http://api_endpoint",
new TokenProviderDefault("username", "password", "http://auth_endpoint");From now, in another samples, we will use the variable name apiClient as our working instance of ApiDataClient
DataApiIntegrationTest is the main unit test for this API and could be use as reference code
- ✅. Lists available Keyspace Names
Stream<String> keyspaceNames = apiClient.keyspaceNames();- ✅. Lists available Keyspaces
Stream<Keyspace> keyspaces = apiClient.keyspaces();- ✅. Find a keyspace by its id
Optional<Keyspace> ns1 = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").find();- ✅. Test if a keyspace exists
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").exist();- ✅. Create a new keyspace
🚨 As of Today, namespaces and keyspaces creations in ASTRA are available only at the DevOps API level but work in in a StandAlone stargate deployment
// Create a keyspace with a single DC dc-1
DataCenter dc1 = new DataCenter("dc-1", 1);
apiClient.keyspace("ns1").create(dc1);
// Create a keyspace providing only the replication factor
apiClient.keyspace("ns1").createSimple(3);- ✅. Delete a keyspace
🚨 As of today namespaces and keyspaces creations are not available in ASTRA but work as expected with standalone stargate.
apiClient.keyspace("ns1").delete();ℹ️ Tips
You can simplify the code by assigning apiClient.keyspace("ks1") to a KeyspaceClient variable as shown below:
KeyspaceClient ks1Client = astraClient.apiStargateData().keyspace("ns1");
// Create if not exist
if (!ks1Client.exist()) {
ks1Client.createSimple(3);
}
// Show datacenters where it lives
ks1Client.find().get().getDatacenters()
.stream().map(DataCenter::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
// Delete
ks1Client.delete();- ✅. Lists available tables in a keyspace
// We can create a local variable to shorten the code.
KeyspaceClient ks1Client = apiClient.keyspace("ks1");
// List names of the tables
Stream<String> tableNames = ks1Client.tableNames();
// List Definitions of the table (primarykey...)
Stream<TableDefinition> tableDefinitions = ks1Client.tables();- ✅. Check if a table exists
TableClient tableXClient = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x");
boolean colExist = tableXClient.exist();- ✅. Retrieve a table definition from its name
Optional<TableDefinition> = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").find();- ✅. Create a table
A TableDefinition is expected to create a table. It will detailed all columns and their specific natures (partition key and clustering columns). It can be pretty verbose as such a Builder is provided TableCreateBuilder.
// Using a builder to define the table structure
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").create(
CreateTable.builder()
.ifNotExist(true)
.addPartitionKey("genre", "text")
.addClusteringKey("year", "int", Ordering.DESC)
.addClusteringKey("title", "text", Ordering.ASC)
.addColumn("upload", "timestamp")
.addColumn("tags", "set<text>")
.addColumn("frames", "list<int>")
.addColumn("tuples", "tuple<text,text,text>")
.addColumn("formats", "frozen<map <text,text>>")
.build()
);- ✅. Update Table options
// You can change the TTL and some clustering columns informations
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x")
.updateOptions(new TableOptions(25, null));- ✅. Delete a table
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").delete();- ✅. Lists available columns in a Table
// Get column Names
Stream<String> columnNames = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").columnNames();
// Get Column Definition
Stream<ColumnDefinition> columns = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").columns();- ✅. Check if columns exists
boolean colExist = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").column("col1").exist();- ✅. Retrieve a columns from its name
Optional<ColumnDefinition> col = apiClient
.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.column("col1")
.find();- ✅. Create an new Column
apiClient.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.column("col1")
.create(new ColumnDefinition("col", "text"));- ✅. Rename a column
apiClient.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.column("col1")
.rename("col2");- ✅. Delete a column
apiClient.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.column("col1").delete();- ✅. Lists available indexes in a Table
// Get column Names
Stream<String> indexesNames = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").indexesNames();
// Get Column Definition
Stream<IndexDefinition> indexes = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").indexes();- ✅. Check if index exists
boolean colExist = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").table("table_x").index("idx1").exist();- ✅. Retrieve a index from its name
Optional<IndexDefinition> idxDef = apiClient
.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.index("idx1")
.find();- ✅. Create an new Index
CreateIndex cIdx = CreateIndex.builder()
.ifNotExist(true)
.name("idx1").column("title")
.sasi()
.build();
apiClient.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.index("idx1")
.create(cIdx);- ✅. Delete an Index
apiClient.keyspace("ks1")
.table("table_x")
.index("idx1")
.delete();- ✅. Lists available types in a keyspace
// We can create a local variable to shorten the code.
KeyspaceClient ks1Client = apiClient.keyspace("ks1");
// List names of the types
Stream<String> typeNames = ks1Client.typeNames();
// List Definitions of the type (attributes...)
Stream<TypeDefinition> typeDefinitions = ks1Client.types();- ✅. Check if a type exists
TypeClient typeVideo = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").type("videos");
boolean colExist = typeVideo.exist();- ✅. Retrieve a type definition from its name
Optional<TypeDefinition> = apiClient.keyspace("ks1").type("videos").find();- ✅. Create a type
// Using a builder to define the table structure
CreateType ct = new CreateType("videos", true);
ct.getFields().add(new TypeFieldDefinition("city", "text"));
ct.getFields().add(new TypeFieldDefinition("zipcode", "int"));
ct.getFields().add(new TypeFieldDefinition("street", "text"));
ct.getFields().add(new TypeFieldDefinition("phone", "list<text>"));
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").type("videos").create(ct);- ✅. Update a type
UpdateType ut= new UpdateType();
// Fields to add
ut.getAddFields().add(new TypeFieldDefinition("country","text" ));
// Fields to rename
ut.getRenameFields().add(new TypeFieldUpdate("city", "town"));
address.update(ut);- ✅. Delete a type
apiClient.keyspace("ks1").type("videos").delete();Stargate and Astra bring great innovation by allowing Apache Cassandra™ to store JSON documents like a document-oriented noSQL database. The same data model is in use for each document collection leveraging a document shredding stratefy.
Main client object initializations (
AstraClientandStargateClient) have been detailed on the Home page. Moving forward the sample code will reuse those classes but do not initialize them.
ApiDocumentClient is the core class when it comes to work with documents.
// Option1. Retrieved from astraClient
ApiDocumentClient apiDocClient1 = astraClient.apiStargateDocument();
ApiDocumentClient apiDocClient2 = astraClient.getStargateClient().apiDocument()
// Option 2. Retrieved from StargateClient
ApiDocumentClient astraClient3 = stargateClient.apiDocument();
// Option 3. Built from the endpoint and credentials
ApiDocumentClient astraClient4 = new ApiDocumentClient("http://api_endpoint", "apiToken");
ApiDocumentClient astraClient5 = new ApiDocumentClient("http://api_endpoint",
new TokenProviderDefault("username", "password", "http://auth_endpoint");For the rest of the document apiDocClient will refer to ApiDocumentClient but the initialization code will not be duplicated.
Namespace if the term used to talk about keyspaces when dealing with the document API.
DocumentApiIntegrationTest is the unit test class for this API where you can find more sample usage of the SDK.
- ✅. List
NamespacesNames
Stream<String> namespaces = apiDocClient.namespaceNames();- ✅. List
Namespacesobjects
Stream<Namespace> namespaces = apiDocClient.namespaces();The Namespace class provides the replication factor and or the datacenter list for a namespace.
public class Namespace {
protected String name;
protected Integer replicas;
protected List<DataCenter> datacenters;
}- ✅. Find
Namespaceby its name
The parameter ns1 is here the unique identifier for the namespace
Optional<Namespace> ns1 = apiDocClient.namespace("ns1").find();- ✅. Test if
Namespaceexists
The parameter ns1 is here the unique identifier for the namespace
apiDocClient.namespace("ns1").exist();- ✅. Create
Namespace
🚨 As of Today, in Astra, Namespaces and Keyspaces creations are only available at the DevOps API level or through the user interface.
// Create a namespace with a single DC dc-1
DataCenter dc1 = new DataCenter("dc-1", 1);
apiDocClient.namespace("ns1").create(dc1);
// Create a namespace providing only the replication factor
apiDocClient.namespace("ns1").createSimple(3);- ✅. Delete a namespace
🚨 As of Today, in Astra, Namespaces and Keyspaces deletions are only available at the DevOps API level or through the user interface.
The parameter ns1 is here the unique identifier for the namespace.
apiDocClient.namespace("ns1").delete();ℹ️ Fluent API
You can assign apiDocClient.namespace("ns1") to a NamespaceClient variable as shown below to simplify your code.
NamespaceClient ns1Client = astraClient.apiStargateDocument().namespace("ns1");
// Create if not exist
if (!ns1Client.exist()) ns1Client.createSimple(3);
// Show datacenters
ns1Client.find().get()
.getDatacenters()
.stream()
.map(DataCenter::getName)
.forEach(System.out::println);
// Delete
ns1Client.delete();Thanks to fluent API code is simplified by assigning ns1Client as NamespaceClient for ns1.
NamespaceClient ns1Client = astraClient.apiStargateDocument().namespace("ns1");- ✅. List
Collectionsin namespace
Stream<String> colNames = ns1Client.collectionNames();- ✅. Test if
Collectionexists
The parameter col1 is here the unique identifier for the collection in the current namespace.
boolean colExist = = ns1Client.collection("col1").exist();- ✅. Retrieve a
Collectionfrom its name
The parameter col1 is here the unique identifier for the collection in the current namespace.
Optional<CollectionDefinition> = ns1Client.collection("col1").find();- ✅. Create an empty
Collection
The parameter col1 is here the unique identifier for the collection in the current namespace.
ns1Client.collection("col1").create();- ✅. Delete a collection
The parameter col1 is here the unique identifier for the collection in the current namespace.
ns1Client.collection("col1").delete();ℹ️ Fluent API
Code can be simplified by assigning col1Client as CollectionClient for collection col1 in namespace ns1.
CollectionClient col1Client = astraClient.apiStargateDocument().namespace("ns1").collection("col1");- 📘. About
Document
With Stargate document API, documents are retrieved with a Json payload and an unique identifier (UUID).
{
"data": {
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ab": { "p1": "v1", "p2": "v2"},
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ac": { "p1": "v11", "p2": "v21"},
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ad": { "p1": "v12", "p2": "v22"}
}
}Document states as a wrapper to give access to both documentId (unique identifier) and document (payload).
public class Document<T> {
private String documentId;
private T document;
// Constructor, Getters, Setters
}- 📘. Paging
Due the verbose nature of the document API the maximum number of items one could retrieve from an Api call is 20 at maximum. As such, every request is paged. If the number of records is greater than the page size a field called pagingStateis provided in the response.
{
"pagingState": "jhfekwfkwejefejwhkjewhehwrjhewjkrhewjrhewklrhewklrhewj"
"data": {
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ab": { "p1": "v1", "p2": "v2"},
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ac": { "p1": "v11", "p2": "v21"},
"9e14db1c-0a05-47d2-9f27-df881f7f37ad": { "p1": "v12", "p2": "v22"}
}
}This value pagingState has to be populated in the Query input object in order to request the next page.
// Query initialization
PageableQuery query = PageableQuery.builder().build();
// No pagingState provided = page 1
Page<Document<String>> page1 = cp.findPage(query);
// Updating the query with pagingState of page1
query.setPageState(page1.getPageState().get());
// Fetching page2
Page<Document<String>> page2 = cp.findPage(query);🚨The following chapters propose
findAllmethods. Under the hood pages are fetched one after the other until exhausting the dataset. It could be slow - use it with caution.
Document payloads can be deserialized as beans or left unchanged as Json. To build the expected beans you can either leverage on Jackson or implement your custom DocumentMapper.
// Query initialization
PageableQuery query = PageableQuery.builder().build();
// Retrieve data as JSON, no mapper
Page<Document<String>> pageOfJsonRecords = cp.findPage(query);
// Retrieve data with default JACKSON Mapper
Page<Document<Person>> pageOfPersonRecords1 = cp.findPage(query, Person.class);
// Retrieve data with a CUSTOM Mapper
Page<Document<Person>> pageOfPersonRecords2 = cp.findPage(query, new DocumentMapper<Person>() {
public Person map(String record) {
return new Person();
}
});- ✅. Search Documents in a collection (with Paging)
The document Api allows to search on any fields in the document providing a where clause.
In the API where clause looks like:
{"age": {"$gte":30}, "lastname": {"$eq":"PersonAstra2"}}This SDK provides dedicated queries and builders to help create the queries. They are of 2 kinds Query and PageableQuery.
Using the fluent API, the client collection is defined as col1Client
CollectionClient col1Client = astraClient.apiStargateDocument().namespace("ns1").collection("col1");Build a Query and find page with no mapper
// Build pageable query
PageableQuery query = PageableQuery.builder()
.selectAll() // can be select("field1", "field2", ...)
.where("firstName").isEqualsTo("John")
.and("lastName").isEqualsTo("Connor")
.pageSize(3)
//.pageState() if not page 1
.build();
// Retrieve `Page<Document<String>>` if no marshaller, Json String are retrieved
Page<Document<String>> page1 = col1Client.findPage(query);
// Use pagingState in page1 to retrieve page2
if (page1.getPageState().isPresent()) {
query.setPageState(page1.getPageState().get());
Page<Document<String>> page2 = col1Client.findPage(query);
}- Retrieve
Page<Document<T>>using default Jackson Mapper
Page<Document<Person>> page1 = col1Client.findPage(query, Person.class);
// Use pagingState in page1 to retrieve page2
if (page1.getPageState().isPresent()) {
query.setPageState(page1.getPageState().get());
Page<Document<Person>> page2 = col1Client.findPage(query, Person.class);
}- Retrieve your
Page<Document<T>>using a custom mapper
public static class PersonMapper implements DocumentMapper<Person> {
@Override
public Person map(String record) {
Person p = new Person();
// custom logic
return p;
}
}
Page<Document<Person>> page1 = col1Client.findPage(query, new PersonMapper());-
✅. Search Documents in a collection (without Paging)
-
Build
Query
Query query = Query.builder()
.select("field1", "field2", ...) // to get .selectAll()
.where("firstName").isEqualsTo("John")
.and("lastName").isEqualsTo("Connor")
.build();- Retrieve
Stream<Document<String>>, if you do not provide any marshaller you get a Json String.
Stream<Document<String>> result = col1Client.findAll(query);- Retrieve your
Stream<Document<T>>using default Jackson Mapper
Stream<Document<Person>> res1 = col1Client.findAll(query, Person.class);- Retrieve your
Stream<Document<T>>using your custom mapping
public static class PersonMapper implements DocumentMapper<Person> {
@Override
public Person map(String record) {
Person p = new Person();
// custom logic
return p;
}
}
Stream<Document<Person>> page1 = col1Client.findAll(query, new PersonMapper());- Retrieving all collection documents is possible, it is the default query.
// Get all documents
Stream<Document<String>> allDocs1 = col1Client.findAll();
// Equivalent to
Stream<Document<String>> allDocs2 = ccol1Clientp.findAll(Query.builder().build());
// Also available
Stream<Document<Person>> allDocs3 = col1Client.findAll(Person.class);
Stream<Document<Person>> allDocs4 = col1Client.findAll(new DocumentMapper());- ✅. Get a
Documentby its identifier
// doc1 is the document Id in the collection
boolean docExist = col1Client.document("doc1").exist();
// Find if it exists (no mapper)
Optional<String> p = col1Client.document("doc1").find();
// Find if it exists (default mapper)
Optional<Person> p = col1Client.document("doc1").find(Person.class);
// Find if it exists (custom mapper)
Optional<Person> p = col1Client.document("doc1").find(new DocumentMapper<Person>() { ...});- ✅. Create a new document (without providing identifier)
The method createNewDocument in CollectionClient will create a document generating the unique identifier as a UUID. (this is how the underlying api works).
// Define an object
Person john = new Person("John", "Doe", 20, new Address("Paris", 75000));
// As no id has been provided, the API will create a UUID and returned it to you
String docId = col1Client.createNewDocument(john);- ✅. Create/update document by providing identifier
// Define an object
Person john2 = new Person("John", "Doe", 20, new Address("Paris", 75000));
// Now the id is provided (myId) and we can upsert
String docId = col1Client.document("myId").upsert(john2, Person.class);- ✅. Delete a document from its identifier
col1Client.document("myId").delete();✅. Count documents in a collection
🚨 This operation can be slow as it leverage on
findAllminimizing the payloads
int docNum = col1Client.count();- ✅. Find part of a document
The document API allows to work with nested structure in a document. {document-path} (subpath) is required at the URL level
http://{doc-api-endpoint}/namespaces/{namespace-id}/collections/{collection-id}/{document-id}/{document-path}
Given a Json DOCUMENT with UUID e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818 :
{
"age": 25,
"firstname": "PersonAstra5",
"lastname": "PersonAstra1",
"address": {
"city": "Paris",
"zipCode": 75000
},
}You can retrieve the zipCode with:
http://{doc-api-endpoint}/namespaces/ns1/collections/person/e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818/address/zipCode
The SDK provides some utility methods to work with :
// Retrieve an object and marshall
Optional<Address> address = col1Client
.document("e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818")
.findSubDocument("address", Address.class);
// Retrieve a scalar deeper in the tree
Optional<Integer> zipcode = col1Client
.document("e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818")
.findSubDocument("address/zipCode", Integer.class);- ✅. Update a sub document
// Update an existing attribute of the JSON
col1Client.document("e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818")
.updateSubDocument("address", new Address("city2", 8000));
// Create a new attribute in the document
col1Client.document("e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818")
.updateSubDocument("secondAddress", new Address("city2", 8000));- ✅. Delete part of a documents
col1Client.document("e8c5021b-2c91-4015-aec6-14a16e449818")
.deleteSubDocument("secondAddress");- 📘.
StargateDocumentRepositoryoverview
If you have work with Spring Data or Active Record before you might already know what the repository are. Those are classes that provides you CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations without you having to code anything.
Here this is not different, if you provide an object for a collection this is what is available for you
public interface StargateDocumentRepository <DOC> {
// Create
String insert(DOC p);
void insert(String docId, DOC doc);
// Read unitary
boolean exists(String docId);
Optional<DOC> find(String docId);
// Read records
int count();
DocumentResultPage<DOC> findPage();
DocumentResultPage<DOC> findPage(SearchDocumentQuery query) ;
Stream<ApiDocument<DOC>> findAll();
Stream<ApiDocument<DOC>> findAll(SearchDocumentQuery query);
// Update
void save(String docId, DOC doc);
// Delete
void delete(String docId);
}- ✅. Initialization of repository
// Initialization (from namespaceClients)
NamespaceClient ns1Client = astraClient.apiStargateDocument().namespace("ns1");
StargateDocumentRepository<Person> personRepository1 =
new StargateDocumentRepository<Person>(ns1Client, Person.class);Points to note:
- No collection name is provided here. By default the SDK will use the class name in lower case (here
person) - If you want to override the collection name you can annotate your bean
Personwith@Collection("my_collection_name")
// Initialization from CollectionClient, no ambiguity on collection name
CollectionClient colPersonClient = astraClient.apiStargateDocument()
.namespace("ns1").collection("person");
StargateDocumentRepository<Person> personRepository2 =
new StargateDocumentRepository<Person>(colPersonClient, Person.class);- ✅. CRUD
We assume that the repository has been initialized as describe above and name personRepo.
if (!personRepo.exists("Cedrick")) {
personRepo.save("Cedrick", new Person("Cedrick", "Lunven", new Address()));
}
// Yeah
personRepository.findAll() // Stream<ApiDocument<Person>>
.map(ApiDocument::getDocument) // Stream<Person>
.map(PersonRepo::getFirstname) // Stream<String>
.forEach(System.out::println);