This tutorial demonstrates how to deploy the Online Boutique microservices demo application across multiple Kubernetes clusters that are located in different public and private cloud providers. This project contains a 10-tier microservices application developed by Google to demonstrate the use of technologies like Kubernetes.
In this tutorial, you will create a Virtual Application Network that enables communications across the public and private clusters. You will then deploy a subset of the application's grpc based microservices to each cluster. You will then access the Online Boutique web interface to browse items, add them to the cart and purchase them.
Top complete this tutorial, do the following:
- Prerequisites
- Step 1: Set up the demo
- Step 2: Deploy the Virtual Application Network
- Step 3: Deploy the application microservices
- Step 4: Expose the microservices to the Virtual Application Network
- Step 5: Access the Online Boutique Application
- Cleaning up
- Next steps
- The
occommand-line tool (installation guide) - The
skuppercommand-line tool, the latest version (installation guide)
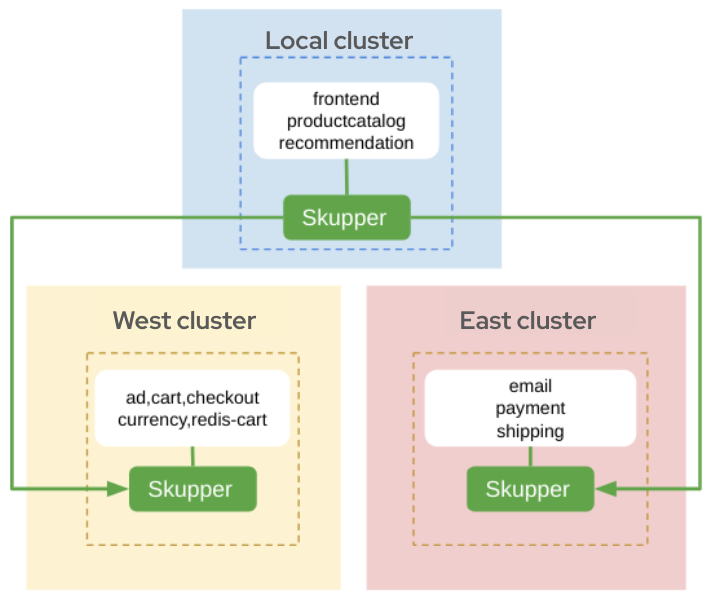
The basis for this demonstration is to depict the deployment of member microservices for an application across both private and public clusters and for the ability of these microsservices to communicate across a Virtual Application Network. As an example, the cluster deployment might be comprised of:
- A private cloud cluster running on your local machine or any cloud provider
- Two public cloud clusters running in public cloud providers
While the detailed steps are not included here, this demonstration can alternatively be performed with three separate namespaces on a single cluster.
-
On your local machine, make a directory for this tutorial and clone the example repo:
mkdir boutique-demo cd boutique-demo git clone https://github.com/cmcornejo/skupper-example-grpc.git -
Prepare the target clusters.
- On your local machine, log in to each cluster in a separate terminal session.
- In each cluster, create a namespace to use for the demo.
- In each cluster, set the kubectl config context to use the demo namespace (see kubectl cheat sheet for more information)
oc config set-context --current --namespace <namespace>
- (Optional) I use https://kcli.readthedocs.io/en/latest/[kcli] as a way to handle virtual machines to create separate environments locally.
On each cluster, using the skupper tool, define the Virtual Application Network (VAN) and the connectivity for the peer clusters.
-
In the terminal for the east cluster, deploy the east application router. Create a connection token for connections from the west cluster:
skupper init --site-name east --enable-console=false skupper token create east-token.yaml
-
In the terminal for the east-2 cluster, deploy the east-2 application router, create a connection token for connections from the west cluster:
skupper init --site-name east-02 skupper token create east-02-token.yaml
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, deploy the west application router and define its connections to the east and east-2 clusters.
# we are only deploying the console in this cluster skupper init --site-name west --enable-console --enable-flow-collector --console-auth=openshift skupper link create east-token.yaml skupper link create east-2-token.yaml -
In each of the cluster terminals, verify connectivity has been established
skupper link status
NOTE:
There are ONLY two links between sites:
- east->west
- east-2->west
There isn’t link between east and east-2
After creating the Virtual Application Network, deploy the grpc based microservices for the Online Boutique application. There are three deployment .yaml files
labelled a, b, and c. These files (arbitrarily) define a subset of the application microservices to deploy to a cluster.
| Deployment | Microservices | Site |
|---|---|---|
| deployment-ms-a.yaml | frontend, productcatalog, recommendation | west |
| deployment-ms-b.yaml | ad, cart, checkout, currency, redis-cart | east |
| deployment-ms-c.yaml | email, payment, shipping | east-2 |
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, deploy the following:
oc apply -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-a.yaml
-
In the terminal for the east cluster, deploy the following:
oc apply -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-b.yaml
-
In the terminal for the east-2 cluster, deploy the following:
oc apply -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-c.yaml
There are three script files labelled -a, -b, and -c. These files expose the services created above to join the Virtual Application Network. Note that the frontend service is not assigned to the Virtual Application Network as it is setup for external web access.
| File | Deployments | Site |
|---|---|---|
| expose-deployments-a.sh | productcatalog, recommendation | west |
| expose-deployments-b.sh | ad, cart, checkout, currency, redis-cart | east |
| expose-deployments-c.sh | email, payment, shipping | east-2 |
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, execute the following annotation script:
skupper-example-grpc/expose-deployments-a.sh
-
In the terminal for the east cluster, execute the following annotation script:
skupper-example-grpc/expose-deployments-b.sh
-
In the terminal for the east-2 cluster, execute the following annotation script:
skupper-example-grpc/expose-deployments-c.sh
The web frontend for the Online Boutique application can be accessed via the frontend-external service. In the
terminal for the west cluster, start a firefox browser and access the shop UI.
/usr/bin/firefox --new-window "http://$(oc get route frontend-external -o=jsonpath='{.spec.host}')/"Open a browser and use the url provided above to access the Online Boutique.
The Online Boutique application has a load generator that creates realistic usage patterns on the website.
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, deploy the load generator:
oc apply -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-loadgenerator.yaml
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, observe the output from the load generator:
oc logs -f deploy/loadgenerator
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, stop the load generator:
oc delete -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-loadgenerator.yaml
-
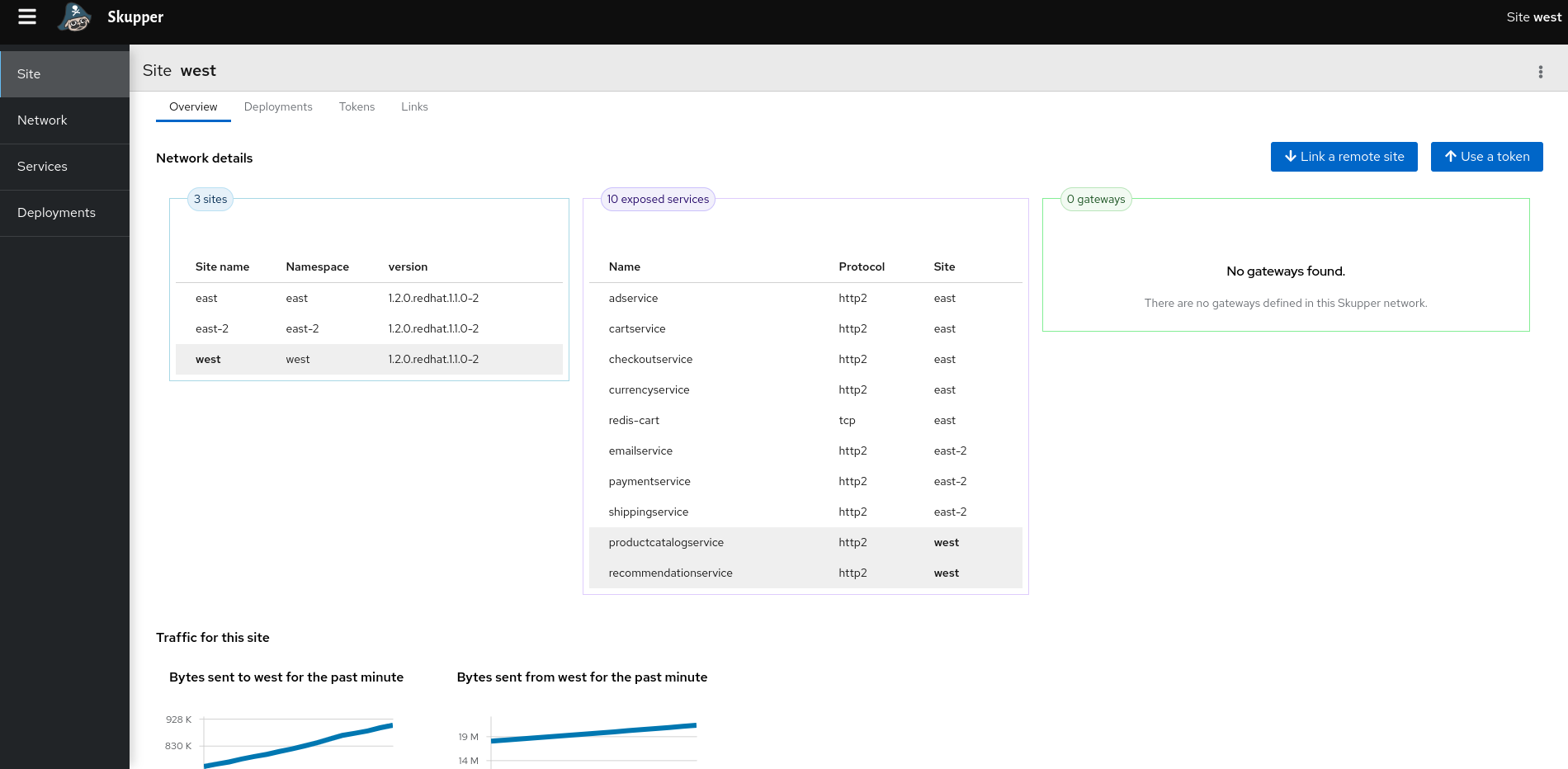
In the terminal for the west cluster, retrieve the skupper console url:
skupper status Skupper is enabled for namespace "west" in interior mode. It is connected to 2 other sites. It has 10 exposed services. The site console url is: https://skupper-west.apps.<ocp-basedomain>
-
Check Site tab:
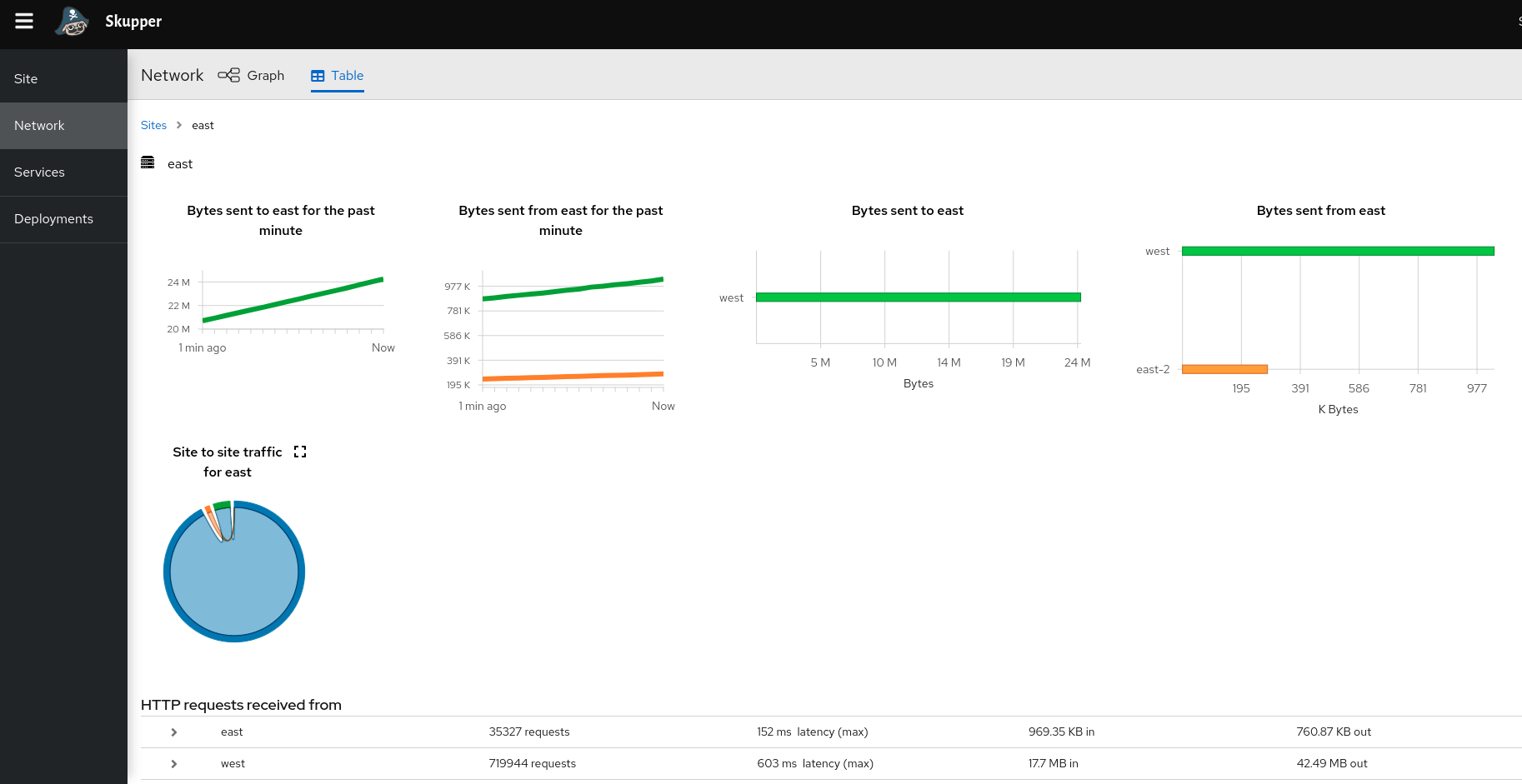
- Check Network tab:
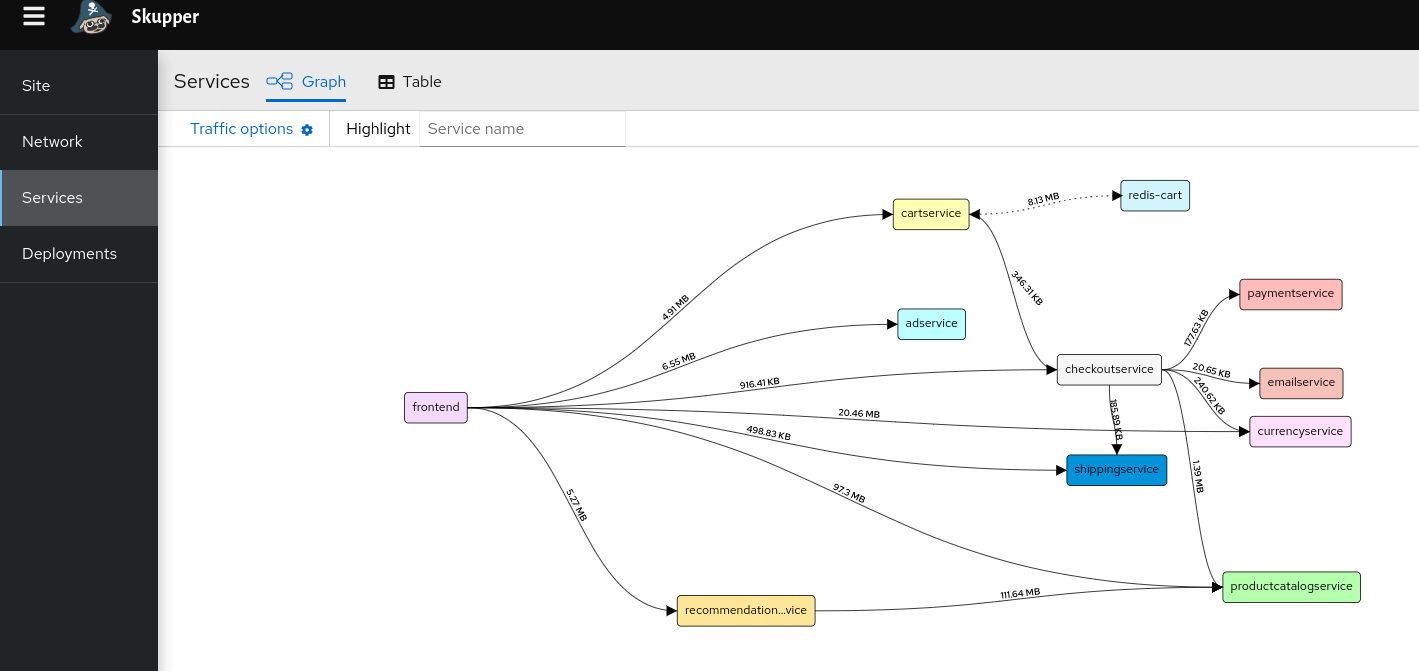
- Check Services tab:
- Check Deployments tab:
Restore your cluster environment by returning the resources created in the demonstration. On each cluster, delete the demo resources and the skupper network:
-
In the terminal for the west cluster, delete the resources:
skupper-example-grpc/unexpose-deployments-a.sh oc delete -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-a.yaml skupper delete
-
In the terminal for the east cluster, delete the resources:
skupper-example-grpc/unexpose-deployments-b.sh oc delete -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-b.yaml skupper delete
-
In the terminal for the east-2 cluster, delete the resources:
skupper-example-grpc/unexpose-deployments-c.sh oc delete -f skupper-example-grpc/deployment-ms-c.yaml skupper delete