The PostgreSQL Operator provides a Kubernetes operator capability for managing PostgreSQL Clusters deployed within a Kubernetes.
The PostgreSQL Operator leverages Kubernetes Third Party Resources to define custom resource types such as:
-
pgcluster
-
pgbackups
-
pgupgrades
-
pgclones
-
pgpolicies
-
pgpolicylogs
Once those custom objects are defined, Kubernetes provides the ability to create and manage those objects similar to any other native Kubernetes object.
The PostgreSQL Operator runs within Kubernetes detecting these new custom object types being created, updated, or removed.
Once the objects are detected, the PostgreSQL Operator enables users to perform operations across the Kubernetes environment, including:
-
Create a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Destroy a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Backup a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Scale a a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Restore a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Upgrade a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
View PVC
-
Test Connections to a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Clone a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Create a SQL-based Policy
-
Apply a SQL-based Policy to a PostgreSQL Cluster
-
Perform User Management
-
Apply User Defined Labels to PostgreSQL Clusters
-
Perform Password Management
What actually gets created on the Kube cluster for a pgcluster resource is defined as a deployment strategy. Strategies are documented in detail in Deployment Strategies.
-
greater than Kubernetes 1.5.3+
-
greater than Openshift Origin 1.5.1+ and Openshift Container Platform 3.5
To build and deploy the Operator on your Kube system, follow the instructions documented on the Build and Install page.
With the operator deployed, the pgo command line interface can execute commands that the postgres-operator understands and reacts to.
You can configure both the client and the operator. The configuration options are documented on the Configuration page.
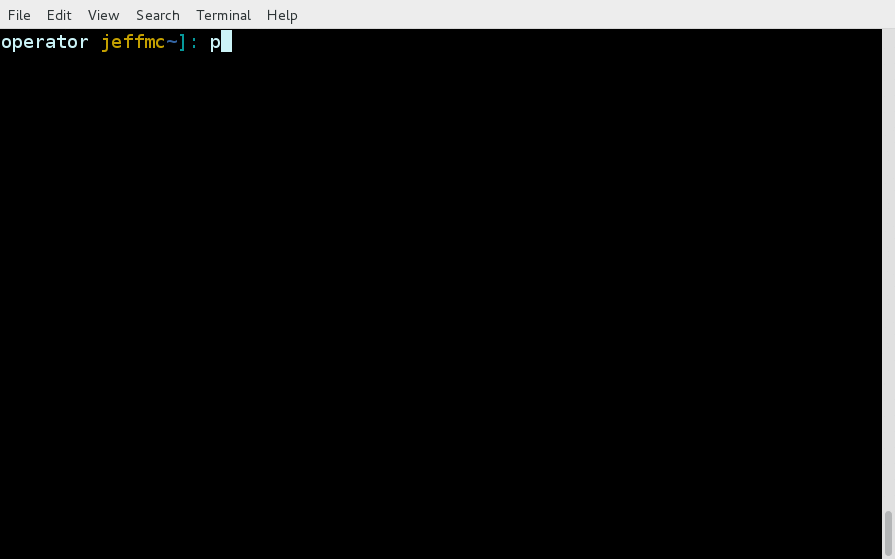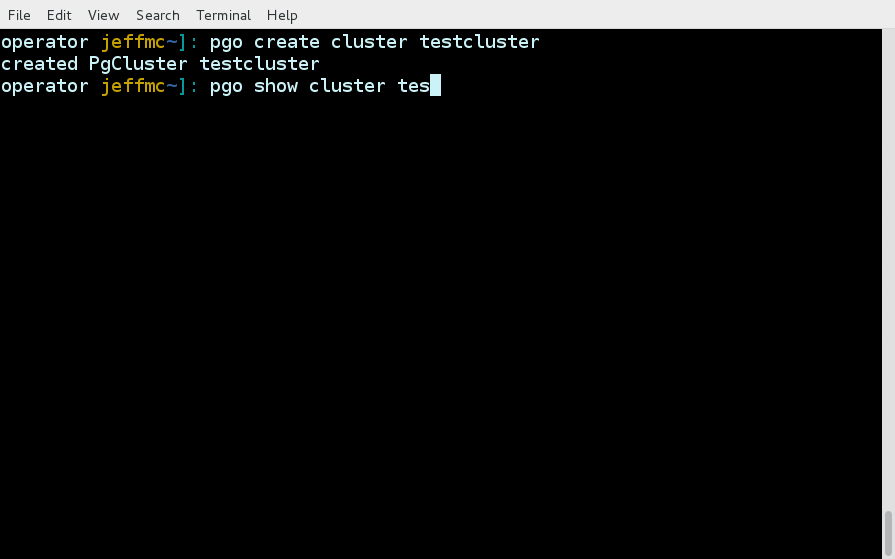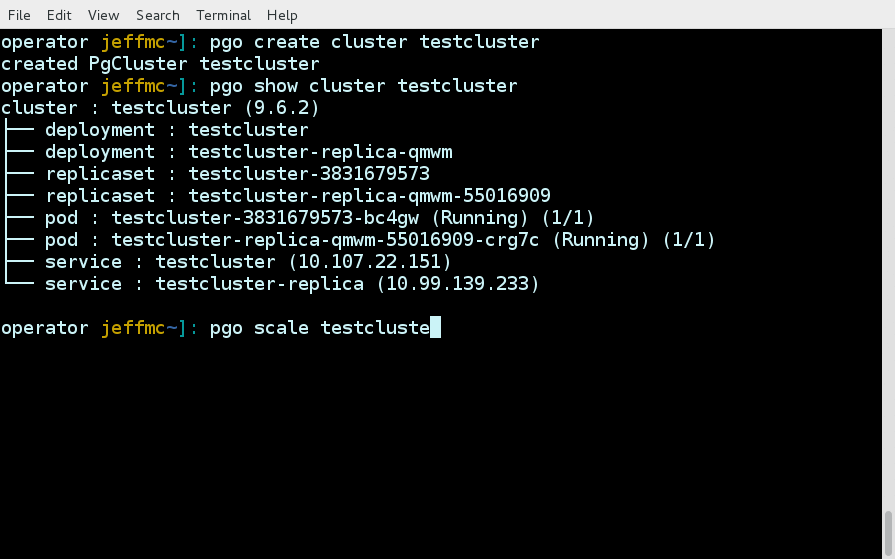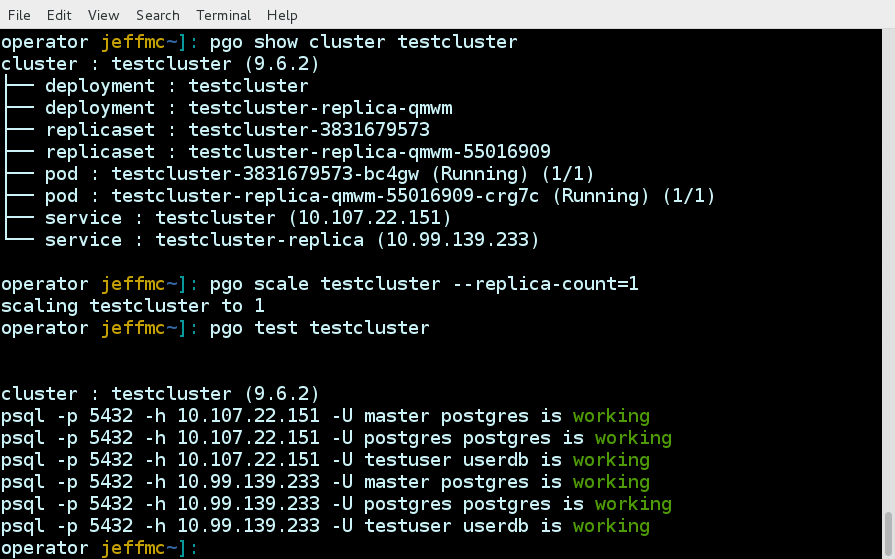
Some examples of using the pgo command line interface are as follows.
pgo show cluster all
pgo show cluster db1 db2 db3
pgo show cluster mycluster
pgo show cluster mycluster --show-secrets=truepgo create cluster myclusterpgo scale mycluster --replica-count=2pgo delete cluster myclusterpgo create backup myclusterpgo create cluster myrestore --secret-from=foo --backup-pvc=mypvc --backup-path=foo-backups/2017-03-21-15-57-21pgo create upgrade myclusterpgo create upgrade mycluster --upgrade-type=majorpgo show pvc mypvcpgo test myclusterpgo clone mycluster --name=myclonepgo create policy policy1 --in-file=./policy1.sql
pgo create policy policy1 --url=https://someurl/policy1.sql|
Warning
|
Apply a Policy
policies are POWERFUL because they are executed as the superuser in PostgreSQL
which allows for any sort of SQL to be executed.
|
pgo apply policy1 --selector=name=myclusterDetails on the pgo commands and complex examples are found in the User Guide
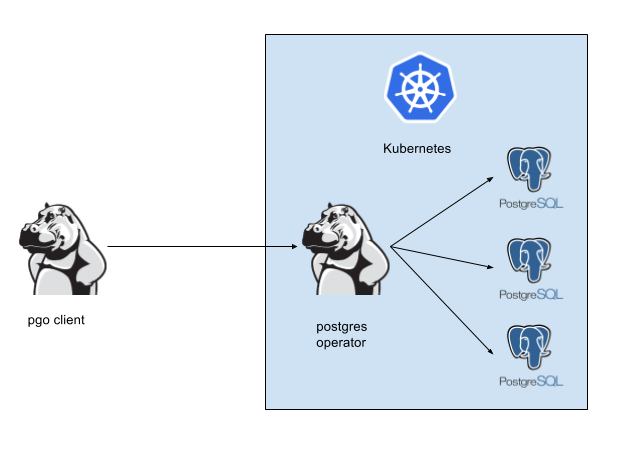
In the following diagram, the postgres operator client, pgo, is shown interacting with the postgres operator that runs within a Kubernetes cluster. The operator is responsible for creating or modifying PostgreSQL databases deployed within the Kube cluster.
The operator functionality runs in a Kubernetes Deployment on your Kubernetes cluster. The postgres-operator Docker container image is available on Dockerhub.
You can also build the Docker image for postgres-operator using the build instructions located on the Build and Setup page.