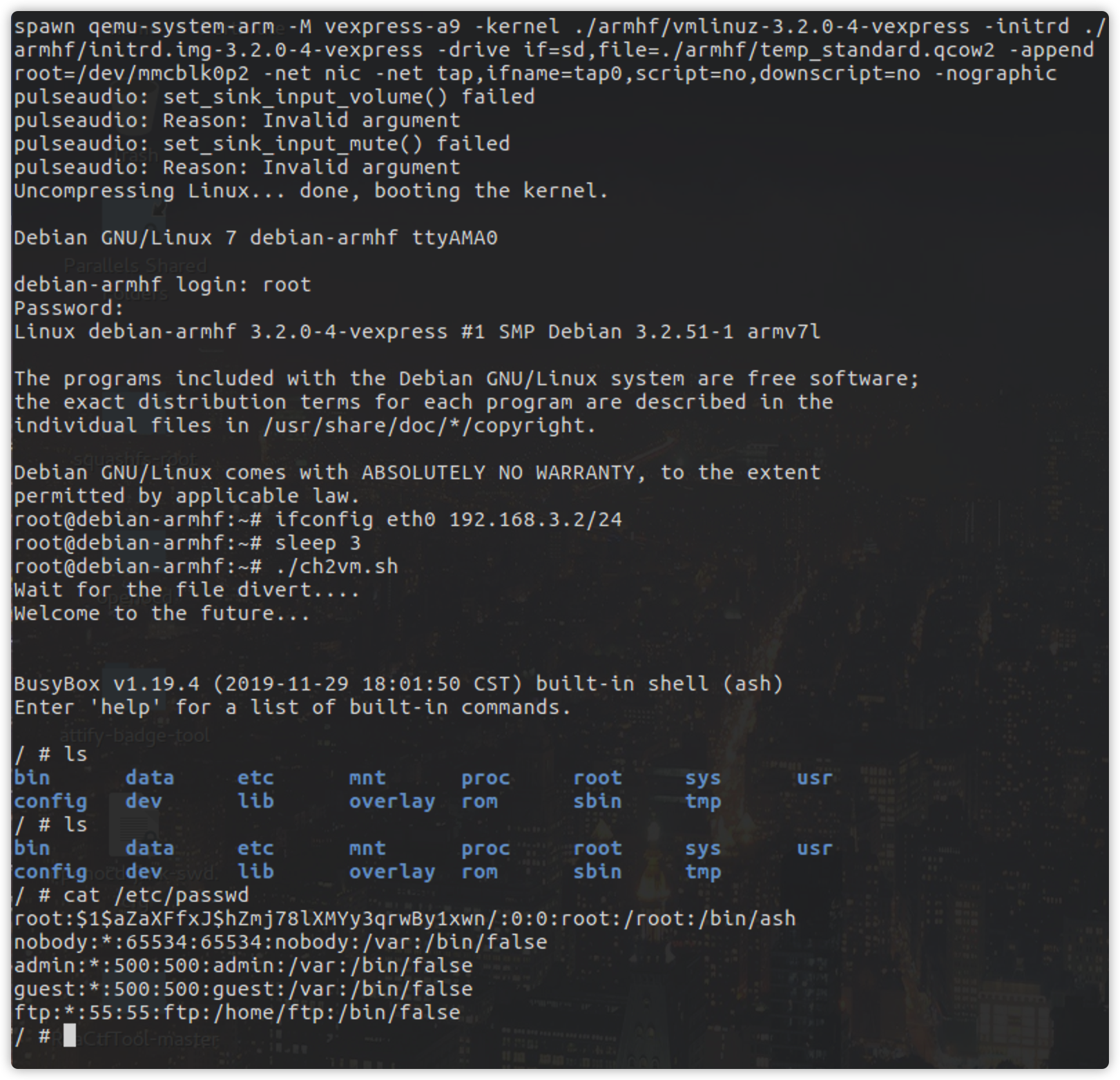
One command to boot the QEMU system
These instructions will get you a copy of the project up and running on your local machine for development and testing purposes. See deployment for notes on how to deploy the project on a live system.
You need to have Ubuntu16 running in your computer, please install them in the download page.
To install all commands in Ubuntu 16.04
> sudo apt-get update
> sudo apt-get install qemu-system-mips
> sudo apt-get install qemu-user
> sudo apt-get install qemu-user-static
> sudo apt-get install qemu-utils
> sudo apt-get install expect
> sudo apt-get install uml-utilities
> sudo apt-get install gnome-terminal
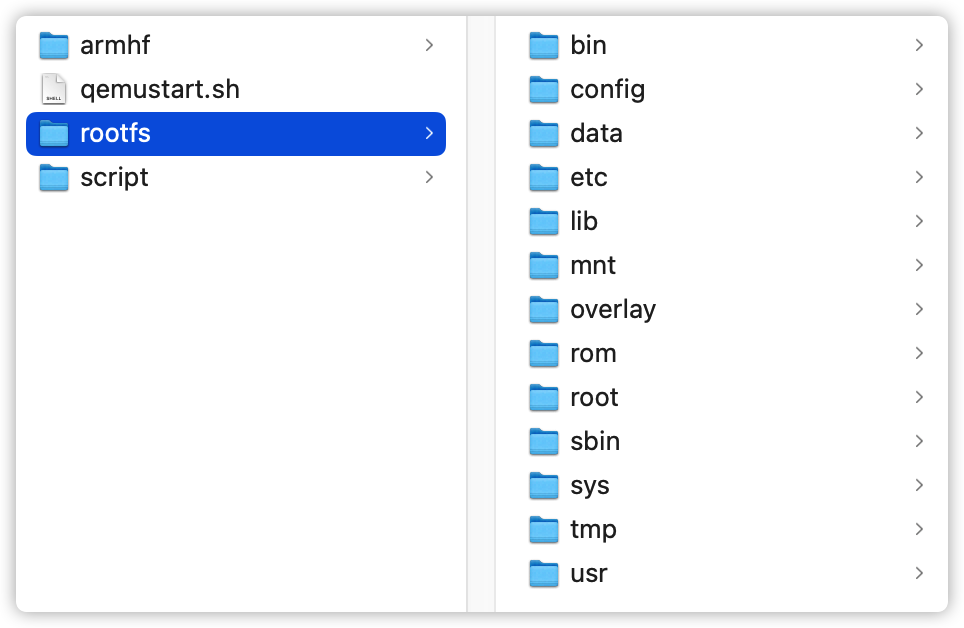
To run the script, you need to copy the equipment file system to the rootfs folder, like flowing picture:
Here are some commands to see how the tool works.
> qemustart.sh armel squeeze
> qemustart.sh armel wheezy
> qemustart.sh armhf wheezy
> qemustart.sh mips squeeze 32
> qemustart.sh mips squeeze 64
> qemustart.sh mips wheezy 32
> qemustart.sh mips wheezy 64
> qemustart.sh mipsel squeeze 32
> qemustart.sh mipsel squeeze 64
> qemustart.sh mipsel wheezy 32
> qemustart.sh mipsel wheezy 64
The ip adress of virtual machine is 192.168.3.2
If you want to distinguish the structure of the device, you can use these commands:
> file ./rootfs/bin/busybox
> checksec ./rootfs/bin/busybox
Hope you enjoy it.