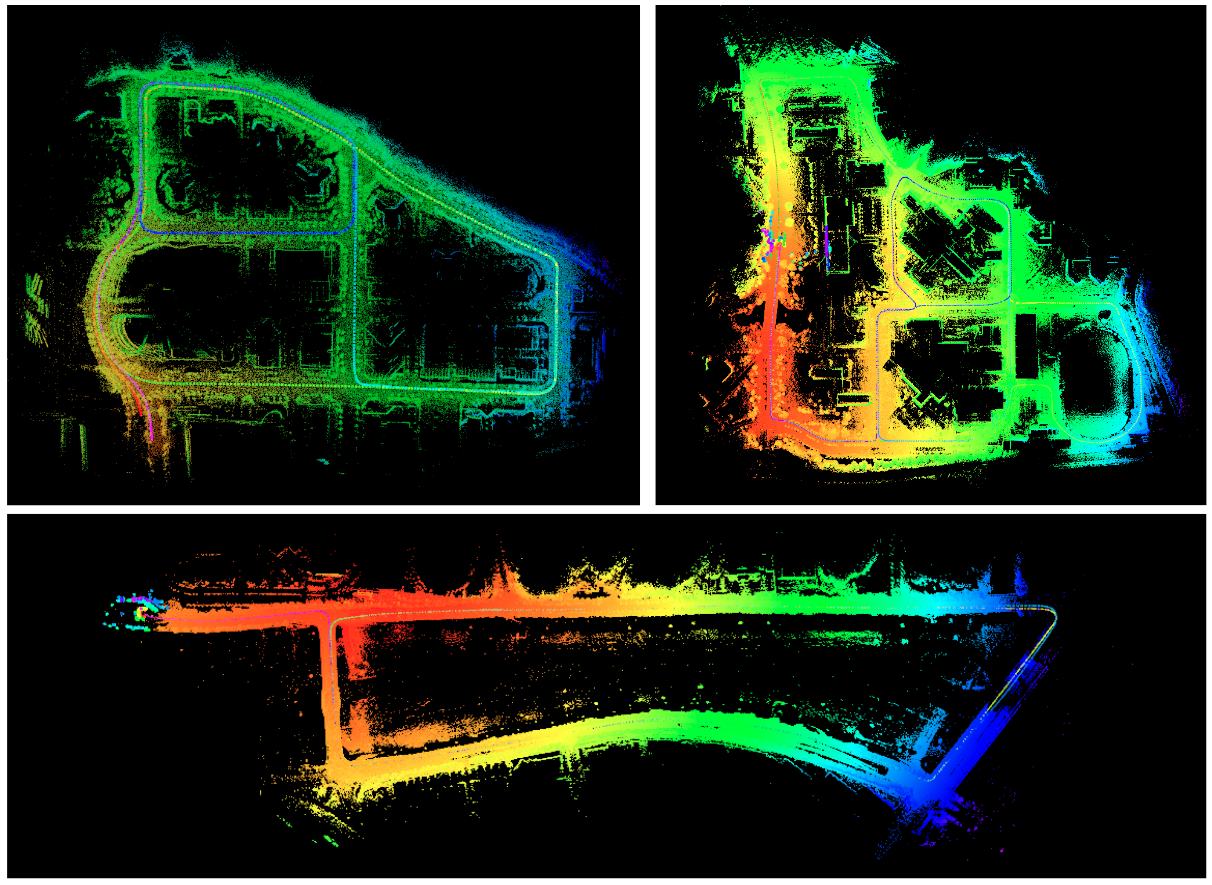
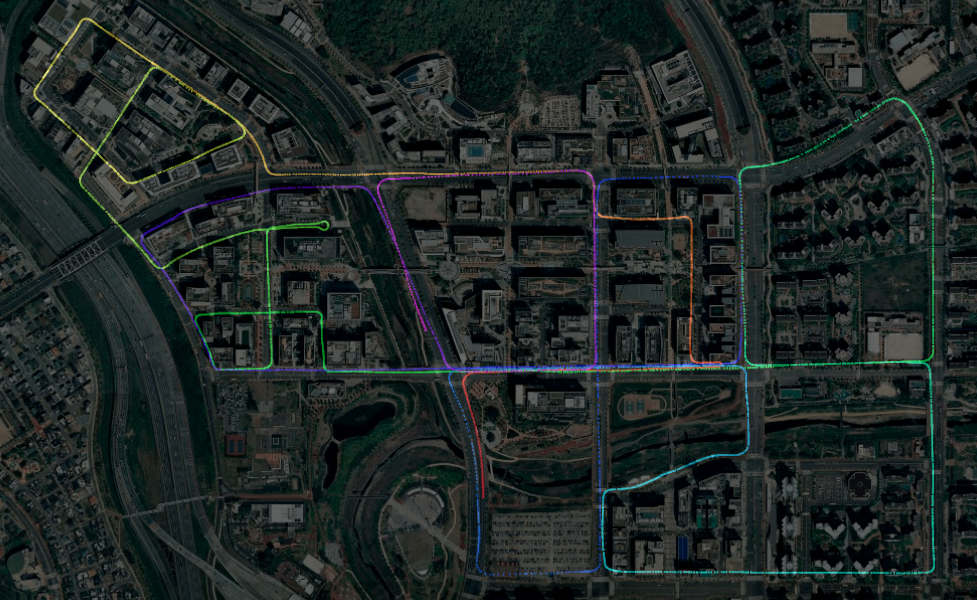
SC-LeGO-LOAM
NEWS (Nov, 2020)
- A Scan Context integration for LIO-SAM, named SC-LIO-SAM (link), is also released.
Real-time LiDAR SLAM: Scan Context (18 IROS) + LeGO-LOAM (18 IROS)
- This repository is an example use-case of Scan Context C++ , the LiDAR place recognition method, for LiDAR SLAM applications.
- For more details for each algorithm please refer to
Scan Context https://github.com/irapkaist/scancontext
LeGO LOAM https://github.com/facontidavide/LeGO-LOAM-BOR - Just include
Scancontext.h. For details see the filemapOptmization.cpp. - This example is integrated with LOAM, but our simple module (i.e.,
Scancontext.h) can be easily integrated with any other key-frame-based odometry (e.g., wheel odometry or ICP-based odometry). - Current version: April, 2020.
Features
- Light-weight: a single header and cpp file named "Scancontext.h" and "Scancontext.cpp"
- Our module has KDtree and we used nanoflann. nanoflann is an also single-header-program and that file is in our directory.
- Easy to use: A user just remembers and uses only two API functions;
makeAndSaveScancontextAndKeysanddetectLoopClosureID. - Fast: The loop detector runs at 10-15Hz (for 20 x 60 size, 10 candidates)
Examples
Scan Context integration
- For implementation details, see the
mapOptmization.cpp; all other files are same as the original LeGO-LOAM. - Some detail comments
- We use non-conservative threshold for Scan Context's nearest distance, so expect to maximise true-positive loop factors, while the number of false-positive increases.
- To prevent the wrong map correction, we used Cauchy (but DCS can be used) kernel for loop factor. See
mapOptmization.cppfor details. (the original LeGO-LOAM used non-robust kernel). We found that Cauchy is emprically enough. - We use both two-type of loop factor additions (i.e., radius search (RS)-based as already implemented in the original LeGO-LOAM and Scan context (SC)-based global revisit detection). See
mapOptmization.cppfor details. SC is good for correcting large drifts and RS is good for fine-stitching. - Originally, Scan Context supports reverse-loop closure (i.e., revisit a place in a reversed direction) and examples in here (py-icp slam) . Our Scancontext.cpp module contains this feature. However, we did not use this for closing a loop in this repository because we found PCL's ICP with non-eye initial is brittle.
How to use
- Place the directory
SC-LeGO-LOAMunder user catkin work space - For example,
cd ~/catkin_ws/src git clone https://github.com/irapkaist/SC-LeGO-LOAM.git cd .. catkin_make source devel/setup.bash roslaunch lego_loam run.launch
MulRan dataset
- If you want to reproduce the results as the above video, you can download the MulRan dataset and use the ROS topic publishing tool .
Dependencies
- All dependencies are same as LeGO-LOAM (i.e., ROS, PCL, and GTSAM).
- We used C++14 to use std::make_unique in Scancontext.cpp but you can use C++11 with slightly modifying only that part.
Cite SC-LeGO-LOAM
@INPROCEEDINGS { gkim-2018-iros,
author = {Kim, Giseop and Kim, Ayoung},
title = { Scan Context: Egocentric Spatial Descriptor for Place Recognition within {3D} Point Cloud Map },
booktitle = { Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems },
year = { 2018 },
month = { Oct. },
address = { Madrid }
}
and
@inproceedings{legoloam2018,
title={LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and Ground-Optimized Lidar Odometry and Mapping on Variable Terrain},
author={Shan, Tixiao and Englot, Brendan},
booktitle={IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
pages={4758-4765},
year={2018},
organization={IEEE}
}
Contact
- Maintainer: Giseop Kim (
paulgkim@kaist.ac.kr)
Misc notes
- You may also be interested in this (from the other author's) implementation :)
- ICRA20, ISCLOAM: Intensity Scan Context + LOAM, https://github.com/wh200720041/iscloam
- Also light-weight and practical LiDAR SLAM codes!