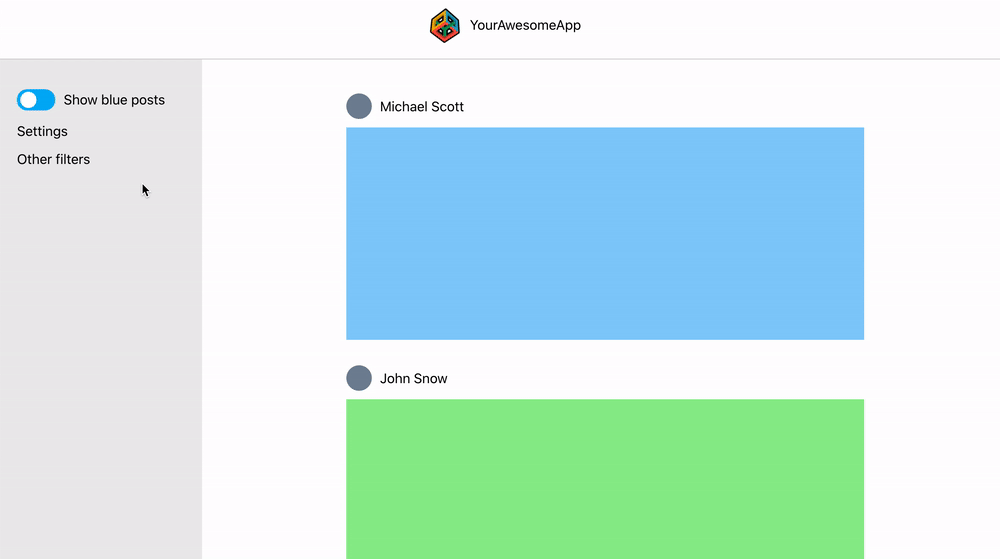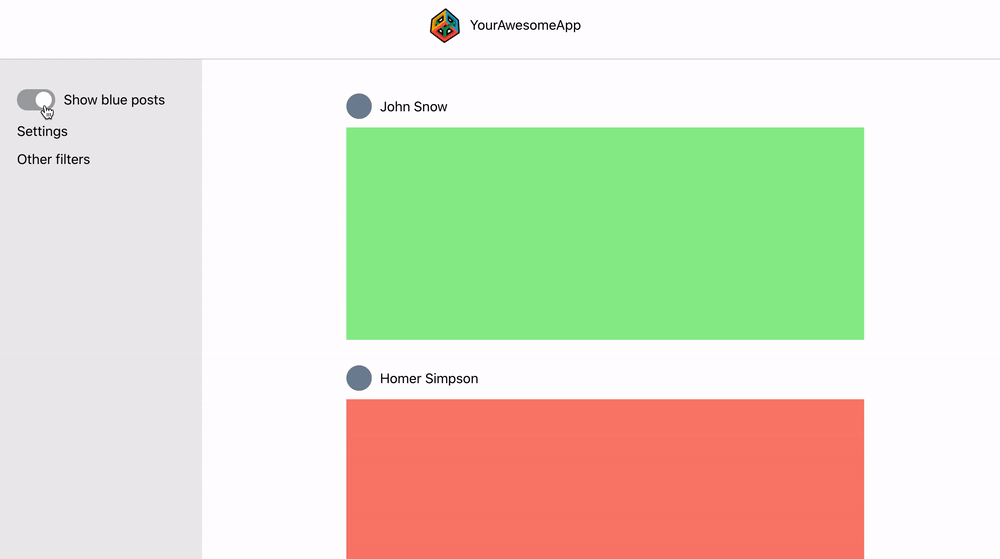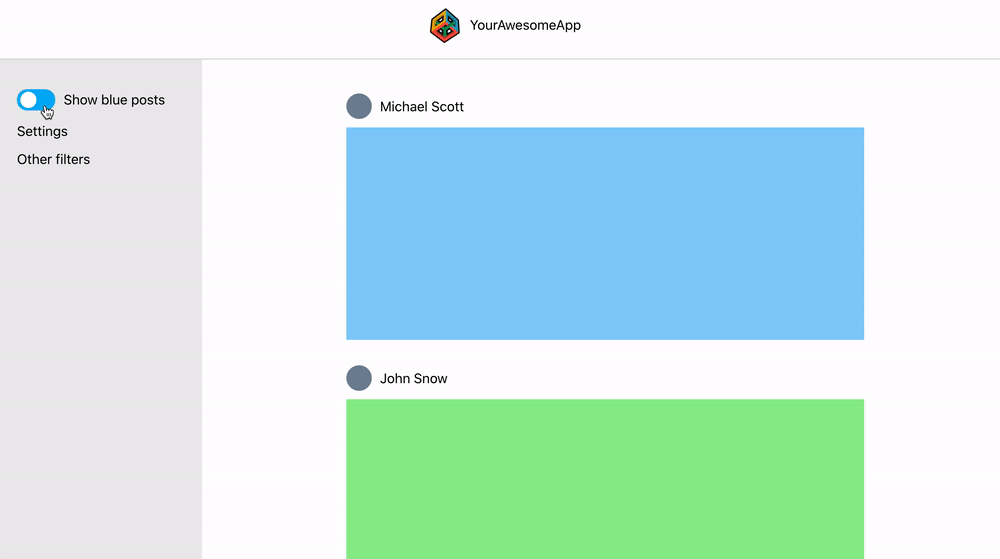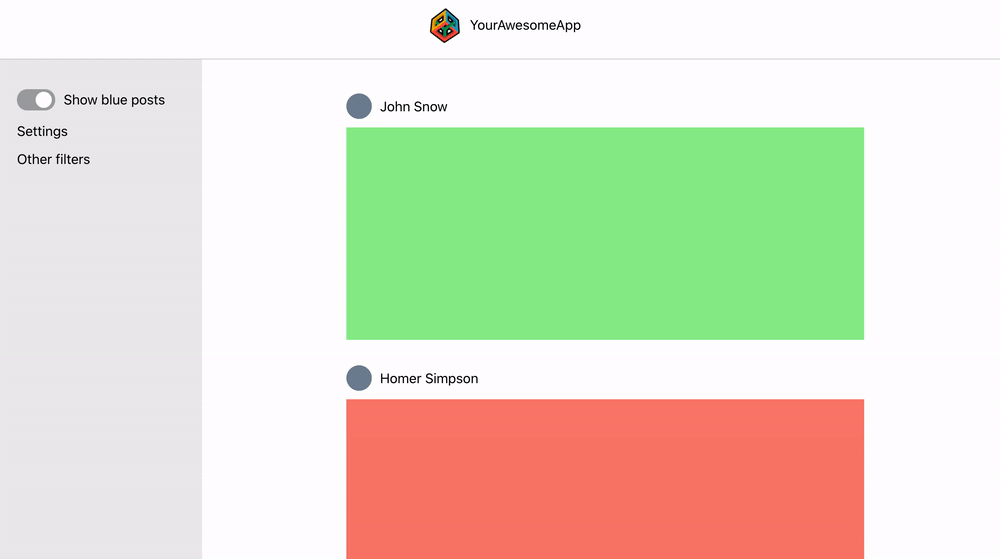
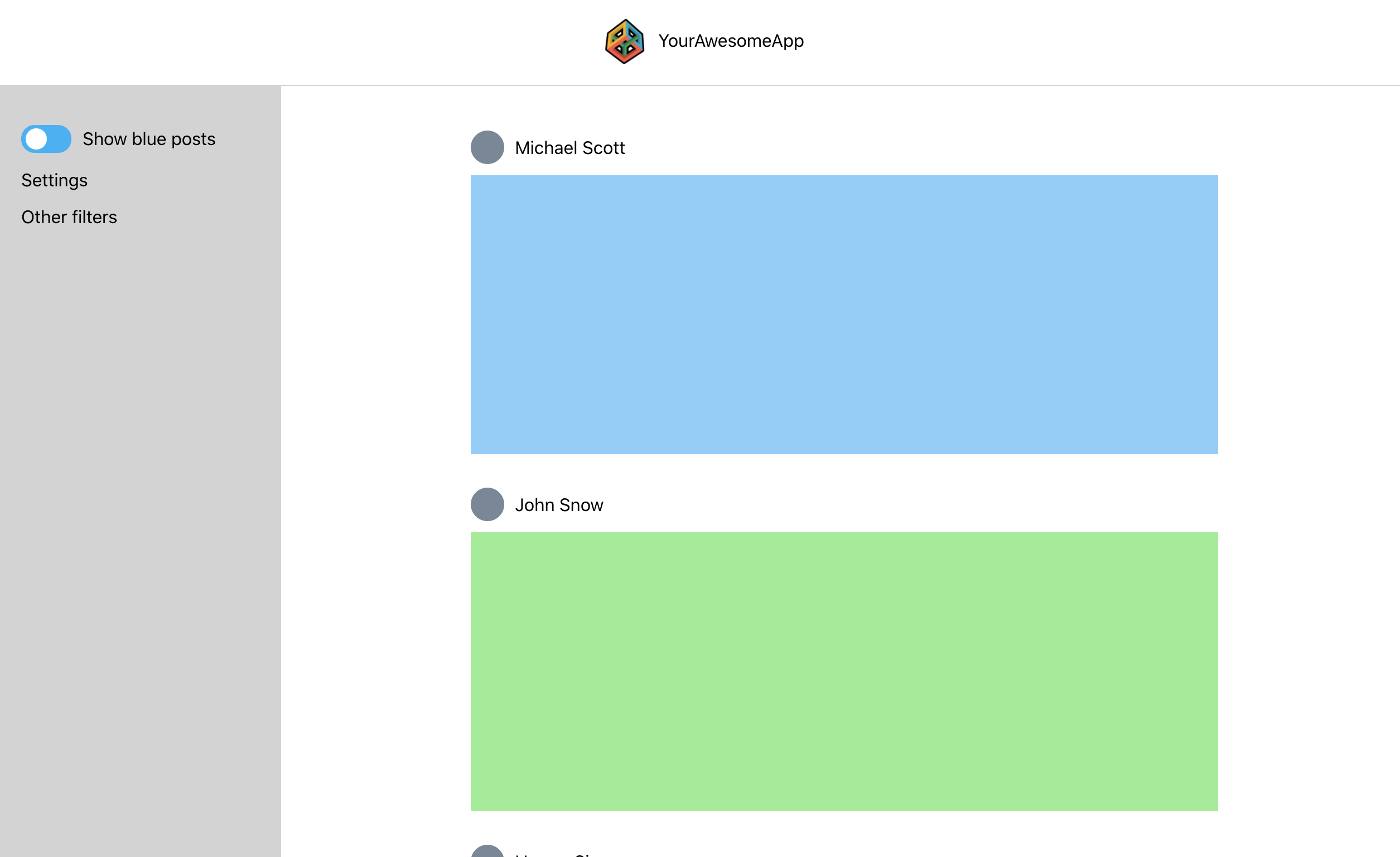
This react web app is a demo project for creating global state without Redux. The web app consists of a header, side panel and a main content with user posts. The side panel has a toggle that should hide/show blue posts in the main content area:
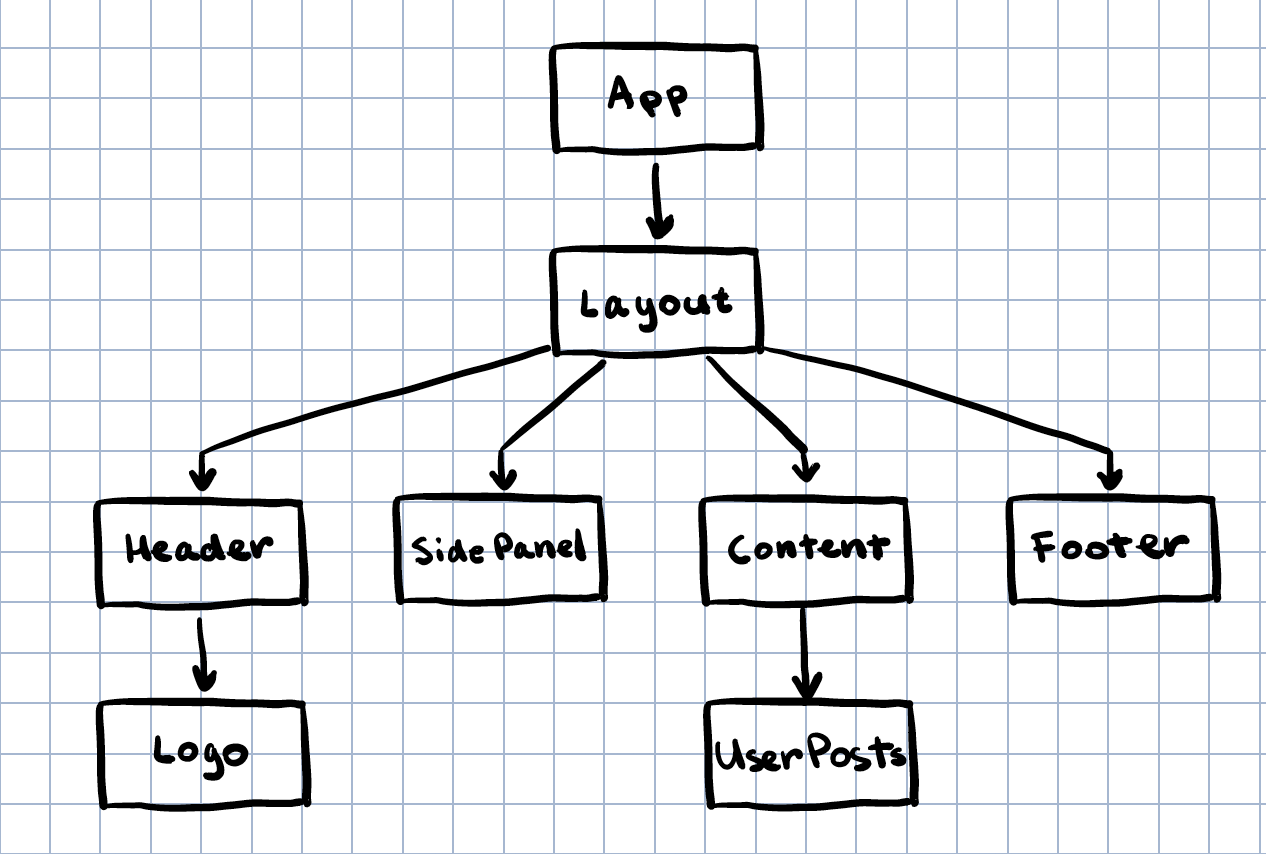
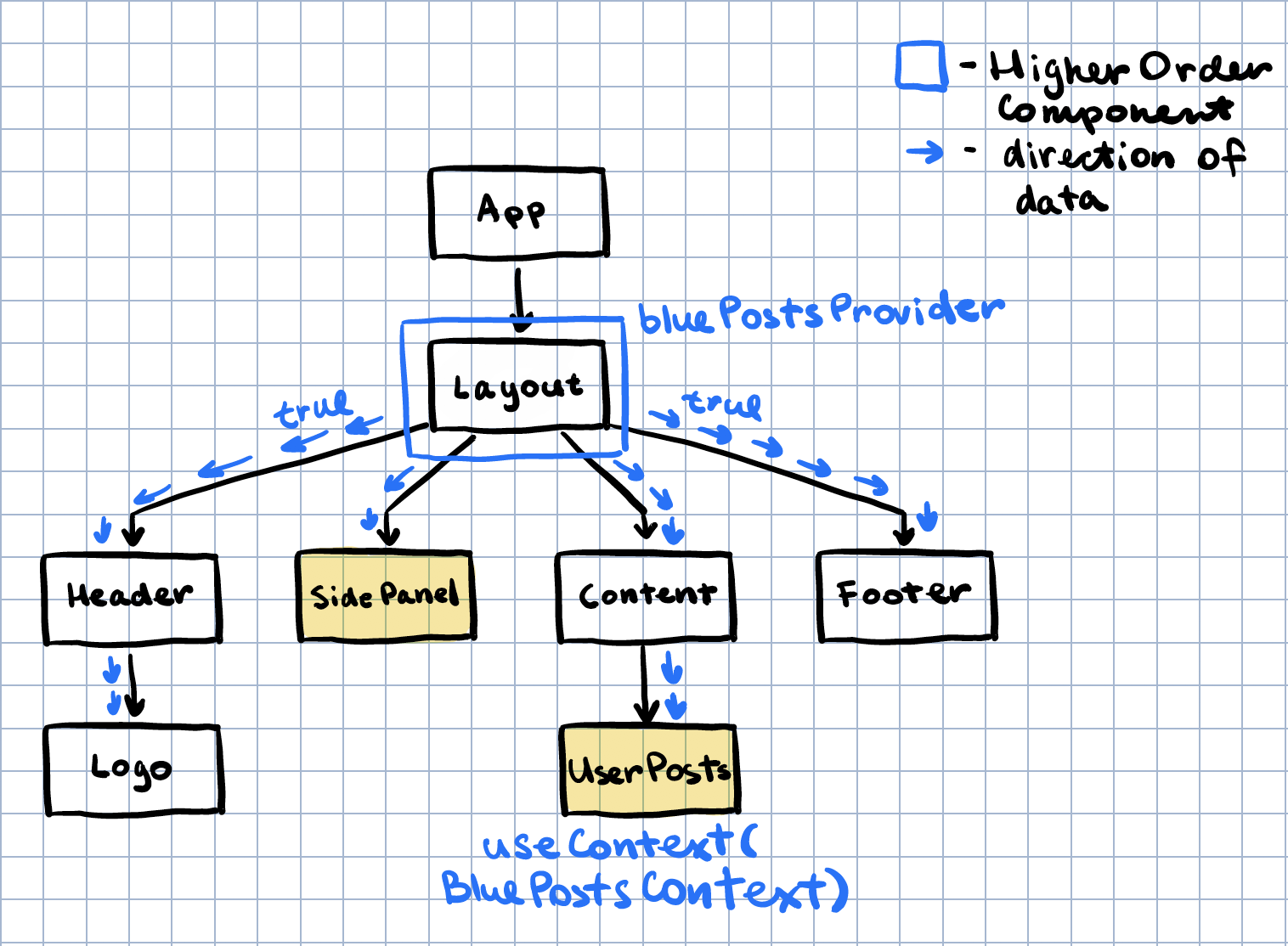
The react component tree looks like this:
This repository has 4 different branches:
- master: this branch contains the app without any state
- 1_simple_context: a simple implementation of the context and its provider wrapper (see Part 1 below)
- 2_bidirectional_context: the provider wrapper holds state and can pass it down to its children to modify (see Part 2)
- 3_generalized_context: refactored version of 2_bidirectional_context to be more generic and reusable (see Part 3)
You can find the copy of the medium article below.
In this article, we will show you how to build a reusable function that lets you create a global state. If you are only interested in how to use it and not the implementation details, jump over to this article.
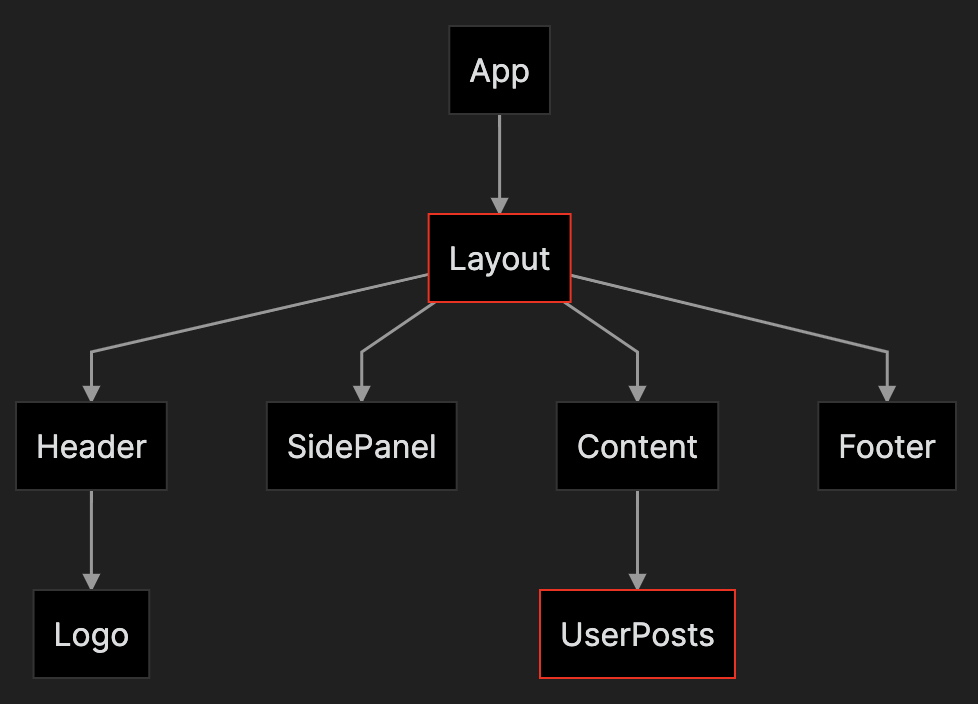
In some cases, two components that are not located close to each other in your react component tree need to share and modify data. For example Layout and UserPosts:
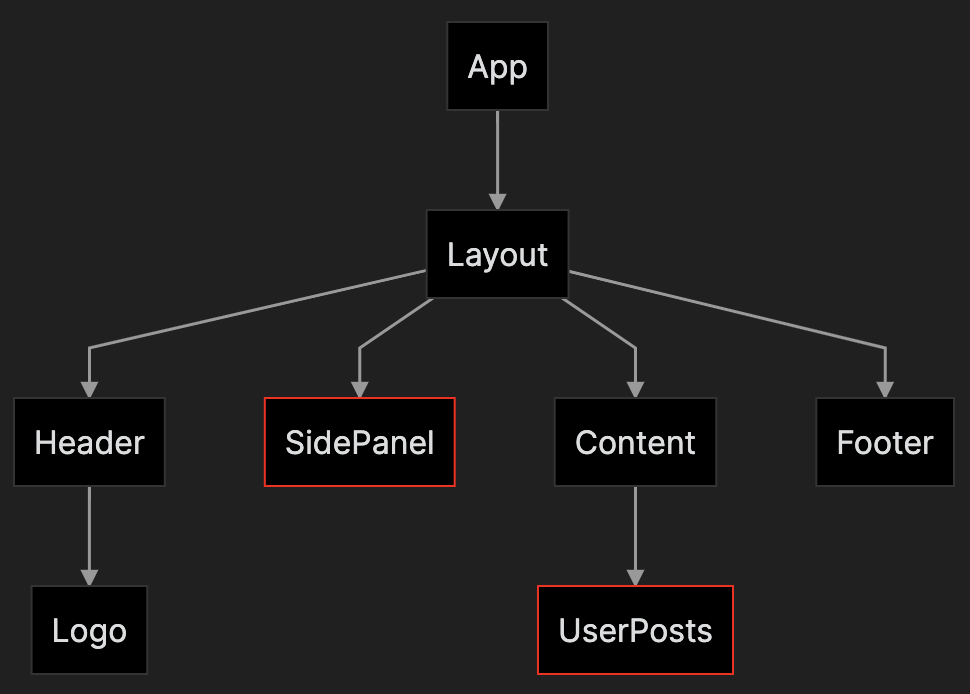
This component tree is simple enough to pass components down via props, but what if the components are not directly connected in a straight line? Like the SidePanel and UserPosts:
Redux is a possible fix to this problem. Although it has plenty of boilerplate and has a steep learning curve especially when not familiar with functional programming. In this article, we discuss how to implement a global state that can be both shared and modified.
This tutorial includes Typescript, Higher Order Components, Functional Components, Generics and React Hooks.
We start with a simple web app that has a header, a side panel, and the main content area with user posts:
You can find the source code here. There are three different branches between which you can switch:
- master: this branch contains the app without any state
- 1_simple_context: a simple implementation of the context and its provider wrapper (see Part 1 below)
- 2_bidirectional_context: the provider wrapper holds state and can pass it down to its children to modify (see Part 2)
- 3_generalized_context: refactored version of 2_bidirectional_context to be more generic and reusable (see Part 3)
The side panel has a toggle (show blue posts) that hides or shows blue posts in the main content. The toggle has to communicate with the main content but this might be messy since the structure of the component tree looks like this:
The most common ancestor between the SidePanel and the Content is the component Layout. We can wrap Layout in a context provider that will pass down a boolean value to all its children:
First, we create the context using React's API nothing too fancy yet:
// context.tsx
import React from 'react';
const BluePostsContext = React.createContext(true); // set to true by default
//....Next is the context provider wrapper, which is a Higher Order Component that simply wraps any Component we pass to it with BluePostsContext:
// context.tsx
// ....
// This function takes in a component and a boolean variable.
// It is applied to a component right before we export it,
// like so:
//
// export default bluePostsProvider(Layout, true);
export function bluePostsProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, value: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => (
<BluePostsContext.Provider value={value}>
<Component {...props} />
</BluePostsContext.Provider>
);
}
export default BluePostsContext;We connect the context to the Layout component by simply wrapping its export with bluePostsProvider (notice here we have to provide the prop type of Layout since typescript doesn't recognize it):
// Layout.tsx
function Layout({ children }: React.PropsWithChildren<{}>) {
return (
// ...
);
}
// See the comment in the provider
export default bluePostsProvider<React.PropsWithChildren<{}>>(Layout, true);The SidePanel and the UserPosts can have access to data in the context using the useContext hook API:
// Panel.tsx
function Panel() {
const showBluePosts = useContext(BluePostsContext);
const onToggle = () => {};
return (
// ...
<Toggle isON={showBluePosts} onToggle={onToggle}>Show blue posts</Toggle>
// ...
);
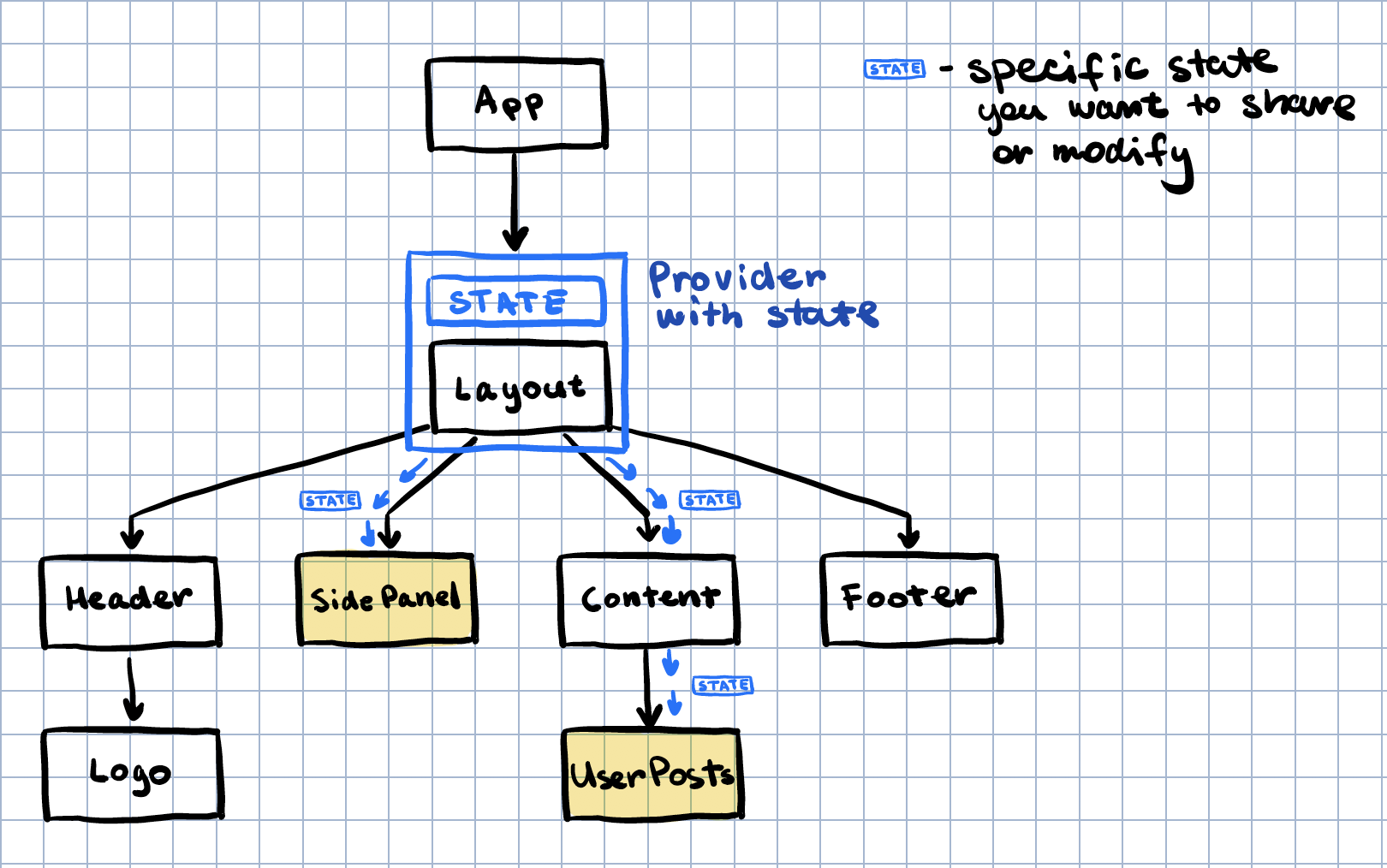
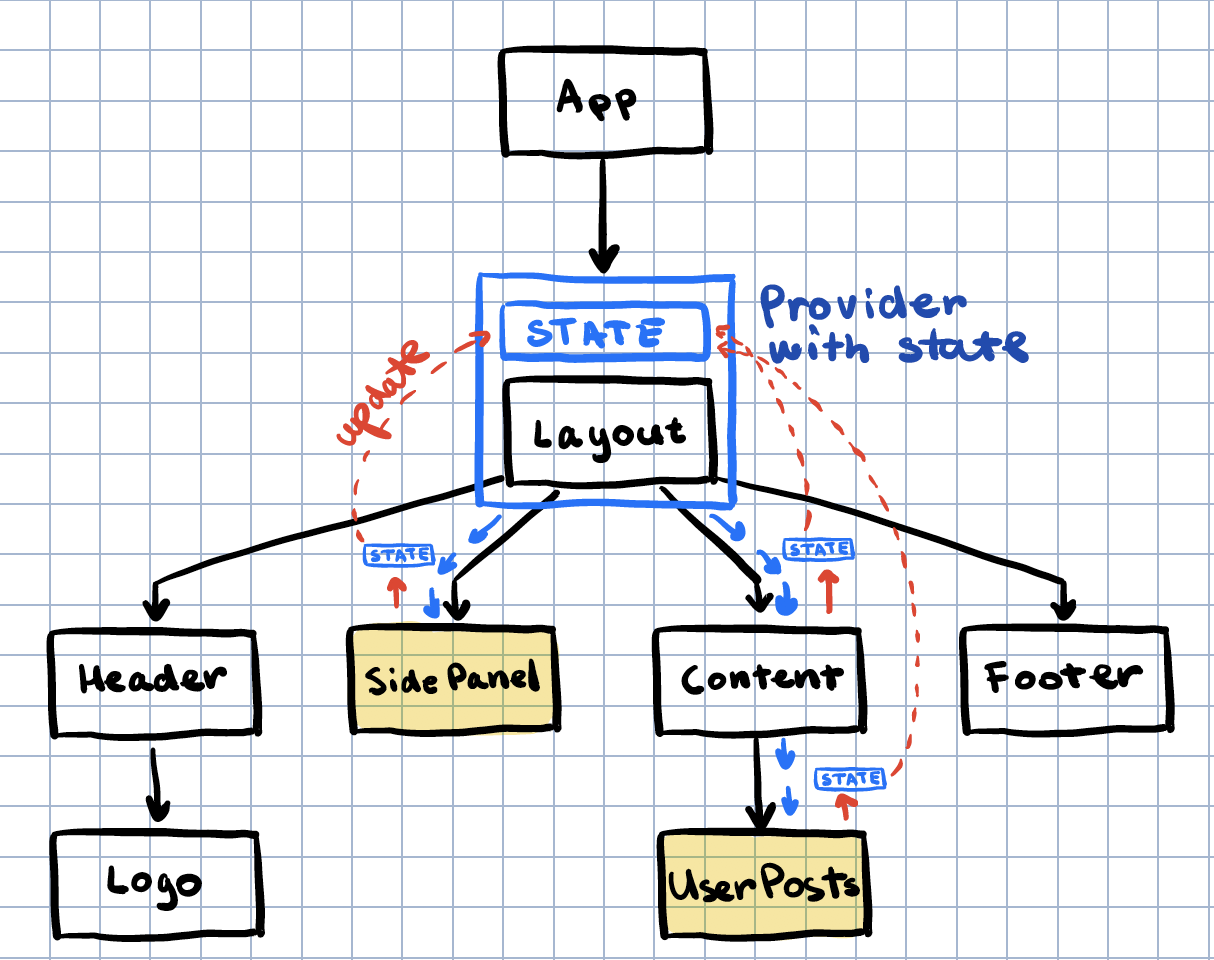
}Components nested in the Layout component have access to this boolean value but none of them can modify it. In the second part, we show how to allow nested components to modify the context value by storing state in the provider.
For the children of Layout to modify the boolean value, the provider has to hold state:
To add state to the provider we simply use useState. The context now should hold the value returned by useState and pass it down to all children. Keep in mind we are now passing around a boolean value wrapped in react state:
// context.tsx
// ... This part is in the code block below
// This provider wraps a component and holds a state via useState.
export function bluePostsProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue); // <--- the provider will store the state here
return (
<BluePostsContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</BluePostsContext.Provider>
);
};
}
export default BluePostsContext;The type returned by useState(true) is a pair [boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>], and it is exactly the type the Context is holding. Since createContext is generic it needs to know about this type by passing it into angle brackets (<>). The default value can be anything since it is just a placeholder until the provider initializes useState. But in order to type-check we simply use [true, value => { }] as the default value:
// context.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
// This context is created to hold a `React State`.
// If you check the type of a react state for a boolean state
// it is a pair of `boolean` and `React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>`.
//
// We have to also add a default value of [true, value => { }].
const BluePostsContext = React.createContext<[boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>]>([true, value => { }]);
// ... The rest is in the code block aboveThe Layout component stays the same, but Panel.tsx and UserPosts.tsx change, since the context now returns a react state and not just a boolean variable. The only change here is to the left-hand side, it is now a pair much like what useState returns:
// Panel.tsx
function Panel() {
const [showBluePosts, setShowBluePosts] = useContext(BluePostsContext);
// ...
}// UserPosts.tsx
function UserPosts() {
const [showBluePosts] = useContext(BluePostsContext); // we can ignore the second tuple value just by not listing it
const userPosts = getUserPosts().filter(post => showBluePosts || post.color !== "Blue");
return (
<div className={style.Posts}>
{userPosts.map(post => <UserPost key={post.id} post={post} />)}
</div>
);
}Here is the result:
In a sense now useContext(BluePostsContext) behaves like a simple useState(true) but on a global scale! We can still improve upon this design since now you might be thinking what if I want to send a string instead of a boolean, or an array, or an object? We would have to copy the context and the provider wrapper again. To avoid that we make the context code generic and reusable in Part 3.
Let's recap, now our context.tsx looks like this:
// context.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const BluePostsContext = React.createContext<[boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>]>([true, value => { }]);
export function bluePostsProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<BluePostsContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</BluePostsContext.Provider>
);
};
}
export default BluePostsContext;It is time to make this code reusable, so we will copy it over to a new file named globalState.tsx and combine both of these functions into another function called createGlobalState:
// globalState.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function createGlobalState() {
const BluePostsContext = React.createContext<[boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>]>([true, value => { }]);
function bluePostsProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<BluePostsContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</BluePostsContext.Provider>
);
};
}
}
export default createGlobalState;We change the name of BluePostsContext to GlobalContext and bluePostsProvider to globalProvider:
// globalState.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function createGlobalState() {
const GlobalContext = React.createContext<[boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>]>([true, value => { }]);
function globalProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<GlobalContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</GlobalContext.Provider>
);
};
}
}
export default createGlobalState;createGlobalStateneeds to return GlobalContext and globalProvider, we can return them both as a tuple. If we simply return return [GlobalContext, globalProvider], Typescript will think that we are returning an array of two elements. To fix this issue we add a helper method called Pair and wrap the tuple with it to typecheck:
// globalContext.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const Pair = <L, R>(pair: [L, R]) => pair;
function createGlobalState() {
const GlobalContext = React.createContext<[boolean, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<boolean>>]>([true, value => { }]);
function globalProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: boolean) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<GlobalContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</GlobalContext.Provider>
);
};
}
return Pair([GlobalContext, globalProvider]); // This wrapper is needed to make the function return type a `tuple` and not a `list`
}
export default createGlobalState;The boolean type is hardcoded above so we need to make it generic by replacing it with a generic type parameter T:
// globalState.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const Pair = <L, R>(pair: [L, R]) => pair;
function createGlobalState<T>() {
const GlobalContext = React.createContext<[T, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<T>>]>([true, value => { }]);
function globalProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>, defaultValue: T) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<GlobalContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</GlobalContext.Provider>
);
};
}
return Pair([GlobalContext, globalProvider]);
}
export default createGlobalState;Instead of injecting the default value through the provider function, we can inject it right away into the createGlobalState function:
// globalState.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const Pair = <L, R>(pair: [L, R]) => pair;
function createGlobalState<T>(defaultValue: T) { // <---
const GlobalContext = React.createContext<[T, React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<T>>]>([defaultValue, value => { }]);
function globalProvider<Props>(Component: React.ComponentType<Props>) {
return (props: Props) => {
const reactState = useState(defaultValue);
return (
<GlobalContext.Provider value={reactState}>
<Component {...props} />
</GlobalContext.Provider>
);
};
}
return Pair([GlobalContext, globalProvider]);
}
export default createGlobalState;And we are done! This is the function that is going to be reused anytime we need a global state.
Since we have the new generic code in globalState.tsx we do not need to ever modify that function, we only need to import it whenever we need to create a global state. The contextBluePostsContext in context.tsx simplifies to a one-liner:
// context.tsx
import createGlobalContext from "./globalContext";
const [BluePostsContext, BluePostsProvider] = createGlobalState(true);
export { BluePostsContext, BluePostsProvider };Now any time you need a global state it is as easy as calling createGlobalState with a default value! It returns a regular React context that can be used in useContext and a provider that wraps the top component.
Now a word about state management. Overusing this method might lead to some complex state logic that will be hard to debug especially with larger codebases and teams. It is by no means a replacement for Redux or other state management libraries so use it sparingly throughout your codebase. And remember, whenever you can use local state, do so!