You already know how role-based authorization works in ASP.NET Core.
[Authorize(Roles = "Administrator")]
public class AdministrationController : Controller
{
}But what if you don't want hardcode roles on the Authorize attribute or create roles later and specify in which controller and action it has access without touching source code?
DynamicAuthorization helps you authorize users without hardcoding role(s) on the Authorize attribute with minimum effort. DynamicAuthorization is built at the top of ASP.NET Core Identity and use identity mechanism for managing roles and authorizing users.
Install the DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.Core NuGet package and DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.JsonStore NuGet package
Install-Package DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.Core
Install-Package DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.JsonStoreor
dotnet add package DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.Core
dotnet add package DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.JsonStoreThen, add AddDynamicAuthorization() to IServiceCollection in ConfigureServices method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
...
services
.AddIdentity<IdentityUser, IdentityRole>(options => options.SignIn.RequireConfirmedAccount = false)
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
services
.AddDynamicAuthorization<ApplicationDbContext>(options => options.DefaultAdminUser = "UserName")
.AddJsonStore(options => options.FilePath = "FilePath");You can set default admin username via DefaultAdminUser config to access everywhere and wihtout needing create default admin role and it's access.
Role access will be saved in JSON file and you can specify the file path FilePath config.
The next step is discovering controllers and actions. IMvcControllerDiscovery return all controllers and actions that decorated with [Authorize] attribute. IMvcControllerDiscovery.GetControllers() method returns list of MvcControllerInfo:
public class MvcControllerInfo
{
public string Id => $"{AreaName}:{Name}";
public string Name { get; set; }
public string DisplayName { get; set; }
public string AreaName { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<MvcActionInfo> Actions { get; set; }
}
public class MvcActionInfo
{
public string Id => $"{ControllerId}:{Name}";
public string Name { get; set; }
public string DisplayName { get; set; }
public string ControllerId { get; set; }
}The next step is creating a role assign acccess to it. Use RoleManager<> to create role and IRoleAccessStore to store role access.
var role = new IdentityRole { Name = "RoleName" };
var result = await _roleManager.CreateAsync(role);
var controllers = _mvcControllerDiscovery.GetControllers();
var roleAccess = new RoleAccess
{
Controllers = controllers.First(),
RoleId = role.Id
};
await _roleAccessStore.AddRoleAccessAsync(roleAccess);The final step is assigning created role to a user:
var user = await _userManager.FindByIdAsync("someId");
await _userManager.AddToRolesAsync(user, new [] { "RoleName" });And now the user only can access those controllers and actions that his roles can access.
Here is an example to create a role and assign access to the role. Check out samples to view full implementation.
public class RoleViewModel
{
[Required]
[StringLength(256, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} characters long.")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<MvcControllerInfo> SelectedControllers { get; set; }
}
[DisplayName("Role Management")]
public class RoleController : Controller
{
private readonly IMvcControllerDiscovery _mvcControllerDiscovery;
private readonly IRoleAccessStore _roleAccessStore;
private readonly RoleManager<IdentityRole> _roleManager;
public RoleController(
IMvcControllerDiscovery mvcControllerDiscovery,
IRoleAccessStore roleAccessStore,
RoleManager<IdentityRole> roleManager
)
{
_mvcControllerDiscovery = mvcControllerDiscovery;
_roleManager = roleManager;
_roleAccessStore = roleAccessStore;
}
// GET: Role/Create
[DisplayName("Create Role")]
public ActionResult Create()
{
var controllers = _mvcControllerDiscovery.GetControllers();
ViewData["Controllers"] = controllers;
return View();
}
// POST: Role/Create
[HttpPost, ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<ActionResult> Create(RoleViewModel viewModel)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
ViewData["Controllers"] = _mvcControllerDiscovery.GetControllers();
return View(viewModel);
}
var role = new IdentityRole { Name = viewModel.Name };
var result = await _roleManager.CreateAsync(role);
if (!result.Succeeded)
{
foreach (var error in result.Errors)
ModelState.AddModelError("", error.Description);
ViewData["Controllers"] = _mvcControllerDiscovery.GetControllers();
return View(viewModel);
}
if (viewModel.SelectedControllers != null && viewModel.SelectedControllers.Any())
{
foreach (var controller in viewModel.SelectedControllers)
foreach (var action in controller.Actions)
action.ControllerId = controller.Id;
var roleAccess = new RoleAccess
{
Controllers = viewModel.SelectedControllers.ToList(),
RoleId = role.Id
};
await _roleAccessStore.AddRoleAccessAsync(roleAccess);
}
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
}You can decorate controllers and actions with DisplayName attribute to show user a more meaningful name instead of controller and action name.
[DisplayName("Access Management")]
public class AccessController : Controller
{
// GET: Access
[DisplayName("Access List")]
public async Task<ActionResult> Index()
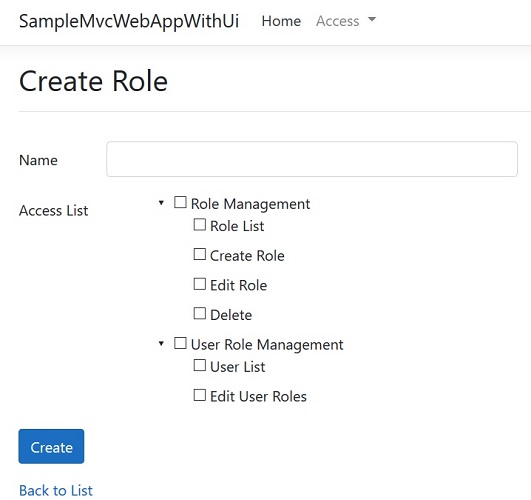
}You can also use default UI to for managing roles and assigning roles to users if you don't want to implement them by yourself.
Install the DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.Ui NuGet package
Install-Package DynamicAuthorization.Mvc.UiThen AddUi to DynamicAuthorization registration:
services
.AddDynamicAuthorization<ApplicationDbContext>(options => options.DefaultAdminUser = "UserName")
.AddJsonStore(options => options.FilePath = "FilePath")
.AddUi();
Use /role url and to manage roles and /userrole to assing roles to users.
You can also use a custom TageHelper to check whether user has access to view a content or not. create a cutome tag helper that inherits from SecureContentTagHelper
[HtmlTargetElement("secure-content")]
public class MySecureContentTagHelper : SecureContentTagHelper<ApplicationDbContext>
{
public MySecureContentTagHelper(
ApplicationDbContext dbContext,
DynamicAuthorizationOptions authorizationOptions,
IRoleAccessStore roleAccessStore
)
: base(dbContext, authorizationOptions, roleAccessStore)
{
}
}In each view wrap a content or an anchor tag inside secure-content tag:
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Home</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="About">About</a></li>
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Contact">Contact</a></li>
<secure-content asp-area="" asp-controller="Role" asp-action="Index">
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Role" asp-action="Index">Role</a></li>
</secure-content>
<secure-content asp-area="" asp-controller="Access" asp-action="Index">
<li><a asp-area="" asp-controller="Access" asp-action="Index">Access</a></li>
</secure-content>
</ul>Don't forget to add your tag halper namespace to _ViewImports.cshtml
@using SampleMvcWebApp
@addTagHelper *, Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.TagHelpers
@addTagHelper *, SampleMvcWebAppIf you extended IdentityUser or you changed user and role key, you should pass user and role type too. for example:
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser> { ... }
public class MySecureContentTagHelper : SecureContentTagHelper<ApplicationDbContext, ApplicationUser> { ... }or
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole, int> { ... }
public class MySecureContentTagHelper : SecureContentTagHelper<ApplicationDbContext, ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole, int> { ... }To implement DynamicAuthorization step by step by yourself checkout manual branch.