KVQuant: Towards 10 Million Context Length LLM Inference with KV Cache Quantization [Paper]
KVQuant is a methodology for efficient KV cache quantization that incorporates several innovations to acheive accurate low-precision quantization, thereby enabling efficient long context length inference.
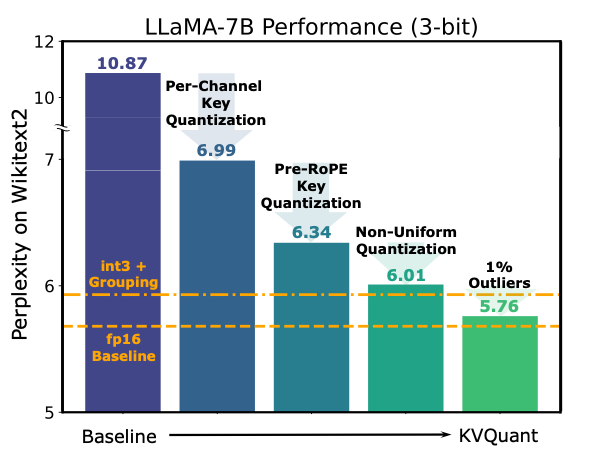
TLDR: KVQuant addresses the memory bottleneck with long context length inference by quantizing the KV cache to low precision. KVQuant achieves high accuracy with low-precision KV cache quantization by considering several consistent patterns observed in cached KV values across different LLMs, and by developing methods to exploit these patterns, including:
- Per-channel, Pre-RoPE Key quantization to better match the outlier channels in Keys
- Non-Uniform Quantization (NUQ) to better represent the non-uniform activations
- Dense-and-Sparse Quantization to mitigate the impacts of numerical outliers on quantization difficulty
KVQuant enables serving the LLaMA-7B model with 1M context length on a single A100-80GB GPU, or even the LLaMA-7B model with 10M context length on an 8-GPU system 🔥
[TLDR: Twitter Thread] [Paper]
Large World Model (LWM) is a recent work that enables training long context length models with up to 1M context length. However, inferring these models is extremely resource intensive due to the large size of the KV cache that must be stored throughout inference. Using KVQuant, we can now infer these long context length models efficiently on a single A100!
The lmw/ directory contains scripts for running inference and evaluation using the quantized Large World Models.
To further improve our methodology for supporting long context length inference, we have made several improvements:
Parallel topK support on GPU and kernels for parallel prompt processing- we have augmented our open-source support with additional kernels to perform parallel packing with multiple input tokens, and also modified our inference code to utilize the GPU for parallel topK when appending many value tokens in parallel.Capping Key Outliers- we have added support for running both calibration and inference with a fixed number of outliers per token for keys. This allows us to design more efficient kernels, since there is a maximum number of outliers per token for both keys and values, and it makes memory allocation easier for our method since we can allocate fixed-size memory for each key.Attention Sink-Aware Quantization- based on the insight from the Attention Sink paper that the model concentrates its attention on the first token, we have added support during both calibration and inference for leaving a small number of initial keys and values (eg. 5) in fp16. This can allow for significant performance gains, and was also introduced as a method for improving quantization performance in another concurrent work IntactKV. More detailed evaluation and analysis for these improvements will be added to the arxiv preprint shortly!
The codebase contains three different subfolders, each of which has its own README file with instructions that you can follow for installing the required environment for that step.
gradients- codebase for computing fisher information - this is required to be able to quantize a new modelquant- codebase for running simulated quantization + eval experiments (need to first compute fisher information)deployment- codebase for running efficient inference with compressed vectors (need to first get quantizers from quant step)lwm- code for running inference with and evaluating quantized LWM modelsbenchmarking- code for benchmarking kernels (need to first get quantizers from quant step)
To reproduce the perplexity numbers reported in the paper, run gradients and then quant.
add deployment codeoptimized kernels- merging optimized kernels with end-to-end inference deployment code
- additional evaluation on long context lengths + different downstream tasks
- multi-GPU inference
This code reuses components from several libraries including GPTQ, GPTQ-For-LLaMA, and SqueezeLLM.
KVQuant has been developed as part of the following paper. We appreciate it if you would please cite the following paper if you found the library useful for your work:
@article{hooper2024kvquant,
title={KVQuant: Towards 10 Million Context Length LLM Inference with KV Cache Quantization},
author={Hooper, Coleman and Kim, Sehoon and Mohammadzadeh, Hiva and Mahoney, Michael W and Shao, Yakun Sophia and Keutzer, Kurt and Gholami, Amir},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.18079},
year={2024}
}