This repository contains iOS project (code examples) to explain how to use ConfigWiseSDK. See more info about ConfigWise service, here: https://www.configwise.io
ConfigWiseSDK (iOS) is distributed through Cocoapods.
The current repository also contains latest version of ConfigWiseSDK.zip packaged framework. You can use it to setup framework in your project in case if you don't use Cocoapods.
The ConfigWiseSDK (iOS) is based on Apple ARKit / SceneKit stack underhood. The architectural design of ConfigWiseSDK hides all boilerplate stuff (of ARKit, SceneKit). It gives simple way of working with AR and 3D experience in your own iOS applications.
ConfigWiseSDK framework is distributed under Apache-2.0 license.
ConfigWiseSDK requires the following minimal requirements:
- Real iPhone (iPad) with installed iOS v14.5 and above.
NOTICE: Unfortunately, AR (augmented reality) doesn't work on simulator.
So, if you plan to use
ArAdapterof ConfigWiseSDK then make sure you run / debug your project on real iPhone (iPad). - Xcode v12.X
- Cocoapods v1.10.X and above
- Swift 4.2 and above (we recommend to use Swift 5)
- If you run your project on real device with installed iOS v13.3.1 and above and if you use FREE 'personal team' as a apple development program, then please upgrade your apple plan to use paid 'personal team', otherwise it's known apple issue if you run your app on real iPhone (iPad). See the following links for more details about this issue:
-
Add the following lines to your
Podfile:pod 'ConfigWiseSDK' -
Then, you also need to add the following properties in the
Info.plistfile. These settings are required for AR usage - to permit your application to access to camera, photos of your phone.<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key> <string>To enable Augmented Reality user experience.</string> <key>NSPhotoLibraryAddUsageDescription</key> <string>To be able to save images.</string> <key>NSPhotoLibraryUsageDescription</key> <string>To be able to attach images.</string> -
Finally, add NodeRender.metal file to your project (as
metalsource code).NodeRender.metalis Apple Metal API based code to show 'glow' visualisation of highlighted 3D objects in the scene. Unfortunately, there are some known issues (restrictions) to pack.metalcode inside of ConfigWiseSDK framework - that's why.metalcode must be part of your project to pass compilation steps.

Examples of code are also distributed here. It is good point to quick start - to get experience of ConfigWiseSDK usage.
Examples project requires:
- Xcode 12.X
- Swift 5
- SwiftUI
- ConfigWise account
Let's download and install ConfigWiseSDK (iOS) framework:
$ cd examples; pod install
Then, let's open examples/examples.xcworkspace in your Xcode.
Set your COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN in the ios-example/AppEnvironment.swift file (see this token in the CBO).
var mode: SdkVariant {
.B2C
}
init() {
// Let's initialize ConfigWiseSDK here
ConfigWiseSDK.initialize([
.variant: self.mode,
.companyAuthToken: "YOUR_COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN",
.dbAccessPeriod: 1 * 60 * 60, // (sec) 1 hr
.lightEstimateEnabled: true,
.debugLogging: true,
.debug3d: false
])
. . .
}
There are 2 authorization modes supported by ConfigWiseSDK:
-
B2C (
COMPANY_AUTH_TOKENis required) - use this method if you NO need ConfigWise users SignIn flow. Eg: to provide public access to your application or if if you want to use own authorization flow.To obtain
COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN, go toCBO (company back office) > Company profile: https://manage.configwise.io/configwise/cbo/profile -
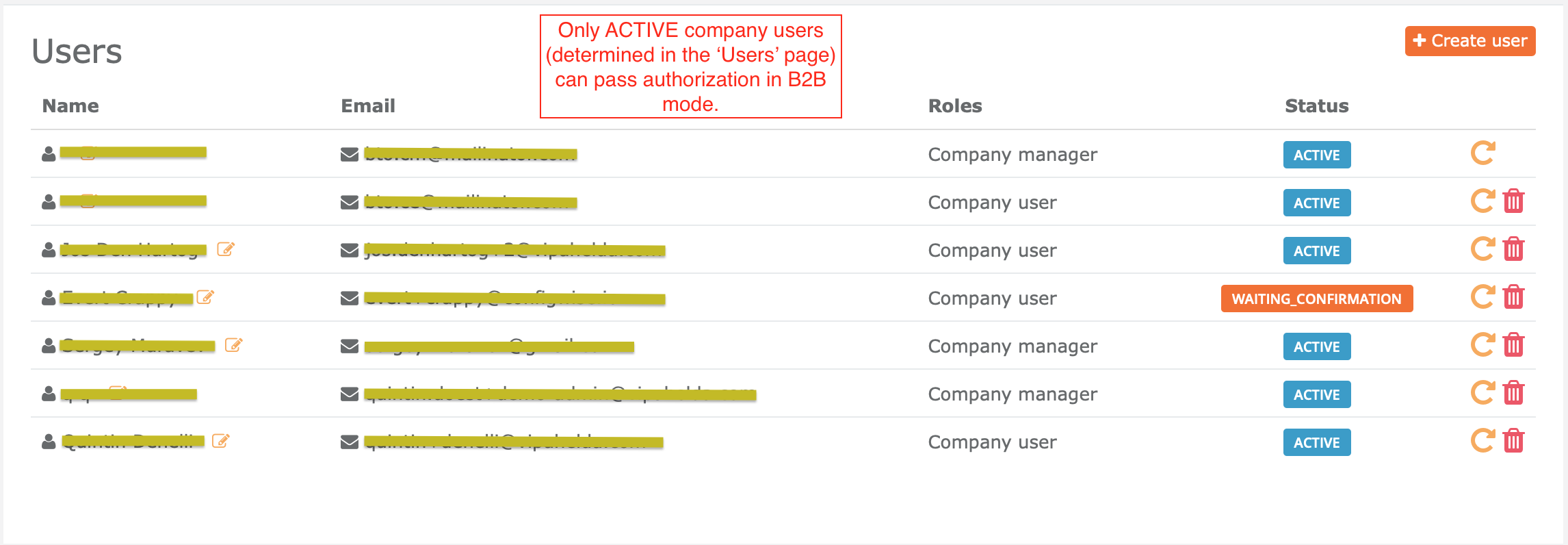
B2B (ConfigWise user credentials are required) - use this method to only permit registered ConfigWise users of your company to access to your mobile application. This method requires to type
email/passwordby your company users to access backend data. To manage your company users, go toCBO > Users: https://manage.configwise.io/configwise/cbo/employeesTo use
B2Bmode - changeSdkVariantto.B2Bmode in theios-example/AppEnvironment.swiftfile.var mode: SdkVariant { .B2B }
So, we are ready to build and run example project - make sure ios-example scheme in selected in Xcode.
Connect your iPhone (iPad) - choose you device in the 'device selector' of Xcode IDE.
Then press 'Build & Run' button in the Xcode.
NOTICE: Example project is SwiftUI based. But all things (what we describe below) are also compatible with UIKit based projects as well.
Before using ConfigWiseSDK in your code, you need to initialize it first. Here is an example of code how to do this:
import ConfigWiseSDK
. . .
ConfigWiseSDK.initialize([
.variant: SdkVariant.B2C, // (mandatory) .B2B | .B2C - see details about these modes above.
.companyAuthToken: "abcdef...12345", // (optional) YOUR_COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN - this token required only in B2C mode,
// skip it if you use B2B variant of initialization.
// You can obtain auth token in CBO > Company profile (see details above).
.dbAccessPeriod: 1 * 60 * 60, // (optional) 1 hr (3600 sec) by default - number of seconds, period while
// app uses locally cached DB data (instead to request it from server).
// NOTICE: if you wish to disable DB data caching (to always request data
// from server), set 0 here.
.lightEstimateEnabled: true, // (optional, true by default) If true then Light stimate mode is enabled in
// the AR session (light estimate works based on real environment light sources).
.debugLogging: false, // (optional) false by default.
// true - prints DEBUG, INFO, WARNING and ERROR messages in the log output
// (useful for Debug build variants of your application).
// false - prints only WARNING and ERROR messages in log output.
// (use it in Release build of your application).
.debug3d: false // (optional) false by default.
// true - shows extra DEBUG visualisations in 3D and AR scenes
// (such as bounding boxes, lights sources, detected AR ancors,
// planes, geometries, number of fps, etc).
// false - no extra DEBUG visualisations shown in the scenes.
// Use it in Release build of your application.
])
In SwiftUI based projects, we recommend to initialize ConfigWiseSDK in the constructor of class what you inject as environmentObject then.
See AppEnvironment.init():
var mode: SdkVariant {
.B2C
}
init() {
// Let's initialize ConfigWiseSDK here
ConfigWiseSDK.initialize([
.variant: self.mode,
.companyAuthToken: "YOUR_COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN",
.debugLogging: true,
.debug3d: false
])
. . .
}
To inject this initialization (in to SwiftUI life cycle), add lazy var appEnvironment = AppEnvironment() as a property of
SceneDelegate.swift. Then register appEnvironment as environmentObject:
class SceneDelegate: UIResponder, UIWindowSceneDelegate {
lazy var appEnvironment = AppEnvironment()
func scene(_ scene: UIScene, willConnectTo session: UISceneSession, options connectionOptions: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) {
. . .
let contentView = ContentView()
.environmentObject(self.appEnvironment)
. . .
}
See our example of SceneDelegate.swift
To access to data of ConfigWise service, application must be authorized first.
ConfigWiseSDK provides AuthService.sharedInstance with the following public functions:
-
signIn()- use this function to pass authorization (supports two modes: B2B and B2C) -
signOut()- sign out from currently authorizes session. -
currentUser()- returns currently authorized user. The following users roles are used in ConfigWise:-
ROLE_COMPANY_MANAGER- B2B company manager user. -
ROLE_COMPANY_EMPLOYEE- B2B company employee user. -
ROLE_COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN- B2C company auth token.
-
-
currentCompany()- returns company of currently authorized user. -
isCurrentUserCompanyManager()- returns true if role of currently authorized user isROLE_COMPANY_MANAGER. -
isCurrentUserCompanyEmployee()- returns true if role of currently authorized user isROLE_COMPANY_EMPLOYEE. -
isCurrentUserCompanyAuthToken()- returns true if role of currently authorized user isROLE_COMPANY_AUTH_TOKEN. -
resetPassword()- starts 'reset password' procedure of B2B users (ROLE_COMPANY_MANAGER,ROLE_COMPANY_EMPLOYEE).
NOTICE: If we pass authorization (using AuthService.sharedInstance.signIn() function) then authorized session
and related user are stored on your device. Next time, you no need to pass authorization again. Instead you need to
invoke AuthService,sharedInstance.currentUser() or AuthService.sharedInstance.currentCompany() function
to retrieve authorized user (company).
NOTICE: If you not authorized and you try to invoke any ConfigWiseSDK function to obtain data from backend service,
then we always retrieve Unauthorized error response.
NOTICE: Locally stored auth session is not permanent. It gets invalid in the following cases:
- Session TTL (time to live) is expired.
- Status of authorized user is changed. Eg: user is temporary disabled, user has been deleted, credentials have been changed, etc.
- Status of company of authorized user has been changed. Eg: company has been disabled, deleted, or paid plan subscription has not been renewed, etc.
- Version of ConfigWiseSDK (what your application use) not supported anymore. Eg: outdated, because critical security or compatibility defect found, backward compatibility issues, etc.
Using AuthService,sharedInstance.currentUser() or AuthService.sharedInstance.currentCompany(), we can check on app startup, if we already authorized or not.
If not authorized yet then:
- We show 'SignIn' screen (form) in B2B mode.
- We start automatic B2C
SignInflow by execution of:AuthService.sharedInstance.signIn()function.
See example of this flow in the constructor of AppEnvironment.swift:
init() {
// Let's initialize ConfigWiseSDK here
ConfigWiseSDK.initialize([
.variant: self.mode,
.companyAuthToken: "abcdef...12345",
.debugLogging: true,
.debug3d: false
])
self.navigation = .signIn
// Auto sign-in
self.company = .isLoading(last: self.company.value)
AuthService.sharedInstance.currentCompany { company, error in
if let error = error {
self.company = .failed(error)
return
}
if let company = company {
self.company = .loaded(company)
self.navigation = .main
return
}
guard self.mode == .B2C else {
self.company = .failed("Unauthorized - company not found.")
return
}
// B2C mode - let's try to automatically sign-in in B2C mode
self.signIn()
}
// Let's add observers
initObservers()
}
// MARK: - AuthN / AuthZ
extension AppEnvironment {
func signIn(email: String? = nil, password: String? = nil) {
self.company = .isLoading(last: self.company.value)
AuthService.sharedInstance.signIn(email: email, password: password) { user, error in
if let error = error {
self.company = .failed(error)
self.navigation = .signIn
return
}
guard user != nil else {
self.company = .failed("Unauthorized - user not found.")
self.navigation = .signIn
return
}
AuthService.sharedInstance.currentCompany { company, error in
if let error = error {
self.company = .failed(error)
self.navigation = .signIn
return
}
guard let company = company else {
self.company = .failed("Unauthorized - company not found.")
self.navigation = .signIn
return
}
self.company = .loaded(company)
self.navigation = .main
}
}
}
}
Finally, to cover all cases of authorization flow, our application must be subscribed on the following ConfigWiseSDK events:
ConfigWiseSDK.signOutNotification- fires if authorized session not valid anymore.ConfigWiseSDK.unsupportedAppVersionNotification- fires if used version of ConfigWiseSDK not supported anymore.
See example of code how to handle these events in the AppEnvironment.swift:
init() {
. . .
// Let's add observers
initObservers()
}
deinit {
// Remove observers
NotificationCenter.default.removeObserver(self)
}
. . .
// MARK: - Observers
extension AppEnvironment {
private func initObservers() {
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
self,
selector: #selector(self.onUnsupportedAppVersion),
name: ConfigWiseSDK.unsupportedAppVersionNotification,
object: nil
)
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
self,
selector: #selector(self.onSignOut),
name: ConfigWiseSDK.signOutNotification,
object: nil
)
}
@objc func onUnsupportedAppVersion(notification: NSNotification) {
// Publishing changes from background threads is not allowed (otherwise runtime crash issue occurs).
// Make sure to publish values from the main thread (via operators like receive(on:)) on model updates.
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.company = .failed("Unsupported ConfigWiseSDK version. Please update it.")
self.catalog = .notRequested
self.components = .notRequested
self.navigation = .signIn
}
}
@objc func onSignOut(notification: NSNotification) {
// Publishing changes from background threads is not allowed (otherwise runtime crash issue occurs).
// Make sure to publish values from the main thread (via operators like receive(on:)) on model updates.
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.company = .notRequested
self.catalog = .notRequested
self.components = .notRequested
self.navigation = .signIn
}
}
}
Now, we are ready to retrieve (obtain) catalog from ConfigWise backend service.
ConfigWise CBO (company back office) tool is used to manage:
- Company users
- Company catalog
- Components
- Materials
- Snappings
- Company settings (profile)
- Scene settings
- etc.
ConfigWiseSDK (iOS) provides service classes to query (to obtain) these kinds of data from backend.
All DAO service classes (data access object) automatically store obtained entities, queries, data in the local cache. This means, SDK supports offline mode as well (eg: if network connection is temporary unavailable then SDK returns cached versions of previously obtained entities). Local DAO cache is also used to increase performance of fetching of data.
You no need to worry about local cache management - it's already managed automatically underhood of ConfigWiseSDK. Such as:
- Cache is periodically cleared. Eg: to keep balance between performance and disk space.
- Cache is automatically updated if any related changes on server side data.
- Smart (automatic) merging of changes between remote and locally cached data.
- etc.
Because (above) we already obtained currently authorized company, we can obtain catalog by the company. Then we can obtain all components by fetched catalog. See an example of code in the AppEnvironment.swift:
// MARK: - Components
extension AppEnvironment {
func obtainComponents() {
self.catalog = .isLoading(last: self.catalog.value)
guard let company = self.company.value else {
self.catalog = .notRequested
self.components = .notRequested
return
}
CatalogService.sharedInstance.obtainCatalogByCompany(company: company) { catalog, error in
if let error = error {
self.catalog = .failed(error)
self.components = .failed(error)
return
}
guard let catalog = catalog else {
let error: Error = "No catalog yet. Please create it first."
self.catalog = .failed(error)
self.components = .failed(error)
return
}
self.catalog = .loaded(catalog)
self.components = .isLoading(last: self.components.value)
ComponentService.sharedInstance.obtainAllComponentsByCatalog(catalog: catalog) { components, error in
if let error = error {
self.components = .failed(error)
return
}
self.components = .loaded(components)
}
}
}
func getComponentById(_ id: String) -> ComponentEntity? {
return self.components.value?.first { $0.objectId == id }
}
}
NOTICE: Every obtainAll...() DAO function supports pagination through optional offset: Int? = nil, max: Int? = nil parameters.
By default, these parameters are nil - this means obtaining whole collection of entities (without pagination).
ConfigWiseSDK provides ModelLoaderService.sharedInstance service class to load 3D models of catalog components.
Here is an example how to use it in your code (see ArView.swift):
self.isLoading = true
self.loadingProgress = 0
ModelLoaderService.sharedInstance.loadModelBy(component: component, block: { model, error in
self.loadingProgress = 100
delay(0.3) {
self.isLoading = false
self.loadingProgress = nil
}
if let error = error {
self.errorMessage = error.localizedDescription
return
}
guard let model = model else {
self.errorMessage = "Loaded model is nil"
return
}
self.arAdapter.addModel(modelNode: model, simdWorldPosition: simdWorldPosition, selectModel: true)
}, progressBlock: { status, completed in
self.loadingProgress = Int(completed * 100)
})
As a result ModelLoaderService.sharedInstance.loadModelBy() function returns ModelNode instance.
ModelNode is compatible with Apple SceneKit / ARKit SCNNode objects. This means you can add it to
scene of SceneKit SCNView or to ARSCNView of ARKit.
NOTICE: All loaded 3D models (of catalog components) and their related assets (eg: texture pictures, lighting schemes) are automatically stored in local cache of your device. All previously cached models are offline available for further loading. You no need to worry about caching management - it's already implemented underhood of ConfigWiseSDK framework.
ConfigWiseSDK makes your live easy - you no need to write tons of code to manage models in the SceneKit / ARKit directly.
Instead, you can use our ArAdapter (or CanvasAdapter) of ConfigWiseSDK.
-
ArAdapter- use this adapter to implement augmented reality experience in your application. This adapter is based and totally compatible with Apple ARKit underhood. -
CanvasAdapter- use this adapter to manage 3D scene with loaded components 3D models inside. This adapter is based and compatible with Apple SceneKit underhood.
Here, we focus on ArAdapter.
See ArView.swift as an example:
import ConfigWiseSDK
struct ArView: View {
. . .
@State private var arAdapter: ArAdapter?
. . .
var body: some View {
. . .
return ZStack {
ArSceneView(
onInitView: { view, arAdapter in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.arAdapter = arAdapter
}
},
Let's create SwiftUI compatible ArSceneView wrapper. It's required to integrate UIKit based ARSCNView of ARKit with SwiftUI based code.
See ArSceneView.swift as an example:
import SwiftUI
import ARKit
import ConfigWiseSDK
struct ArSceneView: UIViewRepresentable {
var onInitView = { (view: ARSCNView, arAdapter: ArAdapter) in }
var onArShowHelpMessage: (ArHelpMessageType?, String) -> Void
var onArHideHelpMessage: () -> Void
var onAdapterError: (Error) -> Void
var onAdapterErrorCritical: (Error) -> Void
var onArSessionStarted: (Bool) -> Void
var onArSessionPaused: () -> Void
var onArUnsupported: (String) -> Void
var onArFirstPlaneDetected: (simd_float3) -> Void
var onModelAdded: (String, String, Error?) -> Void
var onModelDeleted: (String, String) -> Void
var onModelPositionChanged: (String, String, SCNVector3, SCNVector4) -> Void
var onModelSelected: (String, String) -> Void
var onSelectionReset: () -> Void
func makeCoordinator() -> ArSceneView.Coordinator {
return Coordinator(representable: self, arAdapter: ArAdapter())
}
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> ARSCNView {
let view = ARSCNView()
let arAdapter = context.coordinator.arAdapter
arAdapter.managementDelegate = context.coordinator // initialize delegate (ArManagementDelegate
// protocol) to handle callbacks from ArAdapter
arAdapter.sceneView = view // set sceneView in adapter (what used in UI)
arAdapter.modelHighlightingMode = .glow // type of highlighting of selected models in the scene
// the following values are supported: .glow, .levitation
// single tap (on shown 3D object in the scene) selects
// the model in the scene
arAdapter.glowColor = .blue // color of highlighting glow effect
arAdapter.gesturesEnabled = true // enable or disable gestures to manage models in the scene
arAdapter.movementEnabled = true // enable or disable movements of models in the scene
// (one and two fingers pan gesture is used to move 3D objects)
arAdapter.rotationEnabled = true // enable or disable rotation of 3D objects in the scene
// (rotate gesture is used for that)
arAdapter.scalingEnabled = true // enable or disable scaling of shown 3D objects
// (pinch gesture is used for that)
arAdapter.snappingsEnabled = true // enable or disable snappings features in the scene
// double tap (on shown snapping area) moves and connects
// selected model to snapping area.
arAdapter.overlappingOfModelsAllowed = true // enable or disable ability to move models to
// positions where other models already placed.
// if false then ArAdapter doesn't allow to put
// 3D objects in the overlapped positions.
onInitView(view, arAdapter)
arAdapter.runArSession()
return view
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: ARSCNView, context: Context) {
}
static func dismantleUIView(_ uiView: ARSCNView, coordinator: ArSceneView.Coordinator) {
coordinator.arAdapter.pauseArSession()
}
final class Coordinator: ArManagementDelegate {
var arAdapter: ArAdapter
private let representable: ArSceneView
init(representable: ArSceneView, arAdapter: ArAdapter) {
self.representable = representable
self.arAdapter = arAdapter
}
func onArShowHelpMessage(type: ArHelpMessageType?, message: String) {
self.representable.onArShowHelpMessage(type, message)
}
func onArHideHelpMessage() {
self.representable.onArHideHelpMessage()
}
func onAdapterError(error: Error) {
self.representable.onAdapterError(error)
}
func onAdapterErrorCritical(error: Error) {
self.representable.onAdapterErrorCritical(error)
}
func onArSessionStarted(restarted: Bool) {
self.representable.onArSessionStarted(restarted)
}
func onArSessionPaused() {
self.representable.onArSessionPaused()
}
func onArUnsupported(message: String) {
self.representable.onArUnsupported(message)
}
func onArFirstPlaneDetected(simdWorldPosition: simd_float3) {
self.representable.onArFirstPlaneDetected(simdWorldPosition)
}
func onModelAdded(modelId: String, componentId: String, error: Error?) {
self.representable.onModelAdded(modelId, componentId, error)
}
func onModelDeleted(modelId: String, componentId: String) {
self.representable.onModelDeleted(modelId, componentId)
}
func onModelPositionChanged(modelId: String, componentId: String, position: SCNVector3, rotation: SCNVector4) {
self.representable.onModelPositionChanged(modelId, componentId, position, rotation)
}
func onModelSelected(modelId: String, componentId: String) {
self.representable.onModelSelected(modelId, componentId)
}
func onSelectionReset() {
self.representable.onSelectionReset()
}
}
}
Let's add our ArSceneView wrapper in to ArView.
See ArView.swift as an example:
var body: some View {
. . .
return ZStack {
ArSceneView(
onInitView: { view, arAdapter in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.arAdapter = arAdapter
}
},
// This callback function is executed by ArAdapter when needed to show help message
// (for better UX experience in your application).
onArShowHelpMessage: { type, message in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.helpMessage = message
}
},
// Executed if help message must be hidden (for better UX experience).
onArHideHelpMessage: {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.helpMessage = nil
}
},
// This function executed if non critical AR error occurred.
onAdapterError: { error in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.errorMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
},
// This function executed if critical AR error occurred.
onAdapterErrorCritical: { error in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.criticalErrorMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
},
// Executed after AR session started.
onArSessionStarted: { restarted in
},
// Write your code here if you want to handle event when AR session paused.
onArSessionPaused: {
},
// Executed if your device (iPhone / iPad) doesn't support augmented reality
onArUnsupported: { message in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.criticalErrorMessage = message
}
},
// Executed if AR horizontal plane detected in your room.
// Usually after AR session starts, user scans room environment (through back camera)
// by moving phone around the room.
// First ArAdapter detects AR anchors in the room. Then ArAdapter trying to bind anchors
// to detect (to create) horizontal planes where we can put our 3D models in the scene.
// So, after plane detected, ArAdapter informs us about it by callback execution of the current function.
// Well, on this step we can load and add our 3D model to position of detected plane.
onArFirstPlaneDetected: { simdWorldPosition in
self.addModel(of: self.initialComponent, to: simdWorldPosition)
},
// Executed if model has been added to AR scene.
// If model successfully added then 'error' parameter is nil.
// If failed to add model then 'error' is non nil.
onModelAdded: { modelId, componentId, error in
if let error = error {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.errorMessage = error.localizedDescription
}
return
}
},
// Executed if model has been deleted from AR scene.
onModelDeleted: { modelId, componentId in
},
// Executed after 3D model has been moved and/or rotated in the AR scene.
// Eg: if user moved or rotated selected 3D object using gestures.
onModelPositionChanged: { modelId, componentId, position, rotation in
},
// This function is executed by ArAdapter if user selected a model in the scene (by tapping on it).
onModelSelected: { modelId, componentId in
let selectedModel = self.arAdapter?.selectedModelNode
let selectedComponent = self.appEnvironment.getComponentById(componentId)
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.observableState.selectedModel = selectedModel
self.observableState.selectedComponent = selectedComponent
}
},
// Executed if user selection has been reset on previously selected model.
onSelectionReset: {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.observableState.selectedModel = nil
self.observableState.selectedComponent = nil
}
}
)
. . .
iOS ConfigWiseSDK supports Apple Scene (.scn), USD and zipped USD formats only. We recommend to use .usdz.
- .scn
- .usd (.usdz)