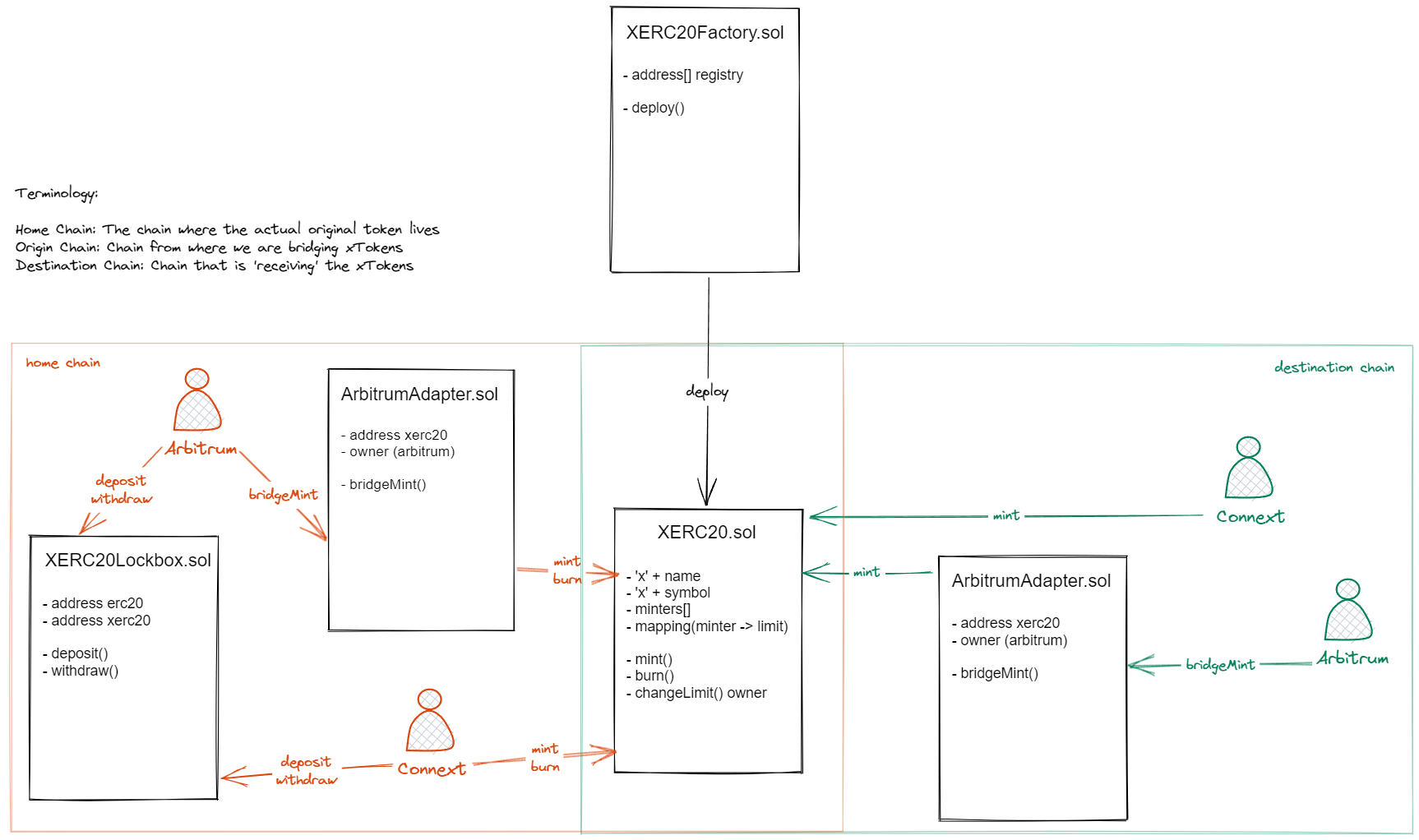
xERC20 is a standard for bridged tokens. A common interface to be used across different implementations of bridges to keep liquidity concentrated and improve user experience on-chain.
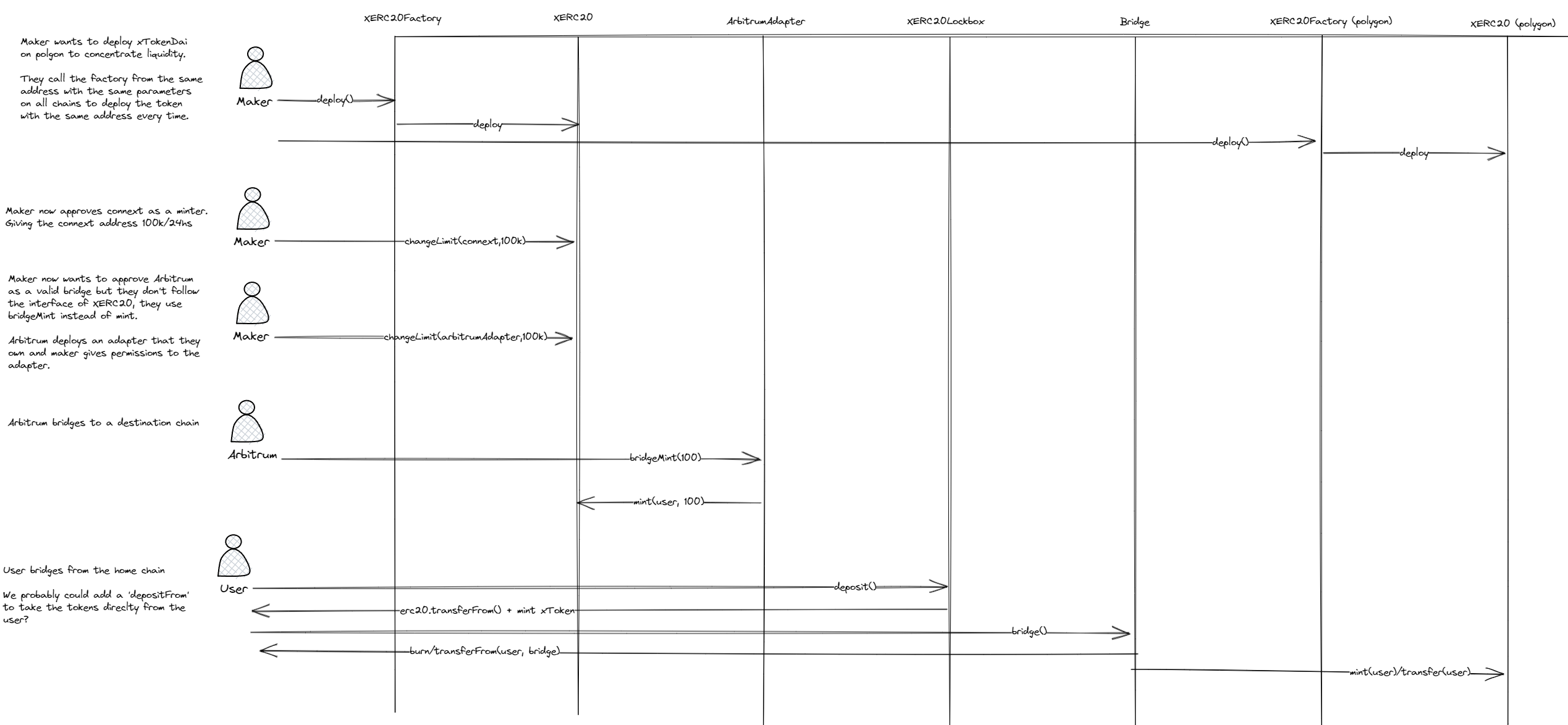
XERC20: A standard for bridges to manage the same liquidity when bridging. It allows its owner to approve bridges and add limits to them for minting and burning the XERC20 token. The XERC20 standard is compatible with two different types of bridge behaviours, bridges calling mint/burn from the user (or other function names through adapters) and bridges that transfer from the user to the bridge contract. On the latter, XERC20 tokens that are received by the bridge get burned and when a bridge transfers tokens out, they get minted again.
XERC20Lockbox: The lockbox works as a wrapper of an ERC20. It mints XERC20 tokens at a 1:1 ratio when receiving ERC20 tokens and it unlocks the ERC20 the other way around. The lockbox can be deployed on any chain that has a canonical token representation, chains that do not currently have a canonical representation can avoid deploying a Lockbox and use the XERC20 as the default implementation for the chain.
XERC20Factory: The factory is used as a helper to deploy an xToken. It allows the owner to deploy the XERC20 and the Lockbox in one transaction while keeping the same token address on every chain used.
*The adapter included is an example into how it would work. Any bridge can build their own.
- Install Foundry by following the instructions from their repository.
- Copy the
.env.examplefile to.envand fill in the variables - Install the dependencies by running :
yarn install && forge install
The default way to build the code is suboptimal but fast, you can run it via:
yarn buildIn order to build a more optimized code (via IR), run:
yarn build:optimizedUnit tests should be isolated from any externalities, while E2E usually run in a fork of the blockchain. In this boilerplate you will find example of both.
In order to run both unit and E2E tests, run:
yarn testIn order to just run unit tests, run:
yarn test:unitIn order to run unit tests and run way more fuzzing than usual (5x), run:
yarn test:unit:deepIn order to just run e2e tests, run:
yarn test:e2eIn order to check your current code coverage, run:
yarn coverage⚠ WARNING: Forge coverage is having some issues...
As stated in this github issue, checking the code coverage with Forge when using abstract contract is not currently working.
Configure the .env variables.
ℹ️ Notice: _Please ensure that all private keys (PKs) are prefixed with
0xbefore using or submitting them. This prefix is necessary for proper formatting and compatibility.*
Example:
- Correct: `0x123abc...`
- Incorrect: `123abc...`
You will need to set your custom name and symbol for your XERC20 to be deployed, no need to add an 'x' infront of it, the contract will do that for you. For more details check the section below.
This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step process to deploy an xERC20 token using this repository. We will first demonstrate how to deploy the xERC20 token alone, and then we’ll cover the scenario in which you want to deploy both the xERC20 token and the lockbox.
Important
Verifying contracts deployed with --via-ir is not working correctly with Foundry. Read the following post for a solution: foundry-rs/foundry#3507 (comment)
Locate and open the XERC20Deploy.sol file, which should be situated within the solidity/scripts directory.
Ensure that you have the corresponding RPC URLs added in your .env file to support these networks. Refer to this section for more information on setting up your environment variables.
Identify the blockchain networks where your token is already deployed and has a canonical representation. On these specific networks, a Lockbox will be required to facilitate interactions. The Lockbox is a contract wrapper that allows users to make the swap between xERC20<->ERC20 1:1. To deploy a lockbox you will need to configure the erc20 value in the deployment config. This value should be the address of the canonical representation of the token in that chain. Using this value means that a lockbox will be deployed.
If you don't need a lockbox for a chain specify "erc20": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000",.
Decide on which blockchains you want to deploy your token and the initial configs for the bridges. After that, update the config file located in /solidity/scripts/xerc20-deployment-config.json:
Caution
isNativeGasToken should only be true if the canonical representation of the token is the native gas token of the chain. Ex: ETH for ethereum or MATIC for polygon.
{
"name": "Test", // The name of your xERC20.
"symbol": "TST", // The symbol of your xERC20.
"chainDetails": [ // The chains that the xERC20 token will be deployed to.
{
"rpcEnvName": "ETHEREUM_GOERLI_RPC", // The name of the RPC to use. It should be added in the .env file.
"erc20": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000001", // The address of the canonical token representation for that chain. A lockbox will be deployed pairing the deployed xERC20 with the specified ERC20 1:1. address(0) in case there is non.
"governor": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000002", // The owner of the xERC20.
"isNativeGasToken": false, // True if the ERC20 token is the native gas token of the chain. Ex: ETH for ethereum or MATIC for polygon.
"bridgeDetails": [ // The bridges to be configured for the xERC20 token on this particular chain.
{
"bridge": "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000003", // The bridge address.
"burnLimit": 1000e18, // The bridge burn limit.
"mintLimit": 1000e18 // The bridge mint limit.
}
]
}
]
}ℹ️ Important Note: An address cannot deploy a token with the same name and symbol more than once on any given chain. Ensure that you have not previously deployed a token with the same name or symbol using your address.
Save your changes to proceed.
Ensure that everything in your smart contract is set up correctly and free of errors by compiling it with the following command:
yarn buildYou should see a confirmation in your terminal, similar to the screenshot below:
Before proceeding with the actual deployment of your token, it is crucial to perform a dry-run. This helps in verifying the deployment process and estimating the gas costs on all the selected chains. Run the following command to initiate a dry-run:
yarn run script:DeployXERC20You will receive the xERC20 token address, transaction details, and gas estimates as shown in the screenshots below:
You are now at the final step of the deployment process. With all the previous steps successfully completed, you are ready to deploy your xERC20 token to the selected blockchain networks. Run the following command to initiate the deployment:
yarn run script:DeployXERC20:broadcastCongratulations! You have successfully deployed your xERC20 token. 🚀
See the Foundry Book for available options.
The primary license for xERC20 is MIT, see LICENSE.