A simple peer-to-peer file sharing system based on Python standard library xmlrpclib
# Enable concurrency logging from different node to the same file
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py
python get-pip.py
pip install ConcurrentLogHandler
# Install fuser to free some port for testing
yum install psmisc
fuser -k 4242/tcp
fuser -k 4243/tcp
# Set up test environment
mkdir -p test/peer1
mkdir -p test/peer2
echo "Test string from peer2" >> test/peer2/test.txt# Install wxPython on Windows and run the exe installer
# Change to shared directory with `pushd \\samba.<domainname>\scratch\<unixpath>`
python client.py test\urls.txt test\peer1 http://localhost:4242
python client.py test\urls.txt test\peer2 http://localhost:4243You can fetch a file, or add a peer from GUI.
A list of available file in current node will also be listed.
See 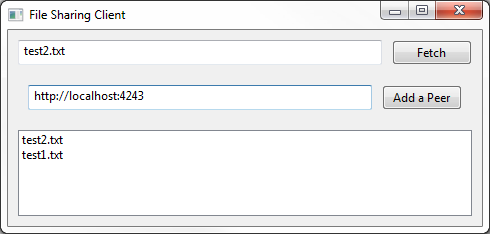
To launch a client, use python client.py $known_peer_urls_file $working_dir $url
Supported commands in client: fetch <filename>, hello <peer url> and exit
Additional step for testing setup
touch test/urls.txtIn the first console, start a client, which will in turn launch peer1
python client.py test/urls.txt test/peer1 http://localhost:4242
>fetch test.txt
Couldn't find the file test.txt
>In the second console, start a client, which will in turn launch peer2
python client.py test/urls.txt test/peer2 http://localhost:4243
>fetch test.txt
>Go back to peer1 and try to introduce itself to peer2 and fetch again
>hello http://localhost:4243
>fetch test.txt
>exitCheck the working directory of peer1, you can see test.txt is fecthed to test/peer1 now
General set up before starting server
yum install psmisc
fuser -k 4242/tcp
fuser -k 4243/tcp
mkdir -p test/peer1
mkdir -p test/peer2
echo "Test string from peer2" >> test/peer2/test.txtIn the first console, launch peer1
python node.py http://localhost:4242 test/peer1 secret1In the second console, launch peer2
python node.py http://localhost:4243 test/peer2 secret2In the third console, open an interactive Python shell
#Connect to peer1 and fail to retrieve data
from xmlrpclib import *
mypeer1 = ServerProxy('http://localhost:4242')
code, data = mypeer1.query('test.txt')
#Connect to peer2 and succeed in retrieving data
mypeer2 = ServerProxy('http://localhost:4243')
code, data = mypeer2.query('test.txt')
#Introduce peer2 to peer1 and succeed in retrieving data
mypeer1.hello('http://localhost:4243')
code, data = mypeer1.query('test.txt')
#Download test file from peer2 to peer1
mypeer1.fetch('test.txt', 'secret1')| Node1 | Node2 |
|---|---|
from SimpleXMLRPCServer import SimpleXMLRPCServer |
from xmlrpclib import ServerProxy |
s = SimpleXMLRPCServer(("", 4242)) |
s = ServerProxy('http://ikeblue3:4242') |
def twice(x): |
s.twice(4) |
....return x*2 |
Result: 8 |
s.register_function(twice) |
|
s.serve_forever() |