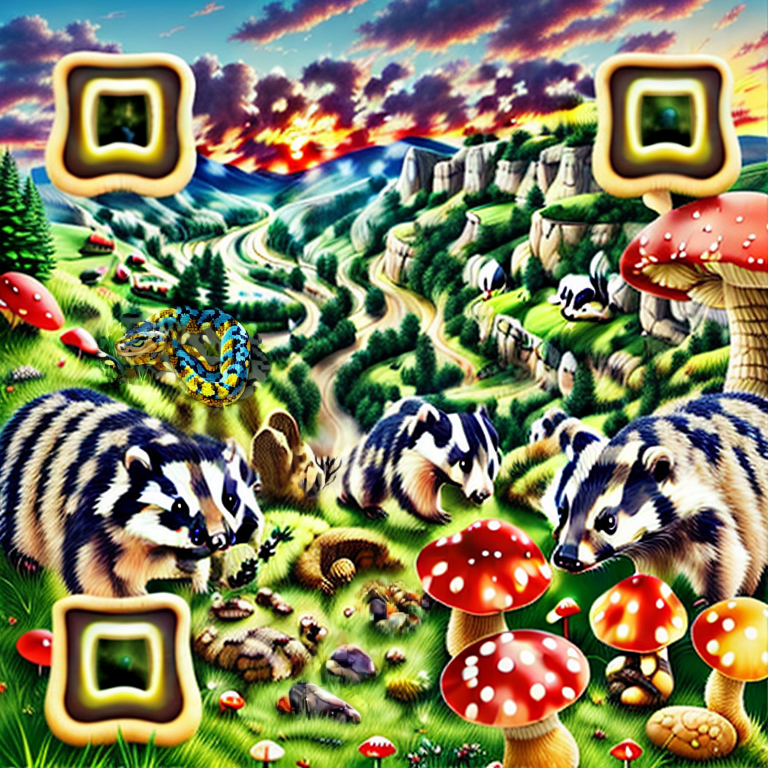
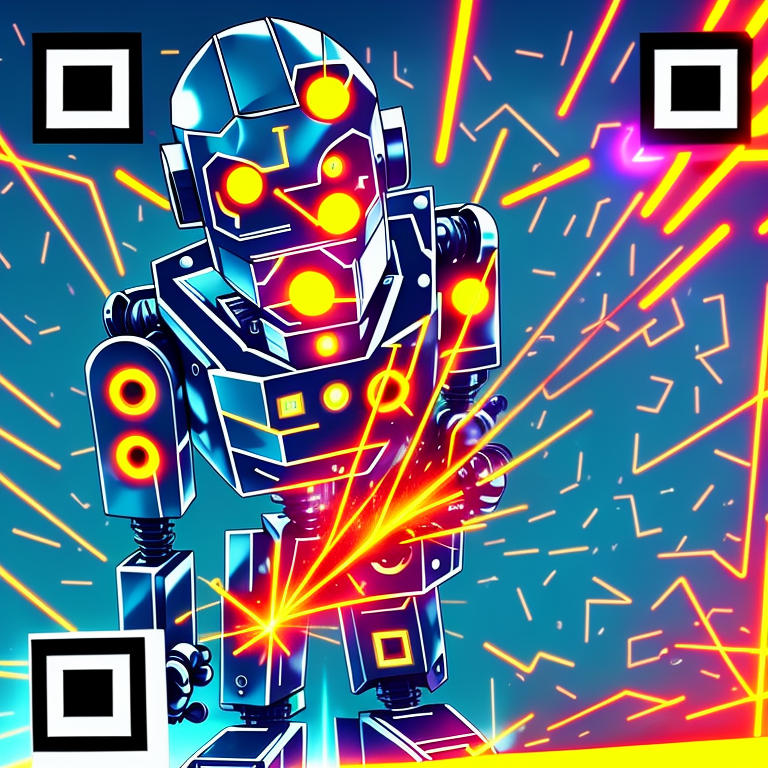
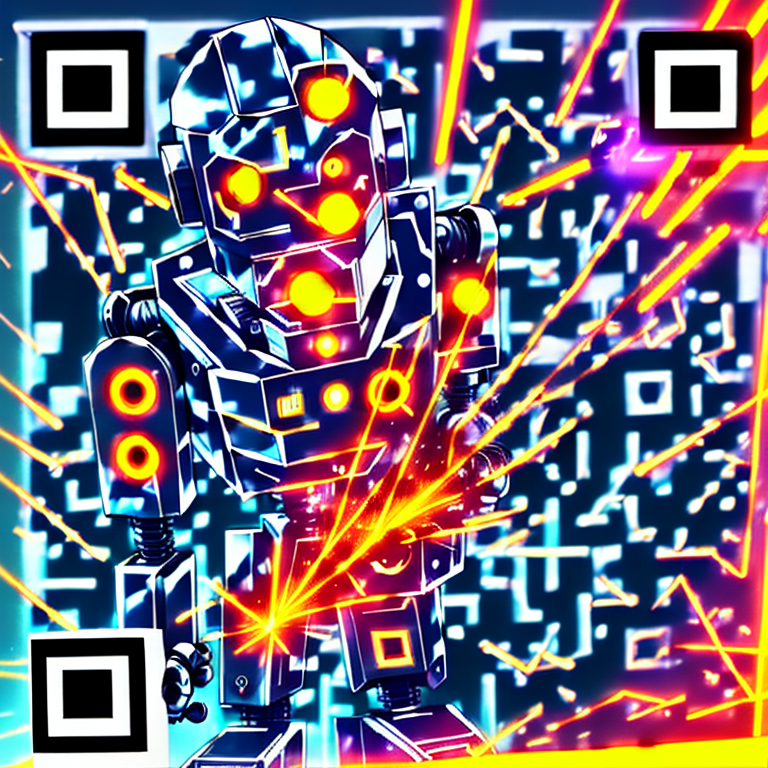
A set of ComfyUI nodes to dynamically create QR image layers for generative QR art without the hassle of leaving the webui.
Everything in this pack is primarily focused on the creation of patterns. While the Mask QR Errors does some basic statistics on the differences between pixels, a more definative node on determining scannability can be found in the companion project ComfyQR-scanning-nodes which uses additional dependencies for the reading of QRs.
This repository is managed publicly on Gitlab, but also mirrored on Github. Please submit any issues or pull requests to the gitlab repo.
This project currently contains two nodes for generating QR codes.
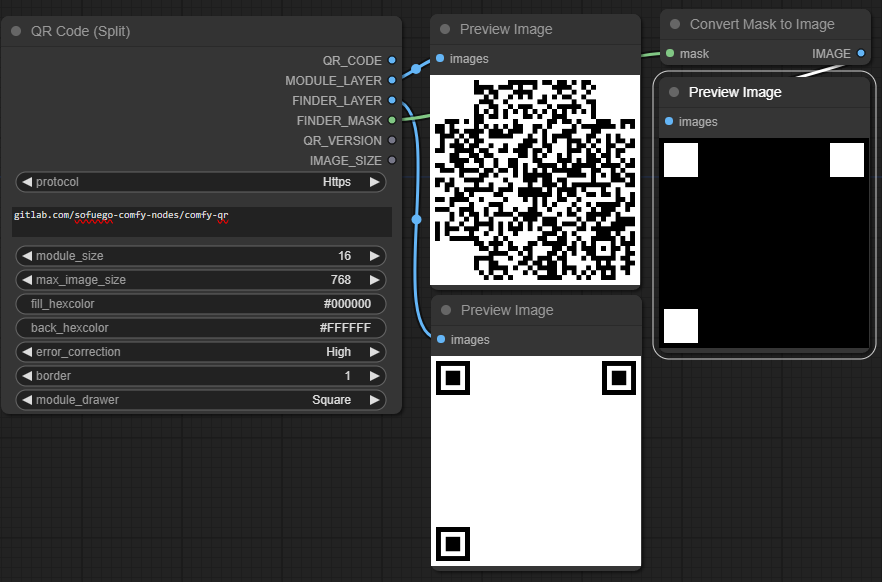
A dynamically sized QR code without any resampling scaled by the text length, the module size, and the error correction level. Use the QR Code for simple workflows and the QR Code (Split) if you want to build more advanced pipelines with additional outputs for the MODULE_LAYER, FINDER_LAYER, or FINDER_MASK.
protocol- If enabled this will prefix the textbox input with a preset to represent the internet protocol. This is included both for convenience and as a workaround for the textbox clipping strings with this character combination.Http- Adds "http://" before the text.Https- Adds "https://" before the text.None- Uses only the contents of thetextbox.
text- What text to build your QR code with. Ifprotocolis specified, this textbox will be combined it with the selected option.module_size- The pixel width of the smallest unit of a QR code.max_image_size- The maximum size of the resulting QR code. If the combination oftext,module_size, anderror_correctioncreate dimensions that exceed this, an error will halt the pipeline.fill_hexcolor- A string of characters representing the hex value of the QR units. Can be 3 or 6 hexadecimal characters with an optional # before.back_hexcolor- A string of characters representing the hex value of the space around the QR units. Can be 3 or 6 hexadecimal characters with an optional # before.error_correction- The level of error correction to apply.Low- 7% error correction.Medium- 15% error correction.Quartile- 25% error correction.High- 30% error correction.
border- The border size (In multiples ofmodulewidths)module_drawer- The shape the QR code modules should be. The default issquare, but see Alternate Module Drawers below for new examples.
QR_CODE- The QR codeMODULE_LAYER- The QR code with theback_hexcolorfilling in the function patterns (to remove their influence from the early diffusion steps).FINDER_LAYER- The isolated finder patterns over theback_hexcolor.FINDER_MASK- A mask that isolates the locations of the 3 finder patterns.QR_VERSION- An integer of the QR version that was selected based on the text length and error correction level.IMAGE_SIZE- An integer based on the pixel width of the resulting QR code.
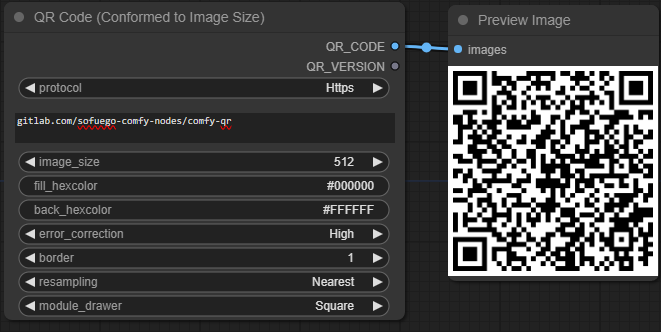
A QR code fixed to specific output dimensions through image resampling.
protocol- If enabled this will prefix the textbox input with a preset to represent the internet protocol. This is included both for convenience and as a workaround for the textbox clipping strings with this character combination.Http- Adds "http://" before the text.Https- Adds "https://" before the text.None- Uses only the contents of thetextbox.
text- What text to build your QR code with. Ifprotocolis specified, this textbox will be combined it with the selected option.image_size- The pixel dimensions to conform the QR code to.fill_hexcolor- A string of characters representing the hex value of the QR units. Can be 3 or 6 hexadecimal characters with an optional # before.back_hexcolor- A string of characters representing the hex value of the space around the QR units. Can be 3 or 6 hexadecimal characters with an optional # before.error_correction- The level of error correction to apply.Low- 7% error correction.Medium- 15% error correction.Quartile- 25% error correction.High- 30% error correction.
border- The border size (In multiples ofmodulewidths)resampling- The resampling algorithm to use when rescaling the QR code.Bicubic- Bicubic interpolationBilinear- Bilinear interpolationBox- Box interpolationHamming- Hamming interpolationLanczos- Lanczos interpolationNearest- Nearest Neighbor interpolation
module_drawer- The shape the QR code modules should be. The default issquare, but see Alternate Module Drawers below for new examples.
QR_CODE- The QR codeQR_VERSION- An integer of the QR version that was selected based on the text length and error correction level.
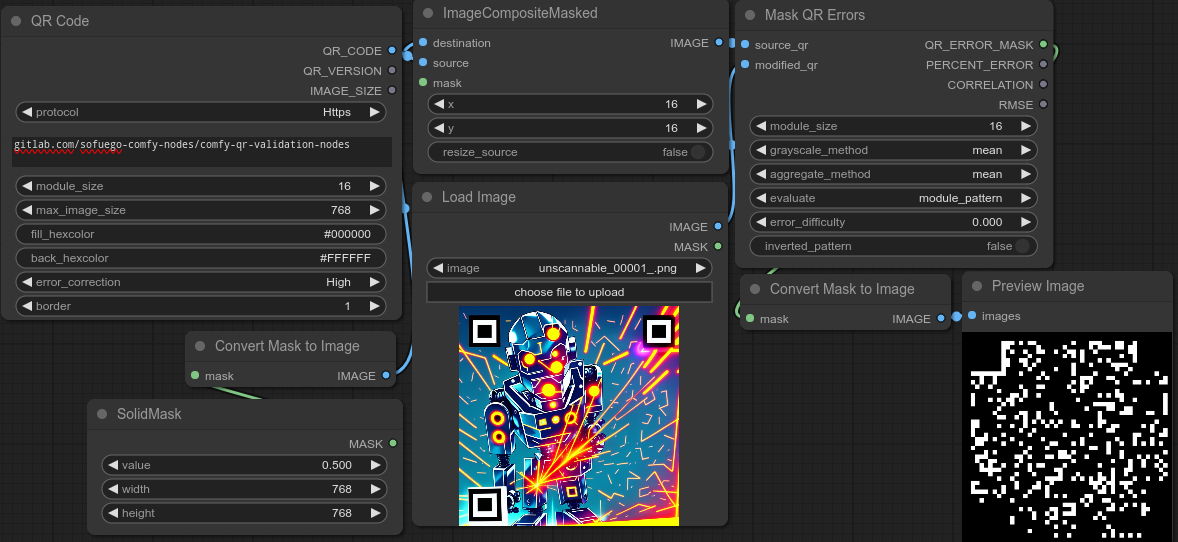
A node that that will analyze the differences between a modified QR and create a mask of the estimated errors.
Note: This is an extremly powerful node but relies on several assumptions in order to be used.
- A QR with a fixed module size that has not been resampled irregularly or distorted.
- Shared allignment between the
source_qrandmodified_qr. - Fill and back colors must be perfectly white and black (
#FFFFFF,#000000) for thesource_qr. - The canvas can be bigger than the QR code, but on the
source_qr, there should be no pixels the same color as the module color outside of the QR exterior.
source_qr- The original QR code used to generate the image (with the same placement and dimensions asmodified_qr).modified_qr- The generated QR art to evaluate (with the same placement and dimensions assource_qr).module_size- The size in pixels of each QR module (the individual blocks that make up a qr code) in the provided images.grayscale_method- How to convert the RGB color channels to a single grayscale value.mean- A simple average of the RGB values.luminance- Converts colors to grayscale using a more advanced formula to better match percieved brightness.
aggregate_method- How to aggregate the many pixels that make up a QR module into a single value.mean- Within each module a simple average is taken of all constituent pixels.
evaluate- Which part of the QR to examine.full_qr- The entire QR code is evaluated.module_pattern- Has the node focus only on the modules while excluding the finder pattern.finder_pattern- Ignores the modules while examining only the 3 finder patterns at the corners of the QR.
error_difficulty- It is possible that while using the same reader a QR code could be easily scannable on one monitor, but not on another. The way the colors are displayed can have a major effect on unsability. By increasing this threshold, you are simulating inability to distinguish midrange pixels for both thePERCENT_ERRORandQR_ERROR_MASKoutputs. It ranges from 0 to 1 where 0 only automatically fails perfect grays while 1 accepts only exactly matched modules that are perfectly black or white.inverted_pattern- If set toTruethis assumes that the QR code has inverted colors (a black background with white modules.)gamma- If using thegrayscalemethod based onluminance, this will influence the formula by appending the gamma expansion and compression formulas before and after the color conversion. A gamma of 2.2 will use the formula specific to srgb, while other gamma values will simply use the gamma amount as an exponent.
QR_ERROR_MASK- A mask with white areas falling on locations of modules with errors (precision set byerror_difficulty). This mask can be used for streamlined img2img operations to salvage unscannable QRs.PERCENT_ERROR- Number of modules that do not fall into the acceptable threshold (set byerror_difficulty) divided by the total number of modules.CORRELATION- The Pearson correlation coefficient between the QR patterns on thesource_qrandmodified_qrRMSE- The root mean squared error between both QR codes. In this case, a value of 0 indicates an identical match to thesource_qr. A value of 1 indicates a perfect inversion where each expected color is the complete opposite.
There is an assortment of workflow examples that can be found in the examples directory or in the metadata of the images in the example_generations folder. For example taking this image.
And then aggressively increasing the strength of the ControlNet on only the error pixels to make something previously completely unscannable more reliably across different monitors and QR readers.
Any workflow in the example that ends with "validated" (and a few image examples) assume the installation of the scanning pack as well.
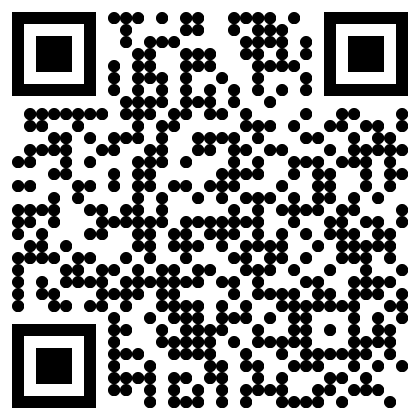
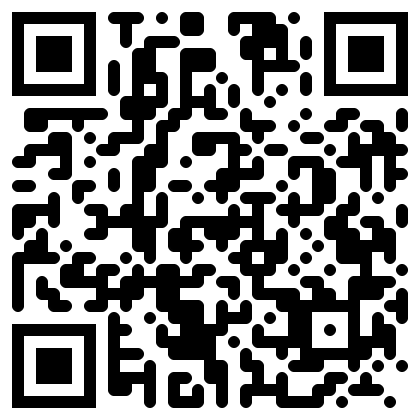
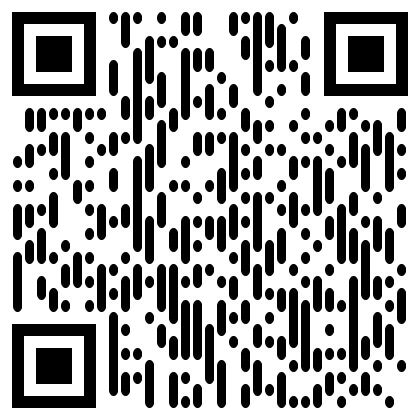
The QR generation nodes now support alternate module styles. Experiment using different ones for greater flexibility during generation.
| Square | Gapped Square | Circle | Rounded | Vertical bars | Horizontal bars |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
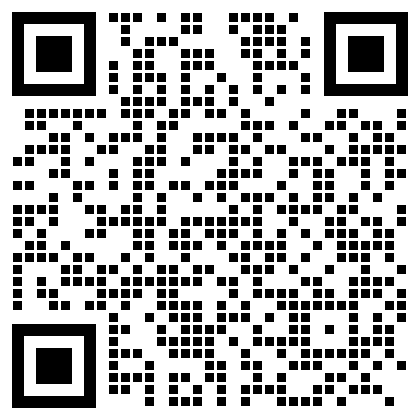 |
 |
 |
 |
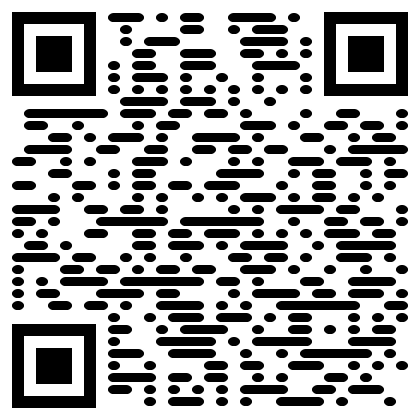 |
Note Even unaltered non square styles will inherently register small deviations from RMSE values and possible minute deviations for correlations when using the Mask QR Errors node. When information is extracted, the source_qr values are rounded so that they can only be 0 or 1 (to allow alternate drawers to be used as inputs) and matched against the unrounded aggregation of the modified_qr values.
If the solution is clean enough and if it can definitively improve scannability, there may be additional plans for the seperation of alignment patterns (based on module_size, border, and QR_VERSION) for more advanced workflows.