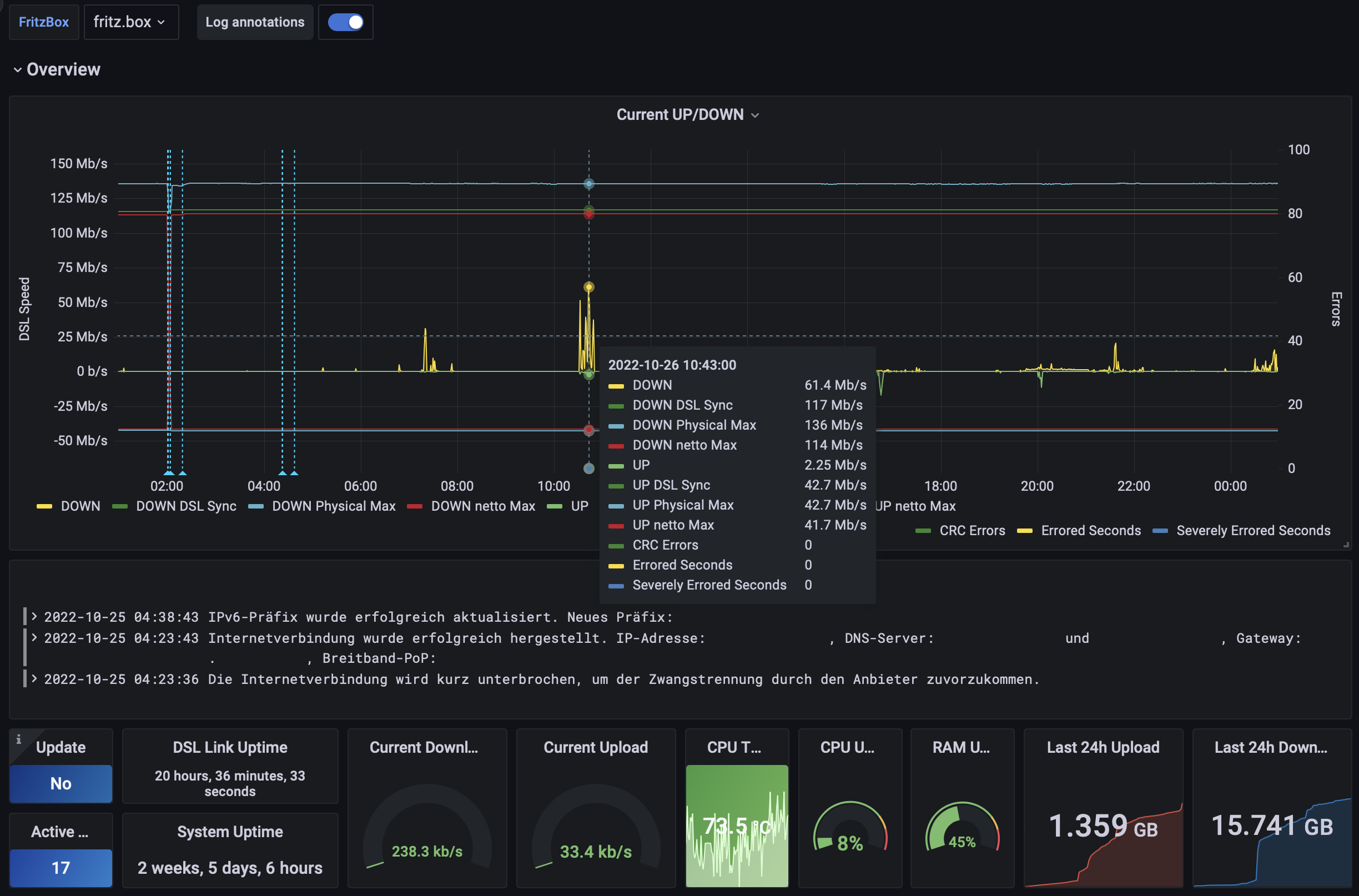
"fritzinfluxdb" is a tool written in python to fetch data from a FritzBox router and writes it to InfluxDB. It is equal capable as fritzcollectd and directly writing to InfluxDB.
Data collected:
- connection related information (amount of data, throughput, daily up/download statistics)
- all log messages
- home automation (temperature, power consumption, heating settings)
- phone call list (incoming, outgoing, missed, blocked)
- system stats (cpu usage/temp, memory usage)
- WLAN information (num clients, status, channels)
- VPN/DynDNS information (active users, vpn hostname, DynDNS settings)
Both InfluxDB 1 and InfluxDB 2 are supported
In order work properly you need to enable "permit access for applications" and "state data via UPnP"
- python3.7 or newer
- influxdb (InfluxDB 1)
- influxdb_client (InfluxDB 2)
- fritzconnection
- pytz
It was tested using FritzOS 7.29. It should work on older versions but some values might be missing.
DSL and Cable Modem FritzBox versions are supported. During startup there are messages about disabled services. This is normal as there are values not available on certain models.
- Grafana >= 9.1.0
- here we assume we install in
/opt
After cloning the repo copy the config from the example
to fritzinfluxdb.ini and edit the settings. All settings are described inside the file.
Config values can also be overwritten using environment variables.
schema: <SECTION_NAME>_<CONFIG_OPTION> (all in capital letters)
example for InfluxDB token:
export INFLUXDB_TOKEN="abcedef"
Environment variables will overwrite options defined in config file.
Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install python3-virtualenv
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/bb-Ricardo/fritzinfluxdb.git
cd fritzinfluxdb
virtualenv -p python3 .venv
. .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txtRHEL/CentOS 7 with EPEL
yum install git python36-virtualenv
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/bb-Ricardo/fritzinfluxdb.git
cd fritzinfluxdb
virtualenv-3 .venv
. .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txtRHEL/Rocky/Alma 8
dnf install git-core python3-virtualenv
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/bb-Ricardo/fritzinfluxdb.git
cd fritzinfluxdb
virtualenv-3 .venv
. .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txtRHEL/Rocky/Alma 9
dnf install git-core
cd /opt
git clone https://github.com/bb-Ricardo/fritzinfluxdb.git
cd fritzinfluxdb
python3 -m venv .venv
. .venv/bin/activate
pip3 install -r requirements.txt- modify your configuration and test it
./fritzinfluxdb.py
Ubuntu
cp /opt/fritzinfluxdb/fritzinfluxdb.service /etc/systemd/system
RHEL/CentOS/Rocky/Alma
sed -e 's/nogroup/nobody/g' /opt/fritzinfluxdb/fritzinfluxdb.service > /etc/systemd/system/fritzinfluxdb.service
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start fritzinfluxdb
systemctl enable fritzinfluxdb
Run the application in a docker container. You can build it yourself or use the ones from docker hub.
Available here: bbricardo/fritzinfluxdb
- The application working directory is
/app
To build it by yourself just run:
docker build -t bbricardo/fritzinfluxdb:latest .To start the container just use:
docker run --rm -d -v /PATH/TO/fritzinfluxdb.ini:/app/fritzinfluxdb.ini --name fritzinfluxdb bbricardo/fritzinfluxdb:latestYou can alternatively use the provided docker-compose.yml:
docker-compose up -d
If you're running the influxdb in a docker on the same host you need to add --link to the run command.
- starting the influx container
docker run --name=influxdb -d -p 8086:8086 influxdb
- set influxdb host in
fritzinfluxdb.initoinfluxdb - run docker container
docker run --link influxdb -d -v /PATH/TO/fritzinfluxdb.ini:/app/fritzinfluxdb.ini --name fritzinfluxdb fritzinfluxdb
- update your virtual env
pip3 install -r requirements.txt - use the updated config and add the credentials and addresses from your old config
To create an InfluxDB 1 database or InfluxDB 2 Bucket (incl. retention policy mapping) it is recommended to use admin credentials/token on the first run. DON'T use an admin token after initial setup has finished.
InfluxDB 1 example:
export INFLUXDB_USERNAME=admin
export INFLUXDB_PASSWORD=SuperSecretInfluxDB 2 example:
export INFLUXDB_TOKEN=InfluxDBAdminTokenIf running via docker this
link describes how to set env vars on a docker run
For InfluxDB 2 it is highly recommended creating a specific write only token for the defined bucket.
usage: fritzinfluxdb.py [-h] [-c fritzinfluxdb.ini [fritzinfluxdb.ini ...]] [-d] [-v]
fritzinfluxdb
Version: 1.2.1 (2023-01-26)
Project URL: https://github.com/bb-Ricardo/fritzinfluxdb
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c fritzinfluxdb.ini [fritzinfluxdb.ini ...], --config fritzinfluxdb.ini [fritzinfluxdb.ini ...]
points to the config file to read config data from which is not installed under the default path './fritzinfluxdb.ini'
-d, --daemon define if the script is run as a systemd daemon
-v, --verbose turn on verbose output to get debug logging. Defining '-vv' will also print out all http calls
Dashboards to display the collected data are included under grafana. Due to some limitations of the InfluxDB 1.8 Flux language implementation the dashboards had to bes separated.
Influx data source configuration:
InfluxDB 1.8:
- the "Query Language"
InfluxQLhas to be selected - DEPRECATED: these dashboards will not be developed/extended any further
InfluxDB >=2.2.0:
- the "Query Language"
Fluxhas to be selected - the bucket with the fritzbox data has to be set as default bucket (all dashboards use the default bucket)
There are following Dashboards included:
InfluxDB 1.8.X (deprecated):
InfluxDB >=2.2.0:
- fritzbox_system_dashboard.json
- fritzbox_logs_dashboard.json
- fritzbox_call_log_dashboard.json
- fritzbox_home_automation_dashboard.json
This was heavily inspired by: https://grafana.com/dashboards/713
check here to find an overview of more attributes which probably could be added https://wiki.fhem.de/w/index.php?title=FRITZBOX
New services can be defined in fritzinfluxdb/classes/fritzbox/service_definitions
You can check out the full license here
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.